Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
PQRS is a rectangle in which PQ = 12cm and PS = 8cm. Calculate the area of ΔPRS.
Solution

Since PQRS is a rectangle, therefore PQ = SR.
SR = 12cm
PS = 8cm
ar(ΔPRS) = `(1)/(2) xx "base" xx "height"`
ar(ΔPRS) = `(1)/(2) xx "SR" xx "PS"`
ar(ΔPRS) = `(1)/(2) xx 12 xx 8`
ar(ΔPRS) = 48cm2.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the diagonals of a parallelogram are equal, then show that it is a rectangle.
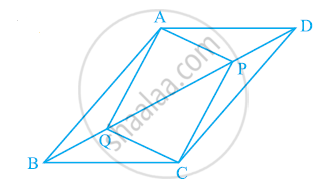
In parallelogram ABCD, two points P and Q are taken on diagonal BD such that DP = BQ (see the given figure). Show that:
- ΔAPD ≅ ΔCQB
- AP = CQ
- ΔAQB ≅ ΔCPD
- AQ = CP
- APCQ is a parallelogram
State, 'true' or 'false'
The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other.
The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 3: 4: 5: 6. Show that the quadrilateral is a trapezium.
In the given figure ABCD is a rhombus with angle A = 67°

If DEC is an equilateral triangle, calculate:
- ∠CBE
- ∠DBE
In the given figure, PQRS is a ∥ gm. A straight line through P cuts SR at point T and QR produced at N. Prove that area of triangle QTR is equal to the area of triangle STN.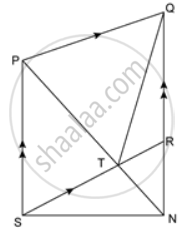
In the figure, PQR is a straight line. SQ is parallel to Tp. Prove that the quadrilateral PQST is equal in area to the ΔPSR.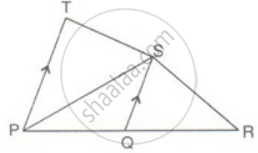
The diagonals of a parallelogram ABCD intersect at O. A line through O meets AB in P and CD in Q. Show that
(a) Area of APQD = `(1)/(2)` area of || gm ABCD
(b) Area of APQD = Area of BPQC
A quadrilateral ABCD is such that diagonals BD divides its area into two equal parts. Prove that BD bisects AC.
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle and AD is the median.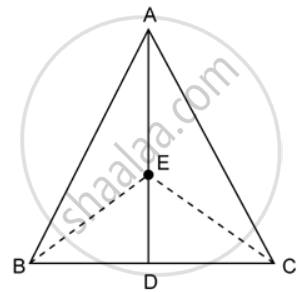
If E is any point on the median AD. Show that: Area of ΔABE = Area of ΔACE.
Find the area of a parallelogram whose base is 12cm and the height is 5cm.
Two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are 34 cm and 20 cm. If one of its diagonal is 42 cm, find: area of the parallelogram.
Two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are 34 cm and 20 cm. If one of its diagonal is 42 cm, find: distance between its shorter sides
A rectangular field 240m long has an area 36000m2. Find the cost of fencing the field at Rs.2.50per m.
Find the perimeter of a rhombus whose diagonals are 24cm and 10cm.
The side of a square exceeds the side of another square by 4cm and the sum of the areas of the squares is 400cm2. Find the dimensions of the squares.
A rectangular field is 240m long and 180m broad. In one corner a farm house is built on a square plot of side 40m. Find the area of the remaining portion and the cost of fencing the open sides Rs.25per m.
The opposite sides of a trapezium are parallel.
A figure is said to be regular if its sides are equal in length and angles are equal in measure. Can you identify the regular quadrilateral?
Examine whether the following is a polygon. If it is not, say why?

