Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the given figure, D is the midpoint of side BC and AE⊥BC. If BC = a, AC = b, AB = c, AD = p and AE = h, prove that
(i)`B^2=p^2+ax+a^2/x`
(ii)` c^2=p^2-ax+a^2/x`
(iii) `b^2+c^2=2p^2+a^2/2`
(iv)`b^2-c^2=2ax`

उत्तर
(1)In right-angled triangle AEC, applying Pythagoras theorem, we have:
`AC^2=AE^2+EC^2`
⇒ `B^2=h^2(x+a/2)^2=h^2+x^2+a^2/4+ax`.......(1)
In right – angled triangle AED, we have:
`AD^2=AE^2+ED^2`
⇒ `p^2=h^2+x^2` .............(2)
Therefore,
from (i) and (ii),
`b^2=p^2+ax+a^2/x`
(2) In right-angled triangle AEB, applying Pythagoras, we have:
`AB^2=AE^2+EB^2`
⇒ `c^2=h^2+(a/2-x)^2 (∵ BD=a/2 and BE=BD-x)`
⇒ `C^2=h^2+x^2-a^2/4 (∵ h^2+x^2=p^2)`
⇒`c^2=p^2-ax+a^2/x`
(3)
Adding (i) and (ii), we get:
⇒` b^2+c^2=p^2+ax+a^2/4+p^2-ax+a^2/4`
`=2p^2+ax-ax+(a^2+a^2)/4`
=`2p^2+a^2/2`
(4)
Subtracting (ii) from (i), we get:
`b^2-c^2=p^2+ax+a^2/4-(p^2-ax+a^2/4)`
`=p^2-p^2+ax+ax+a^2/4-a^2/4`
`=2ax`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If AD = x, DB = x − 2, AE = x + 2 and EC = x − 1, find the value of x.
In a ΔABC, D and E are points on AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC. If AD = 2.4cm, AE = 3.2 cm, DE = 2cm and BC = 5 cm, find BD and CE.
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC such that DE║BC. Find the value of x, when
AD = 4cm, DB = (x – 4) cm, AE = 8cm and EC = (3x – 19) cm.
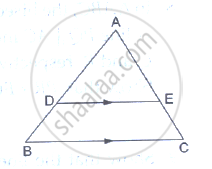
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a ΔABC such that DE║BC. Find the value of x, when
AD = (7x – 4) cm, AE = (5x – 2) cm, DB = (3x + 4) cm and EC = 3x cm.
ΔABC and ΔDBC lie on the same side of BC, as shown in the figure. From a point P on BC, PQ||AB and PR||BD are drawn, meeting AC at Q and CD at R respectively. Prove that QR||AD.
In the given figure, O is a point inside a ΔPQR such that ∠PQR such that ∠POR = 90°, OP = 6cm and OR = 8cm. If PQ = 24cm and QR = 26cm, prove that ΔPQR is right-angled.
In triangle BMP and CNR it is given that PB= 5 cm, MP = 6cm BM = 9 cm and NR = 9cm. If ΔBMP∼ ΔCNR then find the perimeter of ΔCNR
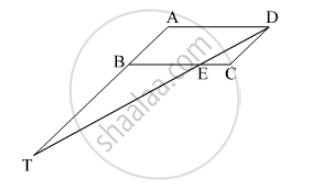
◻ABCD is a parallelogram point E is on side BC. Line DE intersects ray AB in point T. Prove that DE × BE = CE × TE.
In the given figure ΔABC ~ ΔPQR, PM is median of ΔPQR. If ar ΔABC = 289 cm², BC = 17 cm, MR = 6.5 cm then the area of ΔPQM is ______.
 |
 |
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC and P and Q are points on AD and BC, respectively such that PQ || DC. If PD = 18 cm, BQ = 35 cm and QC = 15 cm, find AD.
