Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If cot θ = 2 find all the values of all T-ratios of θ .
उत्तर
Let us first draw a right ΔABC, right angled at B and ∠𝐶 = 𝜃
Now, we know that cot θ = `"𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒"/" 𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑟" = (BC)/(AB) = 2`
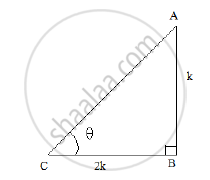
So, if BC = 2k, then AB = k, is a positive number.
Now, using Pythagoras theorem, we have:
`AC^2 = AB^2 + BC^2 = (2K)^2 + (K)^2`
`⟹ AC^2 = 4K^2 + K^2 = 5K^2`
`⟹ AC= sqrt(5k)`
Now, finding the other T-ratios using their definitions, we get:
Sin θ = `(AB)/(AC) = 5/(sqrt(5k)) = 1/(sqrt (2)`
∴ Cos θ = `1/ (cot θ ) = 1/2 , cosec θ = 1/(sin θ ) = sqrt(5) and secθ = 1/ (cos θ) = sqrt(5)/2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If cos θ=0.6 show that (5sin θ -3tan θ) = 0
If a right ΔABC , right-angled at B, if tan A=1 then verify that 2sin A . cos A = 1
Evaluate:
`(sin^2 30^0 + 4 cot^2 45^0-sec^2 60^0)(cosec^2 45^0 sec^2 30^0)`
In the adjoining figure, ΔABC is right-angled at B and ∠A = 450. If AC = 3`sqrt(2)`cm, find (i) BC, (ii) AB.
If sin (A+B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B and cos (A-B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
(i) sin (750)
(ii) cos (150)
From the following figure, find the values of:
- sin A
- cos A
- cot A
- sec C
- cosec C
- tan C

In the given figure, triangle ABC is right-angled at B. D is the foot of the perpendicular from B to AC. Given that BC = 3 cm and AB = 4 cm.
find :
- tan ∠DBC
- sin ∠DBA

If tan A + cot A = 5;
Find the value of tan2 A + cot2 A.
If cosec θ = `(29)/(20)`, find the value of: cosec θ - `(1)/("cot" θ)`
If cosec θ = `(29)/(20)`, find the value of: `("sec" θ)/("tan" θ - "cosec" θ)`
