Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The function f : R → R defined by
`f (x) = 2^x + 2^(|x|)` is
Options
one-one and onto
many-one and onto
one-one and into
many-one and into
Solution
(d) many-one and into
Graph for the given function is as follows.
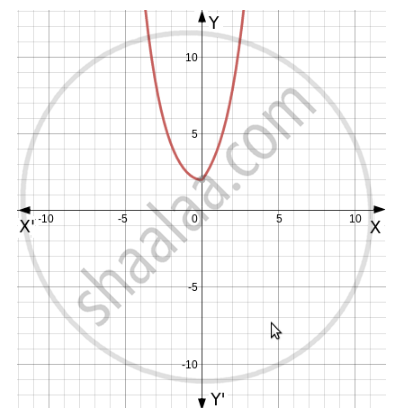
A line parallel to X axis is cutting the graph at two different values.
Therefore, for two different values of x we are getting the same value of y.
That means it is many one function.[2 , ∞ ) and R is the co-domain of the given function.
Hence, Co-domain ≠ Range Therefore, the given function is into.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Show that the Signum Function f: R → R, given by `f(x) = {(1, if x > 0), (0, if x = 0), (-1, if x < 0):}` is neither one-one nor onto
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Show that f is one-one.
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : N → N given by f(x) = x3
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = x3 + 1
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 5x3 + 4
Give examples of two one-one functions f1 and f2 from R to R, such that f1 + f2 : R → R. defined by (f1 + f2) (x) = f1 (x) + f2 (x) is not one-one.
If f : A → B and g : B → C are onto functions, show that gof is a onto function.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x+1, g(x) = `e^x`
.
Find fog and gof if : f(x)= x + 1, g (x) = 2x + 3 .
If f(x) = 2x + 5 and g(x) = x2 + 1 be two real functions, then describe each of the following functions:
(1) fog
(2) gof
(3) fof
(4) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ f2
If f(x) = sin x and g(x) = 2x be two real functions, then describe gof and fog. Are these equal functions?
If f : Q → Q, g : Q → Q are two functions defined by f(x) = 2 x and g(x) = x + 2, show that f and g are bijective maps. Verify that (gof)−1 = f−1 og −1.
If the mapping f : {1, 3, 4} → {1, 2, 5} and g : {1, 2, 5} → {1, 3}, given by f = {(1, 2), (3, 5), (4, 1)} and g = {(2, 3), (5, 1), (1, 3)}, then write fog. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\} = B\] Then, the mapping\[f : A \to \text{B given by} f\left( x \right) = x\left| x \right|\] is
Let
f : R → R be given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \left[ x^2 \right] + \left[ x + 1 \right] - 3\]
where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then, f(x) is
(d) one-one and onto
Let
\[f : R \to R\] be a function defined by
Let
Which of the following functions from
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\}\]
If \[F : [1, \infty ) \to [2, \infty )\] is given by
\[f\left( x \right) = x + \frac{1}{x}, then f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\]
A function f: R→ R defined by f(x) = `(3x) /5 + 2`, x ∈ R. Show that f is one-one and onto. Hence find f−1.
Are the following set of ordered pairs functions? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective.
{(a, b): a is a person, b is an ancestor of a}
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
f = {(1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 5)}
Let A = [–1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on A are one-one, onto or bijective:
g(x) = |x|
Let A = {1, 2, 3, ...n} and B = {a, b}. Then the number of surjections from A into B is ______.
Which of the following functions from Z into Z are bijections?
Let f: R – `{3/5}` → R be defined by f(x) = `(3x + 2)/(5x - 3)`. Then ______.
Let f: `[2, oo)` → R be the function defined by f(x) = x2 – 4x + 5, then the range of f is ______.
Let f: R → R be given by f(x) = tan x. Then f–1(1) is ______.
Let g(x) = x2 – 4x – 5, then ____________.
An organization conducted a bike race under 2 different categories-boys and girls. Totally there were 250 participants. Among all of them finally, three from Category 1 and two from Category 2 were selected for the final race. Ravi forms two sets B and G with these participants for his college project. Let B = {b1,b2,b3} G={g1,g2} where B represents the set of boys selected and G the set of girls who were selected for the final race.
Ravi decides to explore these sets for various types of relations and functions.
- Ravi wants to find the number of injective functions from B to G. How many numbers of injective functions are possible?
A function f: x → y is said to be one – one (or injective) if:
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 4x – 1, ∀ x ∈ R then 'f' is
Let f: R→R be a continuous function such that f(x) + f(x + 1) = 2, for all x ∈ R. If I1 = `int_0^8f(x)dx` and I2 = `int_(-1)^3f(x)dx`, then the value of I1 + 2I2 is equal to ______.
If log102 = 0.3010.log103 = 0.4771 then the number of ciphers after decimal before a significant figure comes in `(5/3)^-100` is ______.
`x^(log_5x) > 5` implies ______.
Let a and b are two positive integers such that b ≠ 1. Let g(a, b) = Number of lattice points inside the quadrilateral formed by lines x = 0, y = 0, x = b and y = a. f(a, b) = `[a/b] + [(2a)/b] + ... + [((b - 1)a)/b]`, then the value of `[(g(101, 37))/(f(101, 37))]` is ______.
(Note P(x, y) is lattice point if x, y ∈ I)
(where [.] denotes greatest integer function)
Let f(1, 3) `rightarrow` R be a function defined by f(x) = `(x[x])/(1 + x^2)`, where [x] denotes the greatest integer ≤ x, Then the range of f is ______.
Let A = {1, 2, 3, ..., 10} and f : A `rightarrow` A be defined as
f(k) = `{{:(k + 1, if k "is odd"),( k, if k "is even"):}`.
Then the number of possible functions g : A `rightarrow` A such that gof = f is ______.
For x ∈ R, x ≠ 0, let f0(x) = `1/(1 - x)` and fn+1 (x) = f0(fn(x)), n = 0, 1, 2, .... Then the value of `f_100(3) + f_1(2/3) + f_2(3/2)` is equal to ______.
