Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If f(x) = x2, find \[\frac{f\left( 1 . 1 \right) - f\left( 1 \right)}{\left( 1 . 1 \right) - 1}\]
Solution
Given:
f(x) = x2
Therefore,
\[\frac{f\left( 1 . 1 \right) - f\left( 1 \right)}{\left( 1 . 1 \right) - 1} = \frac{\left( 1 . 1 \right)^2 - \left( 1 \right)^2}{\left( 1 . 1 - 1 \right)} = \frac{1 . 21 - 1}{0 . 1} = \frac{0 . 21}{0 . 1} = 2 . 1\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
f, g, h are three function defined from R to R as follow:
(i) f(x) = x2
Find the range of function.
The function f is defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \begin{cases}x^2 , & 0 \leq x \leq 3 \\ 3x, & 3 \leq x \leq 10\end{cases}\]
The relation g is defined by \[g\left( x \right) = \begin{cases}x^2 , & 0 \leq x \leq 2 \\ 3x, & 2 \leq x \leq 10\end{cases}\]
Show that f is a function and g is not a function.
If f(x) = (x − a)2 (x − b)2, find f(a + b).
If f(x) = loge (1 − x) and g(x) = [x], then determine function:
(iv) \[\frac{g}{f}\] Also, find (f + g) (−1), (fg) (0),
If f is a real function satisfying \[f\left( x + \frac{1}{x} \right) = x^2 + \frac{1}{x^2}\]
for all x ∈ R − {0}, then write the expression for f(x).
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{\alpha x}{x + 1}, x \neq - 1\] . Then write the value of α satisfying f(f(x)) = x for all x ≠ −1.
Write the domain and range of function f(x) given by \[f\left( x \right) = \sqrt{\left[ x \right] - x}\] .
Let A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {2, 3, 4}. Then which of the following is a function from A to B?
The range of f(x) = cos [x], for π/2 < x < π/2 is
Which of the following are functions?
If 2f (x) − \[3f\left( \frac{1}{x} \right) = x^2\] (x ≠ 0), then f(2) is equal to
If \[f\left( x \right) = 64 x^3 + \frac{1}{x^3}\] and α, β are the roots of \[4x + \frac{1}{x} = 3\] . Then,
If f : R → R be given by for all \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{4^x}{4^x + 2}\] x ∈ R, then
The domain of definition of \[f\left( x \right) = \sqrt{\frac{x + 3}{\left( 2 - x \right) \left( x - 5 \right)}}\] is
If ƒ(m) = m2 − 3m + 1, find f(x + 1)
A function f is defined as follows: f(x) = 5 − x for 0 ≤ x ≤ 4. Find the value of x such that f(x) = 3
If f(x) = ax2 + bx + 2 and f(1) = 3, f(4) = 42, find a and b.
If f(x) = `{(x^2 + 3"," x ≤ 2),(5x + 7"," x > 2):},` then find f(0)
Check if the following relation is a function.
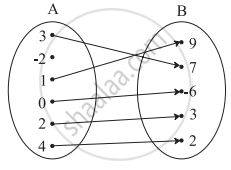
Which sets of ordered pairs represent functions from A = {1, 2, 3, 4} to B = {−1, 0, 1, 2, 3}? Justify.
{(1, 0), (3, 3), (2, −1), (4, 1), (2, 2)}
Check if the relation given by the equation represents y as function of x:
x2 − y = 25
Express the following logarithmic equation in exponential form
`log_5 1/25` = – 2
Prove that `"b"^(log_"b""a"` = a
Answer the following:
Identify the following relation is the function? If it is a function determine its domain and range.
{(2, 1), (4, 2), (6, 3), (8, 4), (10, 5), (12, 6), (14, 7)}
Answer the following:
Find whether the following function is one-one
f : R − {3} → R defined by f(x) = `(5x + 7)/(x - 3)` for x ∈ R − {3}
Answer the following:
If f(x) = 3x4 – 5x2 + 7 find f(x – 1)
Answer the following:
Show that, `log ("a"^2/"bc") + log ("b"^2/"ca") + log ("c"^2/"ab")` = 0
Answer the following:
Show that `7log (15/16) + 6log(8/3) + 5log (2/5) + log(32/25)` = log 3
Answer the following:
If `log_2"a"/4 = log_2"b"/6 = log_2"c"/(3"k")` and a3b2c = 1 find the value of k
Answer the following:
Find the domain of the following function.
f(x) = `(x^2 + 4x + 4)/(x^2 + x - 6)`
A graph representing the function f(x) is given in it is clear that f(9) = 2
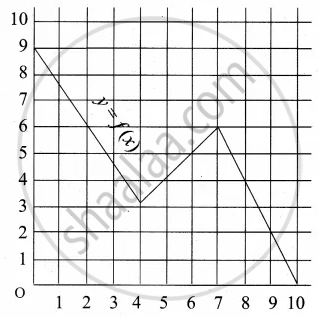
What is the image of 6 under f?
Let f(x) = 2x + 5. If x ≠ 0 then find `(f(x + 2) -"f"(2))/x`
A function f is defined by f(x) = 3 – 2x. Find x such that f(x2) = (f(x))2
The function f and g are defined by f(x) = 6x + 8; g(x) = `(x - 2)/3`
Write an expression for gf(x) in its simplest form
Let f(x) = `sqrt(x)` and g(x) = x be two functions defined in the domain R+ ∪ {0}. Find (fg)(x)
The domain of the function f given by f(x) = `(x^2 + 2x + 1)/(x^2 - x - 6)` is ______.
If f : R – {2} `rightarrow` R i s a function defined by f(x) = `(x^2 - 4)/(x - 2)`, then its range is ______.
