Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a ΔABC , ∠B = 90° , AB = 12 cm and BC = 5 cm Find
(i) cos A (ii) cosec A (iii) cos C (iv) cosec C
उत्तर
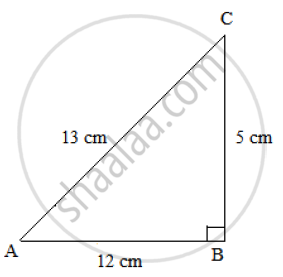
Using Pythagoras theorem, we get:
`AC^2 = AB^2 + BC^2`
`⟹ AC^2 = 12^2 + 5^2 = 144 + 25`
`⟹ AC^2 = 169`
⟹ 𝐴𝐶 = 13 𝑐𝑚
Now, for T-Ratios of ∠𝐴, 𝑏𝑎𝑠𝑒 = 𝐴𝐵 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑟 = 𝐵𝐶
(i)cos 𝐴 = `(AB)/(AC) = 12/13`
(ii) cosec A = `1/sin A=(AC)/(BC)=13/5`
Similarly, for T-Ratios of ∠𝐶, 𝑏𝑎𝑠𝑒 = 𝐵𝐶 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑟 = 𝐴𝐵
(iii)cos 𝐶 = `(BC)/(AC) = 5/13`
(iv) cosec C = `1/sin C=(AC)/(AB) = 13/12`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
if `sin theta = 3/5 " evaluate " (cos theta - 1/(tan theta))/(2 cot theta)`
If A = B = 60°. Verify `tan (A - B) = (tan A - tan B)/(1 + tan tan B)`
If sin θ = cos (θ – 45°), where θ – 45° are acute angles, find the degree measure of θ
If Sec 4A = cosec (A – 20°) where 4A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
If a right ΔABC , right-angled at B, if tan A=1 then verify that 2sin A . cos A = 1
If A = 450, verify that :
(i) sin 2A = 2 sin A cos A
Prove that
cosec (65 °+ θ) sec (25° − θ) − tan (55° − θ) + cot (35° + θ) = 0
Given: tan A = `4/3 , "find" : ("cosec""A")/(cot "A"– sec "A")`
In the given figure, AD is the median on BC from A. If AD = 8 cm and BC = 12 cm, find the value of tan x. cot y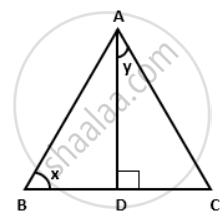
If 2 cos θ = `sqrt(3)`, then find all the trigonometric ratios of angle θ
