Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the following figure, Q is the centre of a circle and PM, PN are tangent segments to the circle. If ∠MPN = 50°, find ∠MQN.

उत्तर
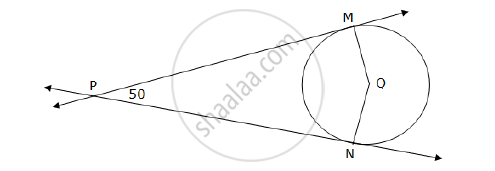
Seg PM and seg PN are tangents to the circle and seg QM and seg QN are the radii from the points of contacts.
m∠PMQ = m∠PNQ = 90° ... (Tangent is perpendicular to the radius) ... (1)
The sum of the measures of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
m∠MPN + m∠PMQ + m∠MQN + m∠PNQ = 360°
50° + 90° + m∠MQN + 90° = 360°
230° + m∠MQN = 360°
m∠MQN = 360° – 230° = 130° ... [From (1)]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the below given figure, two tangents RQ and RP are drawn from an external point R to the circle with centre O. If∠PRQ = 120°, then prove that OR = PR + RQ.

Prove that opposite sides of a quadrilateral circumscribing a circle subtend supplementary angles at the centre of the circle.
Prove that the tangents drawn at the ends of a diameter of a circle are parallel.
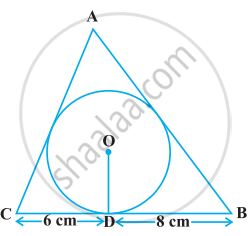
A triangle ABC is drawn to circumscribe a circle of radius 4 cm such that the segments BD and DC into which BC is divided by the point of contact D are of lengths 8 cm and 6 cm respectively (see given figure). Find the sides AB and AC.
Prove that the tangents drawn at the end points of a chord of a circle make equal angles with the chord.
In the given figure PA = 10, PB = 2 and PC = 5. Find PD.
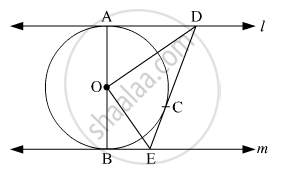
In fig. 6, l and m are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre O, touching the circle at A and B respectively. Another tangent at C intersects the line l at D and m at E. Prove that ∠DOE = 90° ?
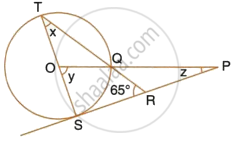
In the figure given below, O is the center of the circle and SP is a tangent. If ∠SRT = 65°, find the value of x, y and Z.
In the given figure, ▢ABCD is a parallelogram. It circumscribes the circle with centre T. Point E, F, G, H are touching points. If AE = 4.5, EB = 5.5, find AD.

Construct a pair of tangents to a circle of radius 4 cm from a point which is at a distance of 6 cm from its centre.
The number of tangents drawn at a point of the circle is/are ______
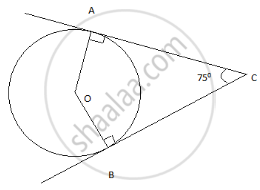
In fig, O is the centre of the circle, CA is tangent at A and CB is tangent at B drawn to the circle. If ∠ACB = 75°, then ∠AOB = ______
A tangent PQ at a point P of a circle of radius 5 cm meets a line through the center O at a point Q such that OQ = 13 cm. Length PQ is ______
The length of tangent from an external point P on a circle with centre O is always less than OP.
If from an external point B of a circle with centre O, two tangents BC and BD are drawn such that ∠DBC = 120°, prove that BC + BD = BO, i.e., BO = 2BC.
From an external point P, two tangents, PA and PB are drawn to a circle with centre O. At one point E on the circle tangent is drawn which intersects PA and PB at C and D, respectively. If PA = 10 cm, find the the perimeter of the triangle PCD.
In the given figure, PQ is a chord of length 8 cm of a circle of radius 5 cm. The tangents at P and Q meet at a point T. Find the length of TP.

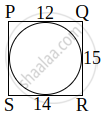
A quadrilateral PQRS is drawn to circumscribe a circle. If PQ = 12 cm, QR = 15 cm and RS = 14 cm, then find the length of SP is ______.
In the given diagram, O is the centre of the circle. PR and PT are two tangents drawn from the external point P and touching the circle at Q and S respectively. MN is a diameter of the circle. Given ∠PQM = 42° and ∠PSM = 25°.
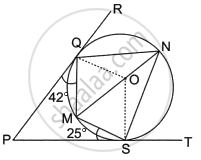
Find:
- ∠OQM
- ∠QNS
- ∠QOS
- ∠QMS
