Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With the help of a neat circuit diagram, explain the working of a photodiode.
Solution

a. A photodiode is a special purpose P-N junction diode fabricated with a transparent window to allow light to fall on the diode.
b. When the photodiode is illuminated with light (photons) with energy h greater than the energy gap Eg of the semiconductor, then electron-hole pairs are generated due to the absorption of photons.
c. The diode is fabricated such that the generation of electron-hole pairs takes place in or near the depletion region of the diode.
d. Due to electric field of the junction, electrons and holes are separated before they recombine.
e. The direction of the electric field is such that electrons reach N-side and holes reach Pside. Electrons are collected on N-side and holes are collected on P-side giving rise to an e.m.f.
f. When an external load is connected, current flows. The magnitude of the photocurrent depends on the intensity of incident light.
g. It is easier to observe the change in the current with change in the light intensity, if a reverse bias is applied. Thus, photodiode can be used as a photodetector to detect optical signals.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Colour of light emitted by LED depends upon__________________ .
- its forward bias
- its reverse bias
- the band gap of the material of semiconductor
- its size
Meeta's father was driving her to school. At the traffic signal, she noticed that each traffic light was made of many tiny lights instead of a single bulb. When Meeta asked this question to her father, he explained the reason for this.
Answer the following questions based on above information:
(i) What were the values displayed by Meeta and her father?
(ii) What answer did Meeta's father give?
(iii) What are the tiny lights in traffic signals called and how do these operate?
How is a Zener diode fabricated?
If a small voltage is applied to a p-n junction diode, how will the barrier potential be affected when it is (i) forward biased
Using the necessary circuit diagrams, show how the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction are obtained in
Reverse biasing
How are these characteristics made use of in rectification?
A p-n photodiode is fabricated from a semiconductor with band gap of 2.8 eV. Can it detect a wavelength of 6000 nm?
Write briefly the important processes that occur during the formation of p−n junction. With the help of necessary diagrams, explain the term 'barrier potential'.
Why is zener diode fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n-sides of the junction?
Briefly explain its working. Draw its V - I characteristics for two different intensities of illumination ?
The current in the forward bias is known to be more (~mA) than the current in the reverse bias (~μA). What is the reason, then, to operate the photodiode in reverse bias?
Show the output waveforms (Y) for the following inputs A and B of (i) OR gate (ii) NAND gate ?
Describe briefly, with the help of a diagram, the role of the two important processes involved in the formation of a p-n junction ?
How does a light emitting diode (LED) work? Give two advantages of LED’s over the conventional incandescent lamps.
Draw the circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode in reverse bias. How is photodiode used to measure light intensity?
Explain the formation of depletion layer and potential barrier in a p−n junction.
The plate resistance of a triode is 8 kΩ and the transconductance is 2.5 millimho. (a) If the plate voltage is increased by 48 V and the grid voltage is kept constant, what will be the increase in the plate current? (b) With plate voltage kept constant at this increased value, by how much should the grid voltage be decreased in order to bring the plate current back to its initial value?
Write the important considerations which are to be taken into account while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of band gap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range? Draw a circuit diagram and explain its action.
Choose the correct answer from given options
The wavelength and intensity of light emitted by a LED depend upon
What is a solar cell?
Answer the following question.
Draw solar cell V-I characteristics.
Answer the following question.
Explain the three processes involved in solar cell working.
With reference to Semiconductor Physics,
Name the process that causes depletion region in a p-n junction.
A p-n photodiode is fabricated from a semiconductor with a band gap of 2.5 eV. lt can detect a signal of wavelength ______.
Which one of the following is not the advantage of LED?
Consider the following statements (A) and (B) and identify the correct answer.
- A Zener diode is connected in reverse bias when used as a voltage regulator.
- The potential barrier of the p-n junction lies between 0.1 V to 0.3 V.
In Figure, assuming the diodes to be ideal ______.

If the resistance R1 is increased (Figure), how will the readings of the ammeter and voltmeter change?
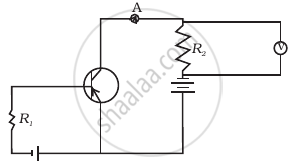
Why a photo-diode is operated in reverse bias whereas the current in the forward bias is much larger than that in the reverse bias? Explain. Mention its two uses.
Draw solar cells of I-V characteristics.
What energy conversion takes place in a solar cell?
