Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of a neat circuit diagram, explain the working of a photodiode.
उत्तर

a. A photodiode is a special purpose P-N junction diode fabricated with a transparent window to allow light to fall on the diode.
b. When the photodiode is illuminated with light (photons) with energy h greater than the energy gap Eg of the semiconductor, then electron-hole pairs are generated due to the absorption of photons.
c. The diode is fabricated such that the generation of electron-hole pairs takes place in or near the depletion region of the diode.
d. Due to electric field of the junction, electrons and holes are separated before they recombine.
e. The direction of the electric field is such that electrons reach N-side and holes reach Pside. Electrons are collected on N-side and holes are collected on P-side giving rise to an e.m.f.
f. When an external load is connected, current flows. The magnitude of the photocurrent depends on the intensity of incident light.
g. It is easier to observe the change in the current with change in the light intensity, if a reverse bias is applied. Thus, photodiode can be used as a photodetector to detect optical signals.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain with the help of a diagram, how depletion region and potential barrier are formed in a junction diode.
If a small voltage is applied to a p-n junction diode, how will the barrier potential be affected when it is (i) forward biased
If a small voltage is applied to a p-n junction diode, how will the barrier potential be affected when it is(ii) reveres biased?
With what considerations in view, a photodiode is fabricated? State its working with the help of a suitable diagram.
Even though the current in the forward bias is known to be more than in the reverse bias, yet the photodiode works in reverse bias. What is the reason?
Using the necessary circuit diagrams, show how the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction are obtained in
Reverse biasing
How are these characteristics made use of in rectification?
Carbon, silicon and germanium have four valence electrons each. These are characterised by valence and conduction bands separated by energy band gap respectively equal to (Eg)C, (Eg)Si and (Eg)Ge. Which of the following statements is true?
A p-n photodiode is fabricated from a semiconductor with band gap of 2.8 eV. Can it detect a wavelength of 6000 nm?
The width of depletion region of p-n junction diode is _______.
(A) 0.5 nm to 1 nm
(B) 5 nm to 10 nm
(C) 50 nm to 500 nm
(D) 500 nm to 1000 nm
Sunil and his parents were travelling to their village in their car. On the way his mother noticed some grey coloured panels installed on the roof of a low building. She enquired from Sunil what those panels were and Sunil told his mother that those were solar panels.
(a) What were the values displayed by Sunil and his mother? State one value for each.
(b) In what way would the use of solar panels prove to be very useful?
(c) Name the semiconductor device used in solar panels. Briefly explain with the help of a diagram, how this device works
Why is zener diode fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n-sides of the junction?
How is a photodiode fabricated?
The current in the forward bias is known to be more (~mA) than the current in the reverse bias (~μA). What is the reason, then, to operate the photodiode in reverse bias?
Draw the circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier using p-n junction diode.
Explain its working and show the output, input waveforms.
Show the output waveforms (Y) for the following inputs A and B of (i) OR gate (ii) NAND gate ?
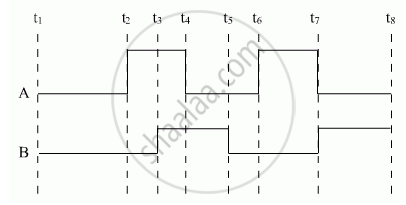
Describe briefly, with the help of a diagram, the role of the two important processes involved in the formation of a p-n junction ?
How does a light emitting diode (LED) work? Give two advantages of LED’s over the conventional incandescent lamps.
Draw the circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode in reverse bias. How is photodiode used to measure light intensity?
Explain the formation of depletion layer and potential barrier in a p−n junction.
The plate resistance of a triode is 8 kΩ and the transconductance is 2.5 millimho. (a) If the plate voltage is increased by 48 V and the grid voltage is kept constant, what will be the increase in the plate current? (b) With plate voltage kept constant at this increased value, by how much should the grid voltage be decreased in order to bring the plate current back to its initial value?
Explain how a potential barrier is developed in a p-n junction diode.
Write the important considerations which are to be taken into account while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of band gap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range? Draw a circuit diagram and explain its action.
Draw the V-I characteristics of an LED. State two advantages of LED lamps over convertional incandescent lamps.
Answer the following question.
Draw solar cell V-I characteristics.
With reference to Semiconductor Physics,
Name the process that causes depletion region in a p-n junction.
Pressure P varies as P = `alpha/beta "exp" (- (alpha x)/"k"_"BT")`, where x denotes the distance, kB is the Boltzmann's constant, T is the absolute temperature and α and β are constant. The dimension of β is ______.
Consider the following statements (A) and (B) and identify the correct answer.
- A Zener diode is connected in reverse bias when used as a voltage regulator.
- The potential barrier of the p-n junction lies between 0.1 V to 0.3 V.
In Figure, assuming the diodes to be ideal ______.

The amplifiers X, Y and Z are connected in series. If the voltage gains of X, Y and Z are 10, 20 and 30, respectively and the input signal is 1 mV peak value, then what is the output signal voltage (peak value)
- if dc supply voltage is 10V?
- if dc supply voltage is 5V?
Draw solar cells of I-V characteristics.
How can a photodiode be used to measure light intensity?
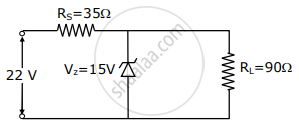
The value of power dissipated across the Zener diode (Vz = 15 V) connected in the circuit as shown in the figure is x × 10–1 watt. The value of x, to the nearest integer, is ______.
What energy conversion takes place in a solar cell?
