Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
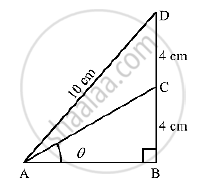
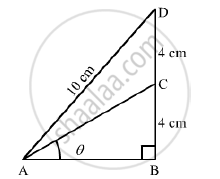
In the adjoining figure, `∠B = 90° , ∠BAC = theta° , BC = CD = 4cm and AD = 10 cm`. find (i) sin theta and (ii) `costheta`
Solution
In ΔABD,
Using Pythagoras theorem, we get
AB= `sqrt(AD^2-BD^2)`
= `sqrt(10^2-8^2)`
=`sqrt(100-64)`
=`sqrt(36)`
=6cm
Again,
In ΔABC,
Using Pythagoras therem, we get
AC= `sqrt(AB^2 +BC^2)`
=`sqrt(6^2+4^2)`
=`sqrt(36+16)`
=`sqrt(52)`
=2`sqrt(13)`cm
Now,
(i) `sintheta = (BC)/(AC)`
=`4/(2sqrt(13))`
=`2/sqrt(13)`
=`(2 sqrt(13))/13`
(ii) `cos theta = (AB)/(AC)`
= `6/(2sqrt(13))`
=`3/sqrt(13)`
=`(3sqrt(13))/13`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If cos 2θ = sin 4θ where 2θ, 4θ are acute angles, find the value of θ.
If sin 3θ = cos (θ – 6°) where 3θ and θ − 6° are acute angles, find the value of θ.
If Sec 4A = cosec (A – 20°) where 4A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
If A = 300 , verify that:
(ii) cos 2A = `(1- tan^2A)/(1+tan^2A)`
If sin (A+B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B and cos (A-B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
(i) sin (750)
(ii) cos (150)
From the following figure, find the values of
(i) sin B
(ii) tan C
(iii) sec2 B - tan2B
(iv) sin2C + cos2C
In the given figure, triangle ABC is right-angled at B. D is the foot of the perpendicular from B to AC. Given that BC = 3 cm and AB = 4 cm.
find :
- tan ∠DBC
- sin ∠DBA

In rectangle ABCD, diagonal BD = 26 cm and cotangent of angle ABD = 1.5. Find the area and the perimeter of the rectangle ABCD.
If cos A = `3/5`, then find the value of `(sin"A" - cos"A")/(2tan"A")`
From the given figure, prove that θ + ∅ = 90°. Also prove that there are two other right angled triangles. Find sin α, cos β and tan ∅
