Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {a, b} be two sets. Write the total number of onto functions from A to B.
उत्तर
Formula:
When two sets A and B have m and n elements respectively, then the number of onto functions from A to B is
\[\binom{ \sum\nolimits_{r = 1}^n \left( - 1 \right)^r n C_r r^m , \text{if m} \geq n}{\text{o if m} < n }\]
Here, number of elements in A = 4 = m
Number of elements in B = 2 = n
So, m > n
Number of onto functions
\[= \sum\nolimits_{r = 1}^2 \left( - 1 \right)^r 2 C_r r^4 \]
\[ = \left( - 1 \right)^1 2 C_1 1^4 + \left( - 1 \right)^2 2 C_2 2^4 \]
\[ = - 2 + 16\]
= 14
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Show that f is one-one.
Let S = {a, b, c} and T = {1, 2, 3}. Find F−1 of the following functions F from S to T, if it exists.
F = {(a, 2), (b, 1), (c, 1)}
Show that the function f: ℝ → ℝ defined by f(x) = `x/(x^2 + 1), ∀x in R`is neither one-one nor onto. Also, if g: ℝ → ℝ is defined as g(x) = 2x - 1. Find fog(x)
Give an example of a function which is not one-one but onto ?
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : N → N given by f(x) = x3
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Z → Z, defined by f(x) = x − 5
Let f = {(3, 1), (9, 3), (12, 4)} and g = {(1, 3), (3, 3) (4, 9) (5, 9)}. Show that gof and fog are both defined. Also, find fog and gof.
Find fog (2) and gof (1) when : f : R → R ; f(x) = x2 + 8 and g : R → R; g(x) = 3x3 + 1.
Let R+ be the set of all non-negative real numbers. If f : R+ → R+ and g : R+ → R+ are defined as `f(x)=x^2` and `g(x)=+sqrtx` , find fog and gof. Are they equal functions ?
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = x + 1. Show that fog ≠ gof.
If f : A → B and g : B → C are onto functions, show that gof is a onto function.
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = c, c ∈ R, g(x) = sin `x^2`
Let f, g, h be real functions given by f(x) = sin x, g (x) = 2x and h (x) = cos x. Prove that fog = go (fh).
if f (x) = `sqrt (x +3) and g (x) = x ^2 + 1` be two real functions, then find fog and gof.
State with reason whether the following functions have inverse :
g : {5, 6, 7, 8} → {1, 2, 3, 4} with g = {(5, 4), (6, 3), (7, 4), (8, 2)}
Consider f : {1, 2, 3} → {a, b, c} and g : {a, b, c} → {apple, ball, cat} defined as f (1) = a, f (2) = b, f (3) = c, g (a) = apple, g (b) = ball and g (c) = cat. Show that f, g and gof are invertible. Find f−1, g−1 and gof−1and show that (gof)−1 = f −1o g−1
Consider f : R+ → [−5, ∞) given by f(x) = 9x2 + 6x − 5. Show that f is invertible with `f^-1 (x) = (sqrt (x +6)-1)/3 .`
If f : R → R is defined by f(x) = x2, write f−1 (25)
If f : R → R, g : R → are given by f(x) = (x + 1)2 and g(x) = x2 + 1, then write the value of fog (−3).
Let f : R → R+ be defined by f(x) = ax, a > 0 and a ≠ 1. Write f−1 (x).
What is the range of the function
`f (x) = ([x - 1])/(x -1) ?`
If the function\[f : R \to \text{A given by} f\left( x \right) = \frac{x^2}{x^2 + 1}\] is a surjection, then A =
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : x \geq 1 \right\}\] The inverse of the function,
\[f : A \to A\] given by
\[f\left( x \right) = 2^{x \left( x - 1 \right)} , is\]
Let
\[f : R \to R\] be given by \[f\left( x \right) = x^2 - 3\] Then, \[f^{- 1}\] is given by
Let A = R − (2) and B = R − (1). If f: A ⟶ B is a function defined by`"f(x)"=("x"-1)/("x"-2),` how that f is one-one and onto. Hence, find f−1.
Which function is used to check whether a character is alphanumeric or not?
Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 3x – 4. Then f–1(x) is given by ______.
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
f = {(1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 5)}
Let A = R – {3}, B = R – {1}. Let f: A → B be defined by f(x) = `(x - 2)/(x - 3)` ∀ x ∈ A . Then show that f is bijective
Let f: R – `{3/5}` → R be defined by f(x) = `(3x + 2)/(5x - 3)`. Then ______.
The function f : R → R defined by f(x) = 3 – 4x is ____________.
Let X = {-1, 0, 1}, Y = {0, 2} and a function f : X → Y defiend by y = 2x4, is ____________.
Let f : R `->` R be a function defined by f(x) = x3 + 4, then f is ______.
Given a function If as f(x) = 5x + 4, x ∈ R. If g : R → R is inverse of function ‘f then
Sherlin and Danju are playing Ludo at home during Covid-19. While rolling the dice, Sherlin’s sister Raji observed and noted the possible outcomes of the throw every time belongs to set {1,2,3,4,5,6}. Let A be the set of players while B be the set of all possible outcomes.
A = {S, D}, B = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
- Raji wants to know the number of functions from A to B. How many number of functions are possible?
If `f : R -> R^+ U {0}` be defined by `f(x) = x^2, x ∈ R`. The mapping is
Let a and b are two positive integers such that b ≠ 1. Let g(a, b) = Number of lattice points inside the quadrilateral formed by lines x = 0, y = 0, x = b and y = a. f(a, b) = `[a/b] + [(2a)/b] + ... + [((b - 1)a)/b]`, then the value of `[(g(101, 37))/(f(101, 37))]` is ______.
(Note P(x, y) is lattice point if x, y ∈ I)
(where [.] denotes greatest integer function)
Let a function `f: N rightarrow N` be defined by
f(n) = `{:[(2n",", n = 2"," 4"," 6"," 8","......),(n - 1",", n = 3"," 7"," 11"," 15","......),((n + 1)/2",", n = 1"," 5"," 9"," 13","......):}`
then f is ______.
Which one of the following graphs is a function of x?
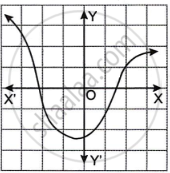 |
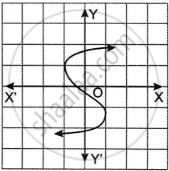 |
| Graph A | Graph B |
