Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose that two cards are drawn at random from a deck of cards. Let X be the number of aces obtained. Then the value of E(X) is
(A) `37/221`
(B) 5/13
(C) 1/13
(D) 2/13
उत्तर
Let X denote the number of aces obtained. Therefore, X can take any of the values of 0, 1, or 2.
In a deck of 52 cards, 4 cards are aces. Therefore, there are 48 non-ace cards
 '
'
Thus, the probability distribution is as follows.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P(X) | 1128/1326 | 192/1326 | 6/1326 |
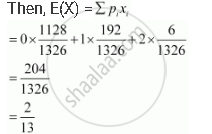
Therefore, the correct answer is D.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the following are not the probability distributions of a random variable. Give reasons for your answer.
| Z | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | -1 |
| P(Z) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
Find the probability distribution of number of tails in the simultaneous tosses of three coins.
Find the probability distribution of number of heads in four tosses of a coin.
An urn contains 25 balls of which 10 balls bear a mark ‘X’ and the remaining 15 bear a mark ‘Y’. A ball is drawn at random from the urn, its mark is noted down and it is replaced. If 6 balls are drawn in this way, find the probability that
(i) all will bear ‘X’ mark.
(ii) not more than 2 will bear ‘Y’ mark.
(iii) at least one ball will bear ‘Y’ mark
(iv) the number of balls with ‘X’ mark and ‘Y’ mark will be equal.
Assume that the chances of the patient having a heart attack are 40%. It is also assumed that a meditation and yoga course reduce the risk of heart attack by 30% and prescription of certain drug reduces its chances by 25%. At a time a patient can choose any one of the two options with equal probabilities. It is given that after going through one of the two options the patient selected at random suffers a heart attack. Find the probability that the patient followed a course of meditation and yoga?
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| Values of X : | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X) : | 0.1 | k | 0.2 | 2k | 0.3 | k |
Find the value of k.
The probability distribution function of a random variable X is given by
| xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| pi : | 3c3 | 4c − 10c2 | 5c-1 |
where c > 0 Find: P (X < 2)
Two cards are drawn successively without replacement from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of aces.
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k |
\[\frac{k}{2}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{8}\]
|
Find P(X ≤ 2) + P(X > 2) .
A fair coin is tossed four times. Let X denote the number of heads occurring. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
In roulette, Figure, the wheel has 13 numbers 0, 1, 2, ...., 12 marked on equally spaced slots. A player sets Rs 10 on a given number. He receives Rs 100 from the organiser of the game if the ball comes to rest in this slot; otherwise he gets nothing. If X denotes the player's net gain/loss, find E (X).
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| X : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| P (X) : | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
For the events E = {X : X is a prime number}, F = {X : X < 4}, the probability P (E ∪ F) is
If X is a random-variable with probability distribution as given below:
| X = xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X = xi) : | k | 3 k | 3 k | k |
The value of k and its variance are
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
For the following probability distribution:
| X : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X) : |
\[\frac{1}{10}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{5}\]
|
\[\frac{3}{10}\]
|
\[\frac{2}{5}\]
|
The value of E(X2) is
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let X be a discrete random variable. Then the variance of X is
Find the probability distribution of the number of doublets in three throws of a pair of dice and find its mean.
The following data gives the marks of 20 students in mathematics (X) and statistics (Y) each out of 10, expressed as (x, y). construct ungrouped frequency distribution considering single number as a class :
(2, 7) (3, 8) (4, 9) (2, 8) (2, 8) (5, 6) (5 , 7) (4, 9) (3, 8) (4, 8) (2, 9) (3, 8) (4, 8) (5, 6) (4, 7) (4, 7) (4, 6 ) (5, 6) (5, 7 ) (4, 6 )
If X ∼ N (4,25), then find P(x ≤ 4)
Amit and Rohit started a business by investing ₹20,000 each. After 3 months Amit withdrew ₹5,000 and Rohit put in ₹5,000 additionally. How should a profit of ₹12,800 be divided between them at the end of the year?
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P(x) | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| y | –1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(y) | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
A die is thrown 4 times. If ‘getting an odd number’ is a success, find the probability of at least 3 successes
The probability that a bulb produced by a factory will fuse after 200 days of use is 0.2. Let X denote the number of bulbs (out of 5) that fuse after 200 days of use. Find the probability of X > 1
Solve the following problem :
The probability that a bomb will hit the target is 0.8. Find the probability that, out of 5 bombs, exactly 2 will miss the target.
Solve the following problem :
The probability that a lamp in the classroom will burn is 0.3. 3 lamps are fitted in the classroom. The classroom is unusable if the number of lamps burning in it is less than 2. Find the probability that the classroom cannot be used on a random occasion.
Solve the following problem :
The probability that a component will survive a check test is 0.6. Find the probability that exactly 2 of the next 4 components tested survive.
Solve the following problem :
A computer installation has 3 terminals. The probability that any one terminal requires attention during a week is 0.1, independent of other terminals. Find the probabilities that 0
Solve the following problem :
In a large school, 80% of the students like mathematics. A visitor asks each of 4 students, selected at random, whether they like mathematics.
Calculate the probabilities of obtaining an answer yes from all of the selected students.
Four balls are to be drawn without replacement from a box containing 8 red and 4 white balls. If X denotes the number of red ball drawn, find the probability distribution of X.
Consider the probability distribution of a random variable X:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X) | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.15 |
Calculate `"V"("X"/2)`
The random variable X can take only the values 0, 1, 2. Given that P(X = 0) = P(X = 1) = p and that E(X2) = E[X], find the value of p
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable X is given as under:
| X | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2A | 3A | 5A |
| P(X) | `1/2` | `1/5` | `3/25` | `1/10` | `1/25` | `1/25` |
Calculate: Variance of X
The probability distribution of a random variable x is given as under:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"x^2, "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3),(2"k"x, "for" x = 4"," 5"," 6),(0, "otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate P(X ≥ 4)
For the following probability distribution:
| X | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X) | `1/10` | `3/10` | `3/10` | `2/5` |
E(X2) is equal to ______.
Find the mean number of defective items in a sample of two items drawn one-by-one without replacement from an urn containing 6 items, which include 2 defective items. Assume that the items are identical in shape and size.
Box I contains 30 cards numbered 1 to 30 and Box II contains 20 cards numbered 31 to 50. A box is selected at random and a card is drawn from it. The number on the card is found to be a nonprime number. The probability that the card was drawn from Box I is ______.
Two balls are drawn at random one by one with replacement from an urn containing equal number of red balls and green balls. Find the probability distribution of number of red balls. Also, find the mean of the random variable.
Five numbers x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 are randomly selected from the numbers 1, 2, 3, ......., 18 and are arranged in the increasing order such that x1 < x2 < x3 < x4 < x5. What is the probability that x2 = 7 and x4 = 11?
