Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the angles of a triangle are 30°, 60°, and 90°, then shown that the side opposite to 30° is half of the hypotenuse, and the side opposite to 60° is `sqrt(3)/2` times of the hypotenuse.
उत्तर
Given : In ΔCAB, m∠A=90°, m∠B = 60°, M∠C=30°
To prove : i AB = `1/2`BC ii. AC = `sqrt(3)/2 BC`
Construction: Take a point 'D' on ray BA such that AB = AD. join point C to point D.
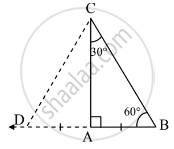
Proof: In ΔCBD,
AD= AB ....[By construction]
∴ A is the midpoint of seg BD ....(i)
Also, m∠CAB = 90° ....[Given]
∴ seg CA ⊥ seg BD .....(ii)
∴ seg CA is the perpendicular bisector of seg BD ....[From(i) and (ii)]
∴ CD = CB ...........[By perpendicular bisector theorem]
∴ ΔCDB is an isosceles triangle
∴ ∠CDB ≅ ∠CBD .....(iii)[By isosceles triangle theorem]
But,∠CBD = 60° ....(iv) [Given]
∴ ∠CDB = 60° ....[from (iii) and (iv)]
∴ ∠BCD = 60° .....[Remaining angle of a triangle ]
∴ ΔCDB is an equilateral triangle ....[All angle are 60°]
∴ BD = BC = CD ....(vi)[Sides of equilateral triabgle ]
AB = `1/2` BD .....(vi) [By construction]
AB = `1/2` BC . ...(vii) [ From (v) and (vi)]
In ΔCAB,
∠CAB = 90° ....[Given]
∴ BC2 = AC2+AB2 ............[ By pythagoras theorem]
∴` BC^2 = AC^2 + (1/2 BC)^2` ...[From (vii)]
∴`BC^2 = AC^2 +1/4 BC^2`
∴ `AC^2 = BC^2 -1/4 BC^2`
∴ `Ac^2 = (4BC^2-BC^32)/4`
∴ `AC^2 = (3BC^2)/4`
∴ `AC = sqrt(3)/2 BC` ...[ Taking square root on both sides]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Prove that the diagonals of a rectangle ABCD, with vertices A(2, -1), B(5, -1), C(5, 6) and D(2, 6), are equal and bisect each other.
Sides of triangle are given below. Determine it is a right triangle or not? In case of a right triangle, write the length of its hypotenuse. 50 cm, 80 cm, 100 cm
PQR is a triangle right angled at P. If PQ = 10 cm and PR = 24 cm, find QR.
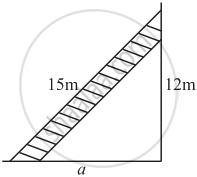
A 15 m long ladder reached a window 12 m high from the ground on placing it against a wall at a distance a. Find the distance of the foot of the ladder from the wall.
A tree is broken at a height of 5 m from the ground and its top touches the ground at a distance of 12 m from the base of the tree. Find the original height of the tree.
Find the side and perimeter of a square whose diagonal is 10 cm.
In the given figure, point T is in the interior of rectangle PQRS, Prove that, TS2 + TQ2 = TP2 + TR2 (As shown in the figure, draw seg AB || side SR and A-T-B)

In ΔABC, Find the sides of the triangle, if:
- AB = ( x - 3 ) cm, BC = ( x + 4 ) cm and AC = ( x + 6 ) cm
- AB = x cm, BC = ( 4x + 4 ) cm and AC = ( 4x + 5) cm
In the figure, given below, AD ⊥ BC.
Prove that: c2 = a2 + b2 - 2ax.
In triangle ABC, angle A = 90o, CA = AB and D is the point on AB produced.
Prove that DC2 - BD2 = 2AB.AD.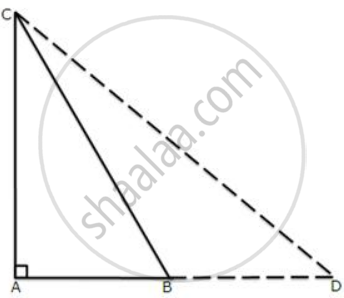
Choose the correct alternative:
In right-angled triangle PQR, if hypotenuse PR = 12 and PQ = 6, then what is the measure of ∠P?
In Fig. 3, ∠ACB = 90° and CD ⊥ AB, prove that CD2 = BD x AD.
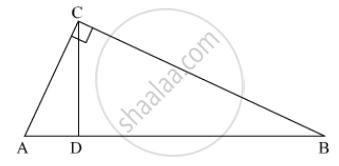
In the figure below, find the value of 'x'.
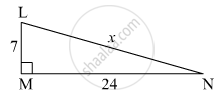
Find the length of the hypotenuse of a triangle whose other two sides are 24cm and 7cm.
A right triangle has hypotenuse p cm and one side q cm. If p - q = 1, find the length of third side of the triangle.
A point OI in the interior of a rectangle ABCD is joined with each of the vertices A, B, C and D. Prove that OB2 + OD2 = OC2 + OA2
In the figure, find AR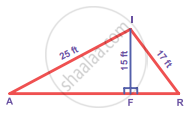
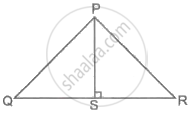
In an equilateral triangle PQR, prove that PS2 = 3(QS)2.
Two rectangles are congruent, if they have same ______ and ______.
Points A and B are on the opposite edges of a pond as shown in figure. To find the distance between the two points, the surveyor makes a right-angled triangle as shown. Find the distance AB.