Advertisements
Chapters
2: Units and Measurements
3: Motion in a Straight Line
▶ 4: Motion in a Plane
5: Laws of Motion
6: Work, Energy and Power
7: System of Particles and Rotational Motion
8: Gravitation
9: Mechanical Properties of Solids
10: Mechanical Properties of Fluids
11: Thermal Properties of Matter
12: Thermodynamics
13: Kinetic Theory
14: Oscillations
15: Waves
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 4: Motion in a Plane
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of CBSE NCERT for Physics [English] Class 11.
NCERT solutions for Physics [English] Class 11 4 Motion in a Plane Exercises [Pages 85 - 88]
State, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector: volume, mass, speed, acceleration, density, number of moles, velocity, angular frequency, displacement, angular velocity.
Pick out the two scalar quantities in the following list:
Force, Angular momentum, Work, Current, Linear momentum, Electric field, Average velocity, Magnetic moment, Relative velocity.
Pick out the only vector quantity in the following list:
Temperature
Pressure
Impulse
Time
Power
Total path length
Energy
Gravitational potential
Coefficient of friction
Charge
State with reasons, whether the following algebraic operations with scalar and vector physical quantities are meaningful:
- adding any two scalars,
- adding a scalar to a vector of the same dimensions,
- multiplying any vector by any scalar,
- multiplying any two scalars,
- adding any two vectors,
- adding a component of a vector to the same vector.
Read the statement below carefully and state with reason, if it is true or false:
The magnitude of a vector is always a scalar.
True
False
Read the statement below carefully and state with reason, if it is true or false:
Each component of a vector is always a scalar.
True
False
Read the statement below carefully and state with reason, if it is true or false:
The total path length is always equal to the magnitude of the displacement vector of a particle.
True
False
Read the statement below carefully and state with reason, if it is true or false:
The average speed of a particle (defined as total path length divided by the time taken to cover the path) is either greater or equal to the magnitude of average velocity of the particle over the same interval of time.
True
False
Read the statement below carefully and state with reason, if it is true or false:
Three vectors not lying in a plane can never add up to give a null vector.
True
False
Establish the following vector inequalities geometrically or otherwise:
- | a+b | ≤ |a| + |b|
- |a + b| ≥ | |a| - |b| |
- |a - b| ≤ |a| + |b|
- |a-b| ≥ | |a| - |b| |
When does the equality sign above apply?
Given a + b + c + d = 0, state whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
a, b, c, and d must each be a null vector.
Correct
Incorrect
Given a + b + c + d = 0, state whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
The magnitude of (a + c) equals the magnitude of (b + d).
Correct
Incorrect
Given a + b + c + d = 0, state whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
The magnitude of a can never be greater than the sum of the magnitudes of b, c, and d.
Correct
Incorrect
Given a + b + c + d = 0, state whether the following statement is correct or incorrect:
b + c must lie in the plane of a and d if a and d are not collinear, and in the line of a and d, if they are collinear.
Correct
Incorrect
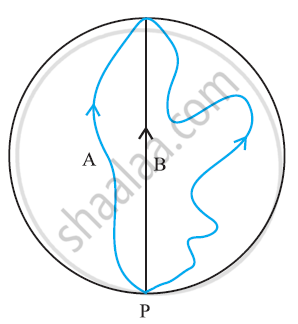
Three girls skating on a circular ice ground of radius 200 m start from a point P on the edge of the ground and reach a point Q diametrically opposite to P following different paths as shown in the figure. What is the magnitude of the displacement vector for each? For which girl is this equal to the actual length of the path skated?
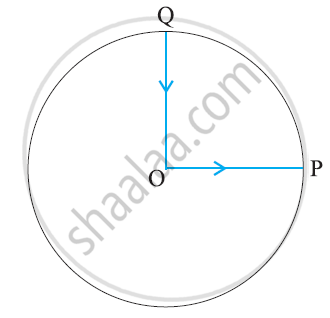
A cyclist starts from the centre O of a circular park of radius 1 km, reaches the edge P of the park, then cycles along the circumference, and returns to the centre along QO as shown in figure. If the round trip takes 10 min, what is the (a) net displacement, (b) average velocity, and (c) average speed of the cyclist?
On an open ground, a motorist follows a track that turns to his left by an angle of 60° after every 500 m. Starting from a given turn, specify the displacement of the motorist at the third, sixth and eighth turn. Compare the magnitude of the displacement with the total path length covered by the motorist in each case.
A passenger arriving in a new town wishes to go from the station to a hotel located 10 km away on a straight road from the station. A dishonest cabman takes him along a circuitous path 23 km long and reaches the hotel in 28 min.
- What is the average speed of the taxi,
- the magnitude of average velocity? Are the two equal?
Rain is falling vertically with a speed of 30 m s–1. A woman rides a bicycle with a speed of 10 m s–1in the north to south direction. What is the direction in which she should hold her umbrella?
A man can swim with a speed of 4.0 km/h in still water. How long does he take to cross a river 1.0 km wide if the river flows steadily at 3.0 km/h and he makes his strokes normal to the river current? How far down the river does he go when he reaches the other bank?
In a harbour, wind is blowing at the speed of 72 km/h and the flag on the mast of a boat anchored in the harbour flutters along the N-E direction. If the boat starts moving at a speed of 51 km/h to the north, what is the direction of the flag on the mast of the boat?
The ceiling of a long hall is 25 m high. What is the maximum horizontal distance that a ball thrown with a speed of 40 m s–1 can go without hitting the ceiling of the hall?
A cricketer can throw a ball to a maximum horizontal distance of 100 m. How much high above the ground can the cricketer throw the same ball?
A stone tied to the end of a string 80 cm long is whirled in a horizontal circle with a constant speed. If the stone makes 14 revolutions in 25 s, what is the magnitude and direction of acceleration of the stone?
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop of radius 1.00 km with a steady speed of 900 km/h. Compare its centripetal acceleration with the acceleration due to gravity.
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason, if it is true or false:
The net acceleration of a particle in circular motion is always along the radius of the circle towards the centre.
True
False
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason, if it is true or false:
The velocity vector of a particle at a point is always along the tangent to the path of the particle at that point.
True
False
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason, if it is true or false:
The acceleration vector of a particle in uniform circular motion averaged over one cycle is a null vector.
True
False
The position of a particle is given by
`r = 3.0t hati − 2.0t 2 hatj + 4.0 hatk m`
Where t is in seconds and the coefficients have the proper units for r to be in metres.
- Find the v and a of the particle?
- What is the magnitude and direction of velocity of the particle at t = 2.0 s?
A particle starts from the origin at t = 0 s with a velocity of 10.0 `hatj "m/s"` and moves in the x-y plane with a constant acceleration of `(8.0 hati + 2.0 hatj) ms^(-2)`.
- At what time is the x-coordinate of the particle 16 m? What is the y-coordinate of the particle at that time?
- What is the speed of the particle at the time?
`hati "and" hatj` are unit vectors along x- and y-axis respectively. What is the magnitude and direction of the vectors `hati+hatj` and `hati-hatj` ? What are the components of a vector `A = 2hati + 3hatj` along the directions of `hati + hatj` and `hati - hatj` ? [You may use graphical method]
For any arbitrary motion in space, state whether the following statement is true:
`"V"_"average"` = `(1/2)("v"("t"_1) + "v"("t"_2))`
(The ‘average’ stands for average of the quantity over the time interval t1 to t2)
True
False
For any arbitrary motion in space, state whether the following statement is true:
`"V"_"average"` = [r(t2) - r(t1) ] /(t2 – t1)
True
False
For any arbitrary motion in space, state whether the following statement is true:
v (t) = v (0) + a t
(The ‘average’ stands for average of the quantity over the time interval t1 to t2)
True
False
For any arbitrary motion in space, state whether the following statement is true:
`"r"("t") = "r"(0) + "v"(0)"t" + 1/2 "a" "t"^2 `
(The ‘average’ stands for average of the quantity over the time interval t1 to t2)
True
False
For any arbitrary motion in space, state whether the following statement is true:
`"a"_"average"=["v"("t"_2) - "v"("t"_1)]/("t"_2 - "t"_1)`
(The ‘average’ stands for average of the quantity over the time interval t1 to t2)
True
False
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason and example, if it is true or false:
A scalar quantity is one that is conserved in a process.
True
False
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason and example, if it is true or false:
A scalar quantity is one that can never take negative values.
True
False
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason and example, if it is true or false:
A scalar quantity is one that must be dimensionless.
True
False
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason and example, if it is true or false:
A scalar quantity is one that does not vary from one point to another in space.
True
False
Read statement below carefully and state, with reasons and examples, if it is true or false:
A scalar quantity is one that has the same value for observers with different orientations of axes
true
false
An aircraft is flying at a height of 3400 m above the ground. If the angle subtended at a ground observation point by the aircraft positions 10.0 s a part is 30°, what is the speed of the aircraft?
A vector has magnitude and direction. Does it have a location in space? Can it vary with time? Will two equal vectors a and b at different locations in space necessarily have identical physical effects? Give examples in support of your answer.
A vector has both magnitude and direction. Does it mean that anything that has magnitude and direction is necessarily a vector? The rotation of a body can be specified by the direction of the axis of rotation, and the angle of rotation about the axis. Does that make any rotation a vector?
Can you associate vectors with (a) the length of a wire bent into a loop, (b) a plane area, (c) a sphere? Explain.
A bullet fired at an angle of 30° with the horizontal hits the ground 3.0 km away. By adjusting its angle of projection, can one hope to hit a target 5.0 km away? Assume the muzzle speed to the fixed, and neglect air resistance.
A fighter plane flying horizontally at an altitude of 1.5 km with speed 720 km/h passes directly overhead an anti-aircraft gun. At what angle from the vertical should the gun be fired for the shell with muzzle speed 600 m s–1 to hit the plane? At what minimum altitude should the pilot fly the plane to avoid being hit? (Take g = 10 m s–2).
A cyclist is riding with a speed of 27 km/h. As he approaches a circular turn on the road of radius 80 m, he applies brakes and reduces his speed at the constant rate of 0.50 m/s every second. What is the magnitude and direction of the net acceleration of the cyclist on the circular turn?
Show that for a projectile the angle between the velocity and the x-axis as a function of time is given by
`theta(t) =tan^(-1) ((v_(0y) - "gt")/v_(o x))`
Show that the projection angle `theta_o` for a projectile launched from the origin is given by
`theta_o =tan^(-1) ((4h_m)/R)`
Where the symbols have their usual meaning
Solutions for 4: Motion in a Plane
NCERT solutions for Physics [English] Class 11 chapter 4 - Motion in a Plane
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 11 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 11 CBSE 4 (Motion in a Plane) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 11 chapter 4 Motion in a Plane are Scalar (Dot) and Vector (Cross) Product of Vectors, Relative Velocity in Two Dimensions, Cases of Uniform Velocity, Scalars and Vectors, Multiplication of Vectors by a Real Number or Scalar, Addition and Subtraction of Vectors - Graphical Method, Resolution of Vectors, Vector Addition – Analytical Method, Motion in a Plane, Motion in a Plane with Constant Acceleration, Projectile Motion, General Vectors and Their Notations, Rectangular Components, Uniform Circular Motion (UCM), Cases of Uniform Acceleration Projectile Motion, Introduction of Motion in One Dimension, Motion in a Plane - Average Velocity and Instantaneous Velocity, Motion in a Plane - Average Acceleration and Instantaneous Acceleration, Angular Velocity, Scalar (Dot) and Vector (Cross) Product of Vectors, Relative Velocity in Two Dimensions, Cases of Uniform Velocity, Scalars and Vectors, Multiplication of Vectors by a Real Number or Scalar, Addition and Subtraction of Vectors - Graphical Method, Resolution of Vectors, Vector Addition – Analytical Method, Motion in a Plane, Motion in a Plane with Constant Acceleration, Projectile Motion, General Vectors and Their Notations, Rectangular Components, Uniform Circular Motion (UCM), Cases of Uniform Acceleration Projectile Motion, Introduction of Motion in One Dimension, Motion in a Plane - Average Velocity and Instantaneous Velocity, Motion in a Plane - Average Acceleration and Instantaneous Acceleration, Angular Velocity.
Using NCERT Physics [English] Class 11 solutions Motion in a Plane exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Physics [English] Class 11 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Motion in a Plane Physics [English] Class 11 additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 11 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
![NCERT solutions for Physics [English] Class 11 chapter 4 - Motion in a Plane NCERT solutions for Physics [English] Class 11 chapter 4 - Motion in a Plane - Shaalaa.com](/images/9788174505088-physics-english-class-11_6:2794bb7b99ab415dafd9ba0a905d4f01.jpg)
