Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If cos A = `(1)/(2)` and sin B = `(1)/(sqrt2)`, find the value of: `(tan"A" – tan"B")/(1+tan"A" tan"B")`.
Are angles A and B from the same triangle? Explain.
Solution
Consider the diagram below:
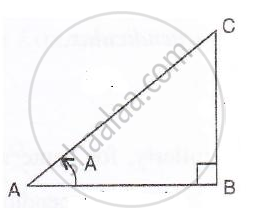
cos A = `(1)/(2)`
i.e.`"base"/"hypotenuse"= (1)/(2)`
⇒ `"AB"/"AC" = (1)/(2)`
Therefore if length of AB = x, length of AC = 2x
Since
AB2 + BC2 = AC2 ...[Using Pythagoras Theorem]
(x)2 + BC2 = (2x)2
BC2 = 4x2 – x2 = 3x2
∴ BC = `sqrt3x` ...(perpendicular)
Consider the diagram below:
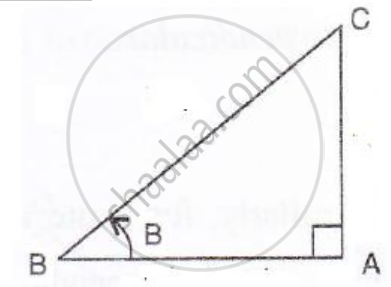
sin B = `(1)/(sqrt2)`
i.e.`"perpendicular"/"hypotenuse" = (1)/(sqrt2)`
⇒ `"AC"/"BC" = (1)/(sqrt2)`
Therefore if length of AC = x, length of BC = `sqrt2`
Since
AB2 + AC2 = BC2 ...[Using Pythagoras Theorem]
AB2 + x2 = `(sqrt2x)^2`
AB2 = 2x2 – x2 = x2
∴ AB = x (base)
Now
tan A = `"perpendicular"/"base" = (sqrt3x)/(x) = sqrt3`
tan B =`"perpendicular"/"base" = (x)/(x) =1`
Thererfore
`(tan"A" – tan"B")/(1+tan"A"tan"B")`
= `(sqrt3 – 1)/(1+sqrt3)`
= `(sqrt3 – 1)/(1+sqrt3) xx (1-sqrt3) /(1-sqrt3)`
= `((sqrt3 - 1) (1-sqrt3))/(1-3) `
= `(sqrt3 - 3 - 1 + sqrt3) / 2`
= `(2sqrt3-4)/2`
= `(cancel2 (sqrt3-2))/cancel2`
= `sqrt3 -2`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In right angled triangle ΔABC at B, ∠A = ∠C. Find the values of Sin A cos C + Cos A Sin C
If Sec 4A = cosec (A – 20°) where 4A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
In a ΔABC , ∠B = 90° , AB= 24 cm and BC = 7 cm find (i) sin A (ii) cos A (iii) sin C (iv) cos C
If a right ΔABC , right-angled at B, if tan A=1 then verify that 2sin A . cos A = 1
Evaluate:
`(sin^2 30^0 + 4 cot^2 45^0-sec^2 60^0)(cosec^2 45^0 sec^2 30^0)`
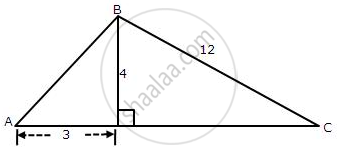
From the following figure, find the values of
(i) cos A
(ii) cosec A
(iii) tan2A - sec2A
(iv) sin C
(v) sec C
(vi) cot2 C - ` 1 / sin^2 "c"`
If 2 sin x = `sqrt3` , evaluate.
(i) 4 sin3 x - 3 sin x.
(ii) 3 cos x - 4 cos3 x.
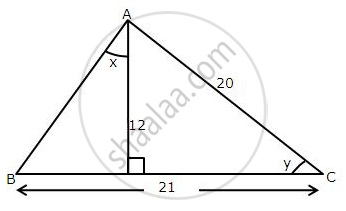
Use the information given in the following figure to evaluate:
`(10)/sin x + (6)/sin y – 6 cot y`.
In each of the following, one trigonometric ratio is given. Find the values of the other trigonometric.
sinA = `(12)/(13)`
From the given figure, prove that θ + ∅ = 90°. Also prove that there are two other right angled triangles. Find sin α, cos β and tan ∅
