Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the image of the point (2, 1) with respect to the line mirror be (5, 2), find the equation of the mirror.
उत्तर
Let the image of A (2, 1) be B (5, 2). Let M be the midpoint of AB.
\[\therefore \text { Coordinates of M } = \left( \frac{2 + 5}{2}, \frac{1 + 2}{2} \right)\]
\[ = \left( \frac{7}{2}, \frac{3}{2} \right)\]
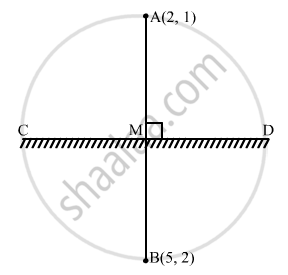
Let CD be the mirror.
The line AB is perpendicular to the mirror CD.
\[\therefore\] Slope of AB \[\times\] Slope of CD = −1
\[\Rightarrow \frac{2 - 1}{5 - 2} \times\text { Slope of CD }= - 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \text { Slope of CD} = - 3\]
Thus, the equation of the mirror CD is
\[y - \frac{3}{2} = - 3\left( x - \frac{7}{2} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2y - 3 = - 6x + 21\]
\[ \Rightarrow 6x + 2y - 24 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3x + y - 12 = 0\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The line through the points (h, 3) and (4, 1) intersects the line 7x – 9y – 19 = 0. at right angle. Find the value of h.
The perpendicular from the origin to the line y = mx + c meets it at the point (–1, 2). Find the values of m and c.
If three lines whose equations are y = m1x + c1, y = m2x + c2 and y = m3x + c3 are concurrent, then show that m1(c2 – c3) + m2 (c3 – c1) + m3 (c1 – c2) = 0.
The hypotenuse of a right angled triangle has its ends at the points (1, 3) and (−4, 1). Find the equation of the legs (perpendicular sides) of the triangle that are parallel to the axes.
Find the equation of a line which makes an angle of tan−1 (3) with the x-axis and cuts off an intercept of 4 units on negative direction of y-axis.
Find the equation of a line that has y-intercept −4 and is parallel to the line joining (2, −5) and (1, 2).
Find the equation of the right bisector of the line segment joining the points (3, 4) and (−1, 2).
Reduce the equation \[\sqrt{3}\] x + y + 2 = 0 to slope-intercept form and find slope and y-intercept;
Reduce the equation\[\sqrt{3}\] x + y + 2 = 0 to intercept form and find intercept on the axes.
Reduce the equation \[\sqrt{3}\] x + y + 2 = 0 to the normal form and find p and α.
Reduce the following equation to the normal form and find p and α in \[x - y + 2\sqrt{2} = 0\].
Reduce the following equation to the normal form and find p and α in y − 2 = 0.
Put the equation \[\frac{x}{a} + \frac{y}{b} = 1\] to the slope intercept form and find its slope and y-intercept.
Reduce the lines 3 x − 4 y + 4 = 0 and 2 x + 4 y − 5 = 0 to the normal form and hence find which line is nearer to the origin.
Find the values of θ and p, if the equation x cos θ + y sin θ = p is the normal form of the line \[\sqrt{3}x + y + 2 = 0\].
Find the coordinates of the vertices of a triangle, the equations of whose sides are
y (t1 + t2) = 2x + 2a t1t2, y (t2 + t3) = 2x + 2a t2t3 and, y (t3 + t1) = 2x + 2a t1t3.
Find the area of the triangle formed by the line x + y − 6 = 0, x − 3y − 2 = 0 and 5x − 3y + 2 = 0.
Find the equation of the line joining the point (3, 5) to the point of intersection of the lines 4x + y − 1 = 0 and 7x − 3y − 35 = 0.
Prove that the following sets of three lines are concurrent:
\[\frac{x}{a} + \frac{y}{b} = 1, \frac{x}{b} + \frac{y}{a} = 1\text { and } y = x .\]
Show that the straight lines L1 = (b + c) x + ay + 1 = 0, L2 = (c + a) x + by + 1 = 0 and L3 = (a + b) x + cy + 1 = 0 are concurrent.
If a, b, c are in A.P., prove that the straight lines ax + 2y + 1 = 0, bx + 3y + 1 = 0 and cx + 4y + 1 = 0 are concurrent.
Find the equation of the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the points (1, 3) and (3, 1).
Find the image of the point (2, 1) with respect to the line mirror x + y − 5 = 0.
Find the projection of the point (1, 0) on the line joining the points (−1, 2) and (5, 4).
Find the values of α so that the point P (α2, α) lies inside or on the triangle formed by the lines x − 5y+ 6 = 0, x − 3y + 2 = 0 and x − 2y − 3 = 0.
Write the area of the figure formed by the lines a |x| + b |y| + c = 0.
The figure formed by the lines ax ± by ± c = 0 is
A point equidistant from the line 4x + 3y + 10 = 0, 5x − 12y + 26 = 0 and 7x+ 24y − 50 = 0 is
Find the equation of the line where length of the perpendicular segment from the origin to the line is 4 and the inclination of the perpendicular segment with the positive direction of x-axis is 30°.
Prove that every straight line has an equation of the form Ax + By + C = 0, where A, B and C are constants.
The inclination of the line x – y + 3 = 0 with the positive direction of x-axis is ______.
Find the equation of the straight line which passes through the point (1, – 2) and cuts off equal intercepts from axes.
Find the equation of the line which passes through the point (– 4, 3) and the portion of the line intercepted between the axes is divided internally in the ratio 5 : 3 by this point.
For specifying a straight line, how many geometrical parameters should be known?
A line passes through (2, 2) and is perpendicular to the line 3x + y = 3. Its y-intercept is ______.
Locus of the mid-points of the portion of the line x sin θ + y cos θ = p intercepted between the axes is ______.
