Advertisements
Advertisements
A man uses a concave mirror for shaving. He keeps his face at a distance of 25 cm from the mirror and gets an image which is 1.4 times enlarged. Find the focal length of the mirror.
Concept: undefined > undefined
The image of an extended object, placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a mirror, will be erect if
(a) the object and the image are both real
(b) the object and the image are both virtual
(c) the object is real but the image is virtual
(d) the object is virtual but the image is real.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Advertisements
Light is incident from glass (μ = 1.5) to air. Sketch the variation of the angle of deviation δ with the angle of incident i for 0 < i < 90°.
Concept: undefined > undefined
A spherical surface of radius 30 cm separates two transparent media A and B with refractive indices 1.33 and 1.48 respectively. The medium A is on the convex side of the surface. Where should a point object be placed in medium A so that the paraxial rays become parallel after refraction at the surface?
Concept: undefined > undefined
A narrow pencil of parallel light is incident normally on a solid transparent sphere of radius r. What should be the refractive index is the pencil is to be focussed (a) at the surface of the sphere, (b) at the centre of the sphere.
Concept: undefined > undefined
A diverging lens of focal length 20 cm and a converging mirror of focal length 10 cm are placed coaxially at a separation of 5 cm. Where should an object be placed so that a real image is formed at the object itself?
Concept: undefined > undefined
A converging lens of focal length 12 cm and a diverging mirror of focal length 7.5 cm are placed 5.0 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. Where should an object be placed so that its image falls on itself?
Concept: undefined > undefined
A converging lens and a diverging mirror are placed at a separation of 15 cm. The focal length of the lens is 25 cm and that of the mirror is 40 cm. Where should a point source be placed between the lens and the mirror so that the light, after getting reflected by the mirror and then getting transmitted by the lens, comes out parallel to the principal axis?
Concept: undefined > undefined
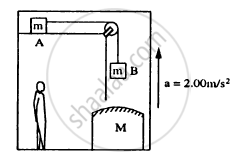
Consider the situation shown in figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration of 2.00 m s−2 and the focal length of the mirror is 12.0 cm. All the surfaces are smooth and the pulley is light. The mass-pulley system is released from rest (with respect to the elevator) at t = 0 when the distance of B from the mirror is 42.0 cm. Find the distance between the image of the block B and the mirror at t = 0.200 s. Take g = 10 m s−2.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Mark out the correct options.
Concept: undefined > undefined
A point charge is brought inside an electric field. The electric field at a nearby point
(a) will increase if the charge is positive
(b) will decrease if the charge is negative
(c) may increase if the charge is positive
(d) may decrease if the charge is negative
Concept: undefined > undefined
A proton and an electron are placed in a uniform electric field.
Concept: undefined > undefined
A point charge q is placed in a cavity in a metal block. If a charge Q is brought outside the metal, will the charge q feel an electric fore?
Concept: undefined > undefined
A hollow metal sphere and a solid metal sphere of equal radii are given equal charges. Which of the two will have higher potential?
Concept: undefined > undefined
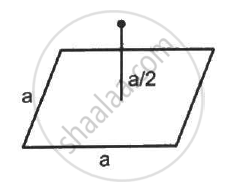
A charge Q is placed at a distance a/2 above the centre of a horizontal, square surface of edge a as shown in the following figure . Find the flux of the electric field through the square surface.
Concept: undefined > undefined
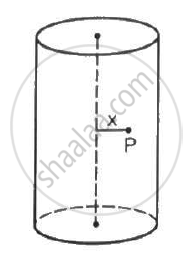
A long cylindrical volume contains a uniformly distributed charge of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the cylindrical volume at a distance x from its axis (see the figure).
Concept: undefined > undefined
Two large conducting plates are placed parallel to each other with a separation of 2⋅00 cm between them. An electron starting from rest near one of the plates reaches the other plate in 2⋅00 microseconds. Find the surface charge density on the inner surfaces.
Concept: undefined > undefined
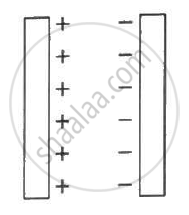
Two large conducting plates are placed parallel to each other and they carry equal and opposite charges with surface density σ as shown in the figure. Find the electric field (a) at the left of the plates (b) in between the plates and (c) at the right of the plates.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Two particles A and B with charges q and 2q, respectively, are placed on a smooth table with a separation d. A third particle C is to be clamped on the table in such a way that the particles A and B remain at rest on the table under electrical forces. What should be the charge on C and where should it be clamped?
Concept: undefined > undefined
Two particles A and B, each with a charge Q, are placed a distance d apart. Where should a particle of charge q be placed on the perpendicular bisector of AB, so that it experiences maximum force? What is the magnitude of this maximum force?
Concept: undefined > undefined
