Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In a ΔABC , ∠B = 90° , AB = 12 cm and BC = 5 cm Find
(i) cos A (ii) cosec A (iii) cos C (iv) cosec C
Solution
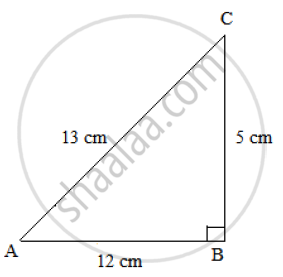
Using Pythagoras theorem, we get:
`AC^2 = AB^2 + BC^2`
`⟹ AC^2 = 12^2 + 5^2 = 144 + 25`
`⟹ AC^2 = 169`
⟹ 𝐴𝐶 = 13 𝑐𝑚
Now, for T-Ratios of ∠𝐴, 𝑏𝑎𝑠𝑒 = 𝐴𝐵 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑟 = 𝐵𝐶
(i)cos 𝐴 = `(AB)/(AC) = 12/13`
(ii) cosec A = `1/sin A=(AC)/(BC)=13/5`
Similarly, for T-Ratios of ∠𝐶, 𝑏𝑎𝑠𝑒 = 𝐵𝐶 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑟 = 𝐴𝐵
(iii)cos 𝐶 = `(BC)/(AC) = 5/13`
(iv) cosec C = `1/sin C=(AC)/(AB) = 13/12`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If 8 tan A = 15, find sin A – cos A.
If A = 600 and B = 300, verify that:
(ii) cos (A – B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
Given: cos A = `( 5 )/ ( 13 )`
Evaluate:
- `(sin "A "–cot "A") / (2 tan "A")`
- `cot "A" + 1/cos"A"`
If cos A = `(1)/(2)` and sin B = `(1)/(sqrt2)`, find the value of: `(tan"A" – tan"B")/(1+tan"A" tan"B")`.
Are angles A and B from the same triangle? Explain.
If tan x = `1(1)/(3)`, find the value of : 4 sin2x - 3 cos2x + 2
From the following figure, find:
(i) y
(ii) sin x°
(iii) (sec x° - tan x°) (sec x° + tan x°)

In the given figure, triangle ABC is right-angled at B. D is the foot of the perpendicular from B to AC. Given that BC = 3 cm and AB = 4 cm.
find :
- tan ∠DBC
- sin ∠DBA

In triangle ABC, ∠B = 90° and tan A = 0.75. If AC = 30 cm, find the lengths of AB and BC.
In an isosceles triangle ABC, AB = BC = 6 cm and ∠B = 90°. Find the values of cos2 C + cosec2 C
From the given figure, find the values of sin B