Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If the angles of a triangle are 30°, 60°, and 90°, then shown that the side opposite to 30° is half of the hypotenuse, and the side opposite to 60° is `sqrt(3)/2` times of the hypotenuse.
Solution
Given : In ΔCAB, m∠A=90°, m∠B = 60°, M∠C=30°
To prove : i AB = `1/2`BC ii. AC = `sqrt(3)/2 BC`
Construction: Take a point 'D' on ray BA such that AB = AD. join point C to point D.
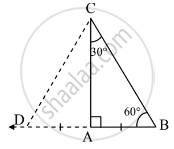
Proof: In ΔCBD,
AD= AB ....[By construction]
∴ A is the midpoint of seg BD ....(i)
Also, m∠CAB = 90° ....[Given]
∴ seg CA ⊥ seg BD .....(ii)
∴ seg CA is the perpendicular bisector of seg BD ....[From(i) and (ii)]
∴ CD = CB ...........[By perpendicular bisector theorem]
∴ ΔCDB is an isosceles triangle
∴ ∠CDB ≅ ∠CBD .....(iii)[By isosceles triangle theorem]
But,∠CBD = 60° ....(iv) [Given]
∴ ∠CDB = 60° ....[from (iii) and (iv)]
∴ ∠BCD = 60° .....[Remaining angle of a triangle ]
∴ ΔCDB is an equilateral triangle ....[All angle are 60°]
∴ BD = BC = CD ....(vi)[Sides of equilateral triabgle ]
AB = `1/2` BD .....(vi) [By construction]
AB = `1/2` BC . ...(vii) [ From (v) and (vi)]
In ΔCAB,
∠CAB = 90° ....[Given]
∴ BC2 = AC2+AB2 ............[ By pythagoras theorem]
∴` BC^2 = AC^2 + (1/2 BC)^2` ...[From (vii)]
∴`BC^2 = AC^2 +1/4 BC^2`
∴ `AC^2 = BC^2 -1/4 BC^2`
∴ `Ac^2 = (4BC^2-BC^32)/4`
∴ `AC^2 = (3BC^2)/4`
∴ `AC = sqrt(3)/2 BC` ...[ Taking square root on both sides]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a ∆ABC, AD ⊥ BC and AD2 = BC × CD. Prove ∆ABC is a right triangle
Sides of triangle are given below. Determine it is a right triangle or not? In case of a right triangle, write the length of its hypotenuse. 50 cm, 80 cm, 100 cm
In Figure, ABD is a triangle right angled at A and AC ⊥ BD. Show that AD2 = BD × CD
Identify, with reason, if the following is a Pythagorean triplet.
(5, 12, 13)
Find the length of the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle if remaining sides are 9 cm and 12 cm.
In right angle ΔABC, if ∠B = 90°, AB = 6, BC = 8, then find AC.
If P and Q are the points on side CA and CB respectively of ΔABC, right angled at C, prove that (AQ2 + BP2 ) = (AB2 + PQ2)
Prove that (1 + cot A - cosec A ) (1 + tan A + sec A) = 2
In the given figure, angle ACP = ∠BDP = 90°, AC = 12 m, BD = 9 m and PA= PB = 15 m. Find:
(i) CP
(ii) PD
(iii) CD

In the given figure, AD = 13 cm, BC = 12 cm, AB = 3 cm and angle ACD = angle ABC = 90°. Find the length of DC.
The sides of the triangle are given below. Find out which one is the right-angled triangle?
40, 20, 30
Each side of rhombus is 10cm. If one of its diagonals is 16cm, find the length of the other diagonals.
In the given figure. PQ = PS, P =R = 90°. RS = 20 cm and QR = 21 cm. Find the length of PQ correct to two decimal places.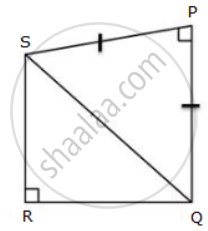
Find the distance between the helicopter and the ship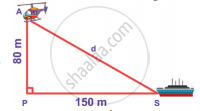
Choose the correct alternative:
If length of sides of a triangle are a, b, c and a2 + b2 = c2, then which type of triangle it is?
In a quadrilateral ABCD, ∠A + ∠D = 90°. Prove that AC2 + BD2 = AD2 + BC2
[Hint: Produce AB and DC to meet at E.]
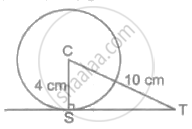
In the adjoining figure, a tangent is drawn to a circle of radius 4 cm and centre C, at the point S. Find the length of the tangent ST, if CT = 10 cm.
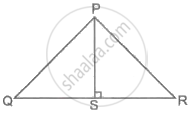
In an equilateral triangle PQR, prove that PS2 = 3(QS)2.
In a right-angled triangle ABC, if angle B = 90°, BC = 3 cm and AC = 5 cm, then the length of side AB is ______.
A right-angled triangle may have all sides equal.
