Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define Mutual Inductance.
Solution
The mutual inductance M of two circuits (or coils) is the magnetic flux (`phi_"s"`) linked with the secondary circuit per unit current (IP) of the primary circuit.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The co-efficient of mutual induction between primary and secondary coil is 2H. Calculate induced e.m.f. if current of 4A is cut off in 2.5 x 10-4 seconds
If the radius of a sphere is doubled without changing the charge on it, then electric flux originating from the sphere is ______.
Define mutual inductance.
Explain the meaning of the term mutual inductance.
In an experiment, two coils c1 and c2 are placed close to each other. Find out the expression for the emf induced in the coil c1 due to a change in the current through the coil c2.
The current flowing through an inductor of self inductance L is continuously increasing. Plot a graph showing the variation of Magnetic potential energy stored versus the current.
A 1.0 m long metallic rod is rotated with an angular frequency of 400 rad s−1 about an axis normal to the rod passing through its one end. The other end of the rod is in contact with a circular metallic ring. A constant and uniform magnetic field of 0.5 T parallel to the axis exists everywhere. Calculate the emf developed between the centre and the ring.
An air-cored solenoid with length 30 cm, area of cross-section 25 cm2 and number of turns 500, carries a current of 2.5 A. The current is suddenly switched off in a brief time of 10−3 s. How much is the average back emf induced across the ends of the open switch in the circuit? Ignore the variation in magnetic field near the ends of the solenoid.
Explain self induction and mutual induction
Explain the phenomenon of mutual induction.
A pair of adjacent coils has a mutual inductance of 1.5 H. If the current in one coil changes from 0 to 20 A in 0.5 s, what is the change of flux linkage with the other coil?
A coil of self-inductance 2.5H and resistance 20Ω is connected to a battery of emf 120V having the internal resistance of 5 n. Find:
1) The time constant of the circuit.
2) The current in the circuit in steady state
Two circular loops are placed with their centres separated by a fixed distance. How would you orient the loops to have (a) the largest mutual inductance (b) the smallest mutual inductance?
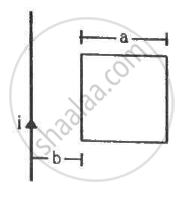
Find the mutual inductance between the straight wire and the square loop of figure.
The current in a long solenoid of radius R and having n turns per unit length is given by i= i0 sin ωt. A coil having N turns is wound around it near the centre. Find (a) the induced emf in the coil and (b) the mutual inductance between the solenoid ant the coil.
A solenoid of length 20 cm, area of cross-section 4.0 cm2 and having 4000 turns is placed inside another solenoid of 2000 turns having a cross-sectional area 8.0 cm2 and length 10 cm. Find the mutual inductance between the solenoids.
An emf of 96.0 mV is induced in the windings of a coil when the current in a nearby coil is increasing at the rate of 1.20 A/s. What is the mutual inductance (M) of the two coils?
The dimensions of self or mutual inductance are given as ______.
In mutual induction, the main current remains same because ____________.
In an induction coil, the coefficient of mutual inductance is 6 henry. If a current of 10 ampere in the primary coil is cut-off in `1/1500"s"`, the e.m.f. at the terminals of the secondary coil will be ____________.
A current I = 10 sin (50 π t) ampere is passed in the first coil which induces a maximum e.m.f. of 5 π volt in the second coil. The mutual inductance between the coils is ______.
An alternating current of frequency 200 rad/s and peak value 1 A is applied to the primary of a transformer. If the coefficient of mutual induction between the primary and the secondary is 1.5H, then the voltage induced in the secondary will be approximately (π = 2217)
A coil of radius 'r' is placed on another coil (whose radius is 'R' and current flowing through it is changing) so that their centres coincide. (R>>r) if both the coils are coplanar then the mutual inductance between them is proportional to ______.
Two different wire loops are concentric and lie in the same plane. The current in the outer loop (I) is clockwise and increases with time. The induced current in the inner loop.
Alternating current of peak value `(2/pi)` ampere flows through the primary coil of transformer. The coefficient of mutual inductance between primary and secondary coil is 1 H. The peak e.m.f. induced in secondary coil is ______. (Frequency of a.c. = 50 Hz)
The mutual inductance between two coplanar concentric rings A and B of radii 'R1' and 'R2' placed in air when a current 'I' flows through ring A is (R1 >> R2) (µ0 = permeability of free space) ____________.
Two coils P and Q have mutual inductance 'M' H. If the current in the primary is I = I0 sin `omega`t, then the maximum vlaue of e.m.f. indued in coil Q is ____________.
The mutual inductance between two coils is 0.09 henry. If the current in the primary coil changes from 0 to 20 A in 0.006 s, the e.m.f. induced in the secondary coil at that instant is ____________.
The coefficient of mutual inductance is 2H and induced e.m.f. across secondary is 2 kV. Current in the primary is reduced from 6 A and 3A. The time required for the change of current is ____________.
A solenoid is connected to a battery so that a steady current flows through it. If an iron core is inserted into the solenoid, the current will ______.
Two coils are placed close to each other. The mutual inductance of the pair of coils depends upon the ______.
Two conducting circular loops of radii R1 and R2 are placed in the same plane with their centres coinciding. If R1 > > R2, the mutual inductance M between them will be directly proportional to ______.
Two conducting circular loops of radii R1 and R2 are placed in the same plane with their centres coinciding. If R1 >> R2, the mutual inductance M between them will be directly proportional to ______.
There are two coils A and B seperated by some distance. If a current of 2A flows through A, a magnetic flux of 10-2 Wb passes through B (no current through B). If no current passes through A and a current of 1A passes through B, what is the flux through A?
A toroid is a long coil of wire wound over a circular core. The major radius and cross-sectional radius of the toroid are R and r, respectively. The coefficient of mutual induction of the toroid is ______.
(The magnetic field in it is uniform, N = number of turns, R >> r, μ0 = permeability of free space)
Two circular loops, one of small radius r and the other of larger radius R, such that R >> r, are placed coaxially with centres coinciding. Obtain the mutual inductance of the arrangement.
The mutual inductance of a pair of adjacent coils is 1.5 H. If the current is one coil changes from 5 A to 10 A in 0.1 s, the rate of change of magnet flux linkage is ______.
