Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The surface tension of water at 0°C is 75.5 dyne/cm. Calculate surface tension of water at 25°C.
(α for water = 2.7×10-3/°C)
उत्तर
Given:
T0 = 75.5 dyne/cm
αwater = 2.7 × 10-3/°C
To find:
Surface tension of water at 25°C
Formula:
T1 = T0(1 - αΔt)
Solution:
T25 = T0(1 - αΔt)
T25 = T0(1 - α(25 - 0))
T25 = 75.5(1 - 2.7 × 10-3 × 25)
T25 = 75.5(1 - 0.0675)
T25 = 70.4 dyne/cm
The surface tension of water at 25°C is 70.4 dyne/cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive Laplace’s law for spherical membrane of bubble due to surface tension.
Angle of contact for the pair of pure water with clean glass is _______.
A raindrop of diameter 4 mm is about to fall on the ground. Calculate the pressure inside the raindrop. [Surface tension of water T = 0.072 N/m, atmospheric pressure = 1.013 x 105 N/m2 ]
In which of the following substances, surface tension increases with increase in temperature ?
- Copper
- Molten copper
- Iron
- Molten iron
Explain why Water on a clean glass surface tends to spread out while mercury on the same surface tends to form drops. (Put differently, water wets glass while mercury does not.)
Mercury has an angle of contact equal to 140° with soda lime glass. A narrow tube of radius 1.00 mm made of this glass is dipped in a trough containing mercury. By what amount does the mercury dip down in the tube relative to the liquid surface outside? Surface tension of mercury at the temperature of the experiment is 0.465 N m–1. Density of mercury = 13.6 × 103 kg m–3
The total free surface energy of a liquid drop is `pisqrt2` times the surface tension of the liquid. Calculate the diameter of the drop in S.l. unit.
When a sparingly soluble substance like alcohol is dissolved in water, surface tension of water
The free surface of a liquid resting in an inertial frame is horizontal. Does the normal to the free surface pass through the centre of the earth? Think separately if the liquid is (a) at the equator (b) at a pole (c) somewhere else.
It is said that a liquid rises or is depressed in capillary due to the surface tension. If a liquid neither rises nor depresses in a capillary, can we conclude that the surface tension of the liquid is zero?
The contact angle between water and glass is 0°. When water is poured in a glass to the maximum of its capacity, the water surface is convex upward. The angle of contact in such a situation is more than 90°. Explain.
If water in one flask and castor oil in other are violently shaken and kept on a table, which will come to rest earlier?
By a surface of a liquid we mean
When water droplets merge to form a bigger drop
Air is pushed into a soap bubble of radius r to double its radius. If the surface tension of the soap solution in S, the work done in the process is
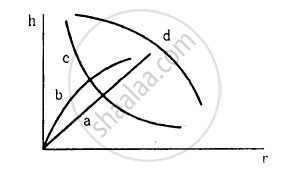
Which of the following graphs may represent the relation between the capillary rise hand the radius r of the capillary?
A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
The properties of a surface are different from those of the bulk liquid because the surface molecules
(a) are smaller than other molecules
(b) acquire charge due to collision from air molecules
(c) find different type of molecules in their range of influence
(d) feel a net force in one direction.
The contact angle between a solid and a liquid is a property of
(a) the material of the solid
(b) the material of the liquid
(c) the shape of the solid
(d) the mass of the solid
A liquid is contained in a vertical tube of semicircular cross section. The contact angle is zero. The force of surface tension on the curved part and on the flat part are in ratio
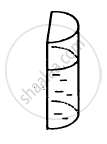
When a capillary tube is dipped into a liquid, the liquid neither rises nor falls in the capillary.
(a) The surface tension of the liquid must be zero.
(b) The contact angle must be 90°.
(c) The surface tension may be zero.
(d) The contact angle may be 90°.
Find the excess pressure inside (a) a drop of mercury of radius 2 mm (b) a soap bubble of radius 4 mm and (c) an air bubble of radius 4 mm formed inside a tank of water. Surface tension of mercury, soap solution and water are 0.465 N m−1, 0.03 N m−1 and 0.076 N m−1 respectively.
Consider a small surface area of 1 mm2 at the top of a mercury drop of radius 4.0 mm. Find the force exerted on this area (a) by the air above it (b) by the mercury below it and (c) by the mercury surface in contact with it. Atmospheric pressure = 1.0 × 105 Pa and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Neglect the effect of gravity. Assume all numbers to be exact.
The lower end of a capillary tube is immersed in mercury. The level of mercury in the tube is found to be 2 cm below the outer level. If the same tube is immersed in water, up to what height will the water rise in the capillary?
A barometer is constructed with its tube having radius 1.0 mm. Assume that the surface of mercury in the tube is spherical in shape. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 76 cm of mercury, what will be the height raised in the barometer tube? The contact angle of mercury with glass = 135° and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Density of mercury = 13600 kg m−3.
A capillary tube of radius 1 mm is kept vertical with the lower end in water. (a) Find the height of water raised in the capillary. (b) If the length of the capillary tube is half the answer of part , find the angle θ made by the water surface in the capillary with the wall.
Consider an ice cube of edge 1.0 cm kept in a gravity-free hall. Find the surface area of the water when the ice melts. Neglect the difference in densities of ice and water.
A cubical block of ice floating in water has to support a metal piece weighing 0.5 kg. Water can be the minimum edge of the block so that it does not sink in water? Specific gravity of ice = 0.9.
A cubical block of wood weighing 200 g has a lead piece fastened underneath. Find the mass of the lead piece which will just allow the block to float in water. Specific gravity of wood is 0.8 and that of lead is 11.3.
A hollow spherical body of inner and outer radii 6 cm and 8 cm respectively floats half-submerged in water. Find the density of the material of the sphere.
The surface tension of a liquid at critical temperature is ______
Water rises to a height of 20 mm in a capillary tube. If the radius made 1/3rd of its previous value, to what height will the water now rise in the tube?
Explain the phenomena of surface tension on the basis of molecular theory.
How does the friction arise between the surfaces of two bodies in relative motion?
Describe an experiment to prove that friction depends on the nature of a surface.
The wettability of a surface by a liquid depends primarily on
How is surface tension related to surface energy?
Two small drops of mercury each of radius 'R' coalesce to form a large single drop. The ratio of the total surface energies before and after the change is ____________.
Two spherical rain drops reach the surface of the earth with terminal velocities having ratio 16 : 9. The ratio of their surface area is ______.
Water rises upto a height h in a capillary tube on the surface of the earth. The value of h will increase, if the experimental setup is kept in [g = acceleration due to gravity]
The excess of pressure, due to surface tension, on a spherical liquid drop of radius 'R' is proportional to ______.
A large number of liquid drops each of radius 'r' coalesce to form a big drop of radius 'R'. The energy released in the process in converted into kinetic energy of the big drop. The speed of the big drop is ______. (T = surface tension of liquid, p = density of liquid)
A water drop of radius R' splits into 'n' smaller drops, each of radius 'r'. The work done in the process is ______.
T = surface tension of water
Under isothermal conditions, two soap bubbles of radii 'r1' and 'r2' coalesce to form a big drop. The radius of the big drop is ______.
The wear and tear in the machine part is due to ______.
What is surface tension? Explain the applications of surface tension.
For a surface molecule ______.
- the net force on it is zero.
- there is a net downward force.
- the potential energy is less than that of a molecule inside.
- the potential energy is more than that of a molecule inside.
Is surface tension a vector?
If a drop of liquid breaks into smaller droplets, it results in lowering of temperature of the droplets. Let a drop of radius R, break into N small droplets each of radius r. Estimate the drop in temperature.
Eight droplets of water each of radius 0.2 mm coalesce into a single drop. Find the decrease in the surface area.
The surface tension of a soap solution is T. The work done in blowing a soap bubble of diameter d to that of a diameter 2d is ______.
Find the work done when a drop of mercury of radius 2 mm breaks into 8 equal droplets. [Surface tension of mercury = 0.4855 J/m2].
