Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If sin θ = cos (θ – 45°), where θ – 45° are acute angles, find the degree measure of θ
Solution
Sin θ = cos (θ – 45°)
Cos θ = cos (90 – θ)
Cos (θ – 45°) = sin (90° - (θ – 45°)) = sin (90 – θ + 45°)
Sin θ(135 – θ)
θ = 135 – θ
2θ = 135
∴ θ = 135°/2
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If A = 30° and B = 60°, verify that cos (A + B) = cos A cos B − sin A sin B
Show that:
(i)` (1-sin 60^0)/(cos 60^0)=(tan60^0-1)/(tan60^0+1)`
In the adjoining figure, ΔABC is a right-angled triangle in which ∠B = 900, ∠300 and AC = 20cm. Find (i) BC, (ii) AB.
Given: cos A = `( 5 )/ ( 13 )`
Evaluate:
- `(sin "A "–cot "A") / (2 tan "A")`
- `cot "A" + 1/cos"A"`
In the diagram, given below, triangle ABC is right-angled at B and BD is perpendicular to AC.
Find:
(i) cos ∠DBC
(ii) cot ∠DBA

In each of the following, one trigonometric ratio is given. Find the values of the other trigonometric.
cosB = `(4)/(5)`
In a right-angled triangle PQR, ∠PQR = 90°, QS ⊥ PR and tan R =`(5)/(12)`, find the value of sin ∠PQS
If sin A = `(7)/(25)`, find the value of : `"cos A" + (1)/"cot A"`
In the given figure, AC = 13cm, BC = 12 cm and ∠B = 90°. Without using tables, find the values of: sin A cos A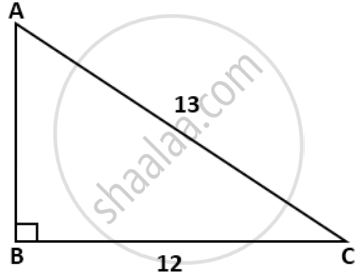
Evaluate: `5/(cot^2 30^circ) + 1/(sin^2 60^circ) - cot^2 45^circ + 2 sin^2 90^circ`.
