Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the given figure, BC ∥ DE.
(a) If area of ΔADC is 20 sq. units, find the area of ΔAEB.
(b) If the area of ΔBFD is 8 square units, find the area of ΔCEF
Solution
(a) Triangles on the same base and between the same parallels are equal in area.
∴ A(ΔDBC) = A9ΔECB) ....(i)
Now,
A(ΔABC) = A(ΔADC) + A(ΔDBC) = A(ΔAEB) + A(ΔECB)
⇒ A(ΔAC) + A(DBC) = A(ΔAEB) + A(ΔECB)
⇒ A(ΔADC) = A(ΔAEB) ....(ii) [from (i)]
Given, A(ΔADC) = 20 sq. units
⇒ A(ΔAEB) = 20 sq. units
(b) A(ΔADC) = A(ΔAEB) ...[From (ii)]
⇒ A(ΔADC) - A(ΔDEF) = A(ΔAEB) - A(ΔDFE)
⇒ A(ΔCEF) = A(ΔBFD)
Given, A(ΔBFD) = 8 sq. units
⇒ A(ΔCEF) = 8 sq. units.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Show that the diagonals of a square are equal and bisect each other at right angles.
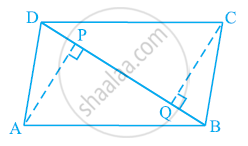
ABCD is a parallelogram and AP and CQ are perpendiculars from vertices A and C on diagonal BD (See the given figure). Show that
- ΔAPB ≅ ΔCQD
- AP = CQ
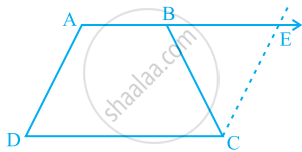
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || CD and AD = BC (see the given figure). Show that
- ∠A = ∠B
- ∠C = ∠D
- ΔABC ≅ ΔBAD
- diagonal AC = diagonal BD
[Hint: Extend AB and draw a line through C parallel to DA intersecting AB produced at E.]
ABCD is a rectangle with ∠ABD = 40°. Determine ∠DBC .
State, 'true' or 'false'
Diagonals of a rhombus are equal.
In the figure, given below, AM bisects angle A and DM bisects angle D of parallelogram ABCD. Prove that: ∠AMD = 90°.

In the following figure, AE and BC are equal and parallel and the three sides AB, CD, and DE are equal to one another. If angle A is 102o. Find angles AEC and BCD.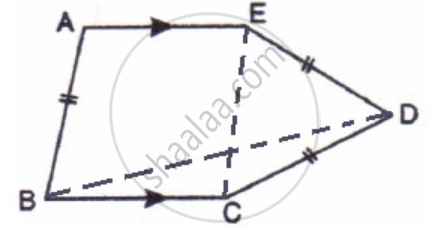
PQRS is a rectangle in which PQ = 12cm and PS = 8cm. Calculate the area of ΔPRS.
In the figure, AE = BE. Prove that the area of triangle ACE is equal in area to the parallelogram ABCD.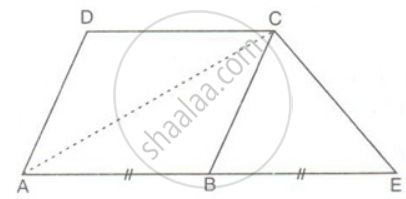
Find the area of each of the following figure:
Find the height of a parallelogram whose area is 144cm2 and the base is 18cm.
The length of a rectangular field is thrice of its width. If the perimeter of this field is 1.6km, find its area in sq.m.
A rectangular floor 45 in long and 12 m broad is to be paved exactly with square tiles, of side 60 cm. Find the total number of tiles required to pave it.
If a carpet is laid on the floor such as a space of 50 cm exists between its edges and the edges of the floor, find what fraction of the floor is uncovered.
Find the area of a square whose diagonal is `12sqrt(12)"cm"`
A footpath of uniform width runs all around the inside of a rectangular garden of 40 m x 30 m. If the path occupies 136 m2, find the width of the path.
PQRS is a square with each side 6cm. T is a point on QR such that the `"area of ΔPQT"/"area of trapezium PTRS" = (1)/(3)` Find the length of TR.
The perimeter of a rectangular plot is 300m. It has an area of 5600m2. Taking the length of the plot as x m, calculate the breadth of the plot in terms of x, form an equation and solve it to find the dimensions of the plot.
All the sides of a parallelogram are of equal length.
Give reason for the following :
Square is also a parallelogram.
Name polygon.

Make two more examples of this.
