Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
x cos2 y dx = y cos2 x dy
उत्तर
We have,
x cos2 y dx = y cos2 x dy
\[\Rightarrow y \sec^2 y dy = x \sec^2 x dx\]
Integrating both sides, we get
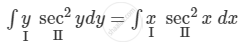
\[\Rightarrow y\int \sec^2 ydy - \int\left( \frac{dy}{dy} \times \int \sec^2 y dy \right)dy = x\int \sec^2 x dx - \int\left( \frac{dx}{dx} \times \int \sec^2 x dx \right)dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow y \tan y - \int\tan y dy = x \tan x - \int\tan x dx - C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y \tan y - \log \left| \sec y \right| = x \tan x - \log \left| \sec x \right| - C\]
\[ \Rightarrow x \tan x - y \tan y = \log\left| \sec x \right| - \log\left| \sec y \right| + C\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Form a differential equation representing the given family of curves by eliminating arbitrary constants a and b.
`x/a + y/b = 1`
Form a differential equation representing the given family of curves by eliminating arbitrary constants a and b.
y = a e3x + b e– 2x
Form a differential equation representing the given family of curves by eliminating arbitrary constants a and b.
y = e2x (a + bx)
Form a differential equation representing the given family of curves by eliminating arbitrary constants a and b.
y = ex (a cos x + b sin x)
Find the particular solution of the differential equation (1 + e2x) dy + (1 + y2) ex dx = 0, given that y = 1 when x = 0.
Find a particular solution of the differential equation (x - y) (dx + dy) = dx - dy, given that y = -1, when x = 0. (Hint: put x - y = t)
The general solution of a differential equation of the type `dx/dy + P_1 x = Q_1` is ______.
Find the differential equation representing the family of curves `y = ae^(bx + 5)`. where a and b are arbitrary constants.
Find the differential equation of all the circles which pass through the origin and whose centres lie on y-axis.
Show that y2 − x2 − xy = a is a solution of the differential equation \[\left( x - 2y \right)\frac{dy}{dx} + 2x + y = 0.\]
Find the differential equation corresponding to y = ae2x + be−3x + cex where a, b, c are arbitrary constants.
Show that the differential equation of all parabolas which have their axes parallel to y-axis is \[\frac{d^3 y}{d x^3} = 0.\]
\[\frac{dy}{dx} = \sin^3 x \cos^4 x + x\sqrt{x + 1}\]
\[\frac{dy}{dx} = y^2 + 2y + 2\]
\[\frac{dy}{dx} = x^2 e^x\]
\[\frac{dy}{dx} - x \sin^2 x = \frac{1}{x \log x}\]
\[(\tan^2 x + 2\tan x + 5)\frac{dy}{dx} = 2(1+\tan x)\sec^2x\]
cos y log (sec x + tan x) dx = cos x log (sec y + tan y) dy
Find the general solution of the differential equation `"dy"/"dx" = y/x`.
A solution of the differential equation `("dy"/"dx")^2 - x "dy"/"dx" + y` = 0 is ______.
Solve the differential equation:
cosec3 x dy − cosec y dx = 0
Find the general solution of the following differential equation:
`x (dy)/(dx) = y - xsin(y/x)`
The general solution of the differential equation `(dy)/(dx) + x/y` = 0 is
If n is any integer, then the general solution of the equation `cos x - sin x = 1/sqrt(2)` is
General solution of tan 5θ = cot 2θ is
Which of the following equations has `y = c_1e^x + c_2e^-x` as the general solution?
The general solution of the differential equation `(dy)/(dx) = e^(x + y)` is
The general solution of the differential equation `(ydx - xdy)/y` = 0
The general solution of the differential equation `x^xdy + (ye^x + 2x) dx` = 0
The general solution of the differential equation y dx – x dy = 0 is ______.
Solve the differential equation: y dx + (x – y2)dy = 0
The general solution of the differential equation ydx – xdy = 0; (Given x, y > 0), is of the form
(Where 'c' is an arbitrary positive constant of integration)
