Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If cos A = `(1)/(2)` and sin B = `(1)/(sqrt2)`, find the value of: `(tan"A" – tan"B")/(1+tan"A" tan"B")`.
Are angles A and B from the same triangle? Explain.
उत्तर
Consider the diagram below:
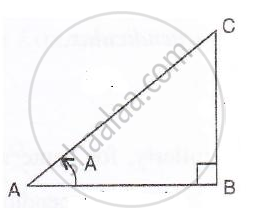
cos A = `(1)/(2)`
i.e.`"base"/"hypotenuse"= (1)/(2)`
⇒ `"AB"/"AC" = (1)/(2)`
Therefore if length of AB = x, length of AC = 2x
Since
AB2 + BC2 = AC2 ...[Using Pythagoras Theorem]
(x)2 + BC2 = (2x)2
BC2 = 4x2 – x2 = 3x2
∴ BC = `sqrt3x` ...(perpendicular)
Consider the diagram below:
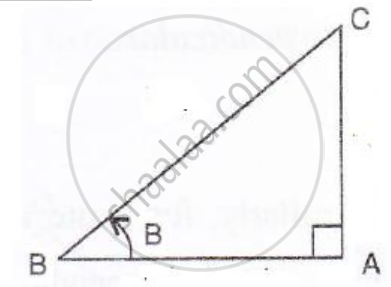
sin B = `(1)/(sqrt2)`
i.e.`"perpendicular"/"hypotenuse" = (1)/(sqrt2)`
⇒ `"AC"/"BC" = (1)/(sqrt2)`
Therefore if length of AC = x, length of BC = `sqrt2`
Since
AB2 + AC2 = BC2 ...[Using Pythagoras Theorem]
AB2 + x2 = `(sqrt2x)^2`
AB2 = 2x2 – x2 = x2
∴ AB = x (base)
Now
tan A = `"perpendicular"/"base" = (sqrt3x)/(x) = sqrt3`
tan B =`"perpendicular"/"base" = (x)/(x) =1`
Thererfore
`(tan"A" – tan"B")/(1+tan"A"tan"B")`
= `(sqrt3 – 1)/(1+sqrt3)`
= `(sqrt3 – 1)/(1+sqrt3) xx (1-sqrt3) /(1-sqrt3)`
= `((sqrt3 - 1) (1-sqrt3))/(1-3) `
= `(sqrt3 - 3 - 1 + sqrt3) / 2`
= `(2sqrt3-4)/2`
= `(cancel2 (sqrt3-2))/cancel2`
= `sqrt3 -2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If A and B are acute angles such that tan A = 1/2, tan B = 1/3 and tan (A + B) = `(tan A + tan B)/(1- tan A tan B)` A + B = ?
If sin θ = ` (a^2 - b^2)/(a^2+b^2)`find all the values of all T-ratios of θ .
If sin ∝ = `1/2` prove that (3cos∝ - `4cos^2` ∝)=0
Verify each of the following:
(iii) `2 sin 30^0 cos 30^0`
`(cos 28°)/(sin 62°)` = ?
In a right-angled triangle, it is given that A is an acute angle and tan A = `(5) /(12)`.
find the value of :
(i) cos A
(ii) sin A
(iii) ` (cosA+sinA)/(cosA– sin A)`
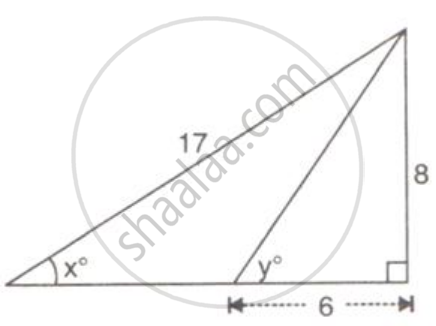
Use the given figure to find :
(i) sin xo
(ii) cos yo
(iii) 3 tan xo - 2 sin yo + 4 cos yo.
In the given figure;
BC = 15 cm and sin B = `(4)/(5)`
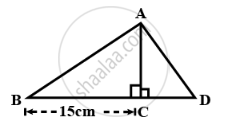
- Calculate the measure of AB and AC.
- Now, if tan ∠ADC = 1; calculate the measures of CD and AD.
Also, show that: tan2B - `1/cos^2 "B" = – 1 .`
If sin A = cos A, find the value of 2 tan2A - 2 sec2 A + 5.
If sec A = `sqrt2` , find : `(3cot^2 "A"+ 2 sin^2 "A")/ (tan^2 "A" – cos ^2 "A")`.
