Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the figure, given below, find: ∠ABC. Show steps of your working.

Solution
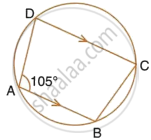
∠ADC + ∠ABC = 180°
(Sum of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180°)
`=>` ∠ABC = 180° – 75° = 105°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
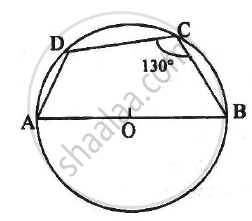
In the given figure, AB is the diameter of a circle with centre O. ∠BCD = 130o. Find:
1) ∠DAB
2) ∠DBA
In cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, ∠DAC = 27°; ∠DBA = 50° and ∠ADB = 33°.
Calculate:
- ∠DBC,
- ∠DCB,
- ∠CAB.

ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. Sides AB and DC produced meet at point E; whereas sides BC and AD produced meet at point F. If ∠DCF : ∠F : ∠E = 3 : 5 : 4, find the angles of the cyclic quadrilateral ABCD.
Bisectors of angles A, B and C of a triangle ABC intersect its circumcircle at D, E and F respectively. Prove that the angles of Δ DEF are 90° - `"A"/2` , 90° - `"B"/2` and 90° - `"C"/2` respectively.
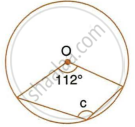
In the following figure, O is the centre of the circle. Find the values of a, b and c.
ABCD is a parallelogram. A circle through vertices A and B meets side BC at point P and side AD at point Q. Show that quadrilateral PCDQ is cyclic.
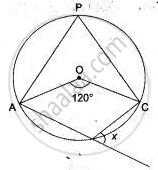
If O is the centre of the circle, find the value of x in each of the following figures
In the figure , Δ PQR is an isosceles triangle with PQ = PR, and m ∠ PQR = 35°. Find m ∠ QSR and ∠ QTR.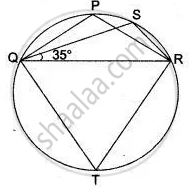
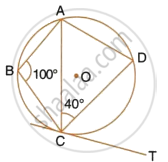
In the given circle with centre O, ∠ABC = 100°, ∠ACD = 40° and CT is a tangent to the circle at C. Find ∠ADC and ∠DCT.
An exterior angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is congruent to the angle opposite to its adjacent interior angle, to prove the theorem complete the activity.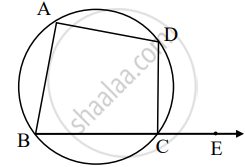
Given: ABCD is cyclic,
`square` is the exterior angle of ABCD
To prove: ∠DCE ≅ ∠BAD
Proof: `square` + ∠BCD = `square` .....[Angles in linear pair] (I)
ABCD is a cyclic.
`square` + ∠BAD = `square` ......[Theorem of cyclic quadrilateral] (II)
By (I) and (II)
∠DCE + ∠BCD = `square` + ∠BAD
∠DCE ≅ ∠BAD
