Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Solutions
3: Electrochemistry
4: Chemical Kinetics
▶ 5: Surface Chemistry
6: General Principle and Processes of Isolation of Elements
7: The p-block Elements
8: The d-and f-Block Elements
9: Coordination Compounds
10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
13: Amines
14: Biomolecules
15: Polymers
16: Chemistry In Everyday Life
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 5 - Surface Chemistry NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 5 - Surface Chemistry - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Surface Chemistry
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Chemistry [English] Class 12.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 5 Surface Chemistry Exercises [Pages 63 - 73]
Multiple Choice Questions (Type - I)
Which of the following process does not occur at the interface of phases?
Crystallisation
Heterogenous catalysis
Homogeneous catalysis
Corrosion
At the equilibrium position in the process of adsorption ______.
∆H > 0
∆H = T∆S
∆H > T∆S
∆H < T∆S
Which of the following interface cannot be obtained?
Liquid-liquid
Solid-liquid
Liquid-gas
Gas-gas
The term ‘sorption’ stands for ______.
absorption
adsorption
both absorption and adsorption
desorption
Extent of physisorption of a gas increases with ______.
increase in temperature.
decrease in temperature.
decrease in surface area of adsorbent.
decrease in strength of van der Waals forces.
Extent of adsorption of adsorbate from solution phase increases with ______.
increase in amount of adsorbate in solution.
decrease in surface area of adsorbent.
increase in temperature of solution.
decrease in amount of adsorbate in solution.
Which one of the following is not applicable to the phenomenon of adsorption?
∆H > O
∆G < CO
∆S < O
∆H < O
Which of the following is not a favourable condition for physical adsorption?
High pressure
Negative ∆H
Higher critical temperature of adsorbate
High temperature
Physical adsorption of a gaseous species may change to chemical adsorption with ______.
decrease in temperature
increase in temperature
increase in surface area of adsorbent
decrease in surface area of adsorbent
In physisorption adsorbent does not show specificity for any particular gas because ______.
involved van der Waals forces are universal.
gases involved behave like ideal gases.
enthalpy of adsorption is low.
it is a reversible process.
Which of the following is an example of absorption?
Water on silica gel
Water on calcium chloride
Hydrogen on finely divided nickel
Oxygen on metal surface
On the basis of data given below predict which of the following gases shows least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal?
| Gas | CO2 | SO2 | CH1 | H2 |
| Critical temp./K | 304 | 630 | 190 | 33 |
CO2
SO2
CH4
H2
In which of the following reactions heterogenous catalysis is involved?
(a) \[\ce{2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ->[NO(g)] 2SO3 (g)}\]
(b) \[\ce{2SO2 (g) ->[Pt(s)] 2SO3 (g)}\]
(c) \[\ce{N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ->[Fe(s)] 2NH3 (g)}\]
(d) \[\ce{CH3COOCH3 (l) + H2O (l) ->[HCI(l)] CH3COOH (aq) + CH3OH (aq)}\]
(b), (c)
(b), (c), (d)
(a), (b), (c)
(d)
At high concentration of soap in water, soap behaves as ______.
molecular colloid
associated colloid
macromolecular colloid
lyophilic colloid
Which of the following will show Tyndall effect?
Aqueous solution of soap below critical micelle concentration.
Aqueous solution of soap above critical micelle concentration.
Aqueous solution of sodium chloride.
Aqueous solution of sugar.
Method by which lyophobic sol can be protected?
By addition of oppositely charged sol.
By addition of an electrolyte.
By addition of lyophilic sol.
By boiling.
Freshly prepared precipitate sometimes gets converted to colloidal solution by ______.
coagulation
electrolysis
diffusion
peptisation
Which of the following electrolytes will have maximum coagulating value for AgI/Ag+ solution?
Na2S
Na3PO4
Na2SO4
NaCl
A colloidal system having a solid substance as a dispersed phase and a liquid as a dispersion medium is classified as ______.
solid sol
gel
emulsion
sol
The values of colligative properties of colloidal solution are of small order in comparison to those shown by true solutions of same concentration because of colloidal particles ______.
exhibit enormous surface area.
remain suspended in the dispersion medium.
form lyophilic colloids.
are comparatively less in number.
Arrange the following diagrams in correct sequence of steps involved in the mechanism of catalysis, in accordance with modern adsorption theory.
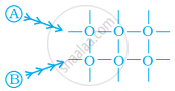
(a)

(b)
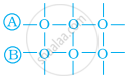
(c)
(d)

(e)
\[\ce{a → b → c → d → e}\]
\[\ce{a → c → b → d → e}\]
\[\ce{a → c → b → e → d}\]
\[\ce{a → b → c → e → d}\]
Which of the following process is responsible for the formation of delta at a place where rivers meet the sea?
Emulsification
Colloid formation
Coagulation
Peptisation
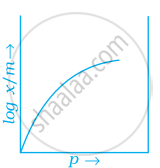
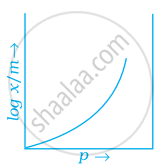
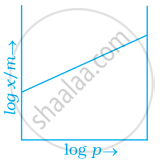
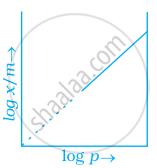
Which of the following curves is in accordance with Freundlich adsorption isotherm?
Which of the following process is not responsible for the presence of electric charge on the sol particles?
Electron capture by sol particles.
Adsorption of ionic species from solution.
Formation of Helmholtz electrical double layer.
Absorption of ionic species from solution.
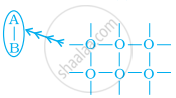
Which of the following phenomenon is applicable to the process shown in the figure?
Absorption
Adsorption
Coagulation
Emulsification
Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II) Note: In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
Which of the following options are correct?
(i) Micelle formation by soap in aqueous solution is possible at all temperatures.
(ii) Micelle formation by soap in aqueous solution occurs above a particular concentration.
(iii) On dilution of soap solution micelles may revert to individual ions.
(iv) Soap solution behaves as a normal strong electrolyte at all concentrations.
Which of the following statements are correct about solid catalyst?
(i) Same reactants may give different product by using different catalysts.
(ii) Catalyst does not change ∆H of reaction.
(iii) Catalyst is required in large quantities to catalyse reactions.
(iv) Catalytic activity of a solid catalyst does not depend upon the strength of chemisorption.
Freundlich adsorption isotherm is given by the expression `x/m = kp^(1/n)` which of the following conclusions can be drawn from this expression.
(i) When `1/n` = 0, the adsorption is independent of pressure.
(ii) When `1/n` = 0, the adsorption is directly proportional to pressure.
(iii) When n = 0, `x/m` vs p graph is a line parallel to x-axis.
(iv) When n = 0, plot of `x/m` vs p is a curve.
\[\ce{H2}\] gas is adsorbed on activated charcoal to a very little extent in comparison to easily liquefiable gases due to:
(i) very strong van der Waal’s interaction.
(ii) very weak van der Waals forces.
(iii) very low critical temperature.
(iv) very high critical temperature.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Mixing two oppositely charged sols neutralises their charges and stabilises the colloid.
(ii) Presence of equal and similar charges on colloidal particles provides stability to the colloids.
(iii) Any amount of dispersed liquid can be added to emulsion without destabilising it.
(iv) Brownian movement stabilises sols.
An emulsion cannot be broken by:
(i) heating
(ii) adding more amount of dispersion medium
(iii) freezing
(iv) adding emulsifying agent
Which of the following substances will precipitate the negatively charged emulsions?
(i) \[\ce{KCl}\]
(ii) glucose
(iii) urea
(iv) \[\ce{NaCl}\]
Which of the following colloids cannot be coagulated easily?
(i) Lyophobic colloids.
(ii) Irreversible colloids.
(iii) Reversible colloids.
(iv) Lyophilic colloids.
What happens when a lyophilic sol is added to a lyophobic sol?
(i) Lyophobic sol is protected.
(ii) Lyophilic sol is protected.
(iii) Film of lyophilic sol is formed over lyophobic sol.
(iv) Film of lyophobic sol is formed over lyophilic sol.
Which phenomenon occurs when an electric field is applied to a colloidal solution and electrophoresis is prevented?
(i) Reverse osmosis takes place.
(ii) Electroosmosis takes place.
(iii) Dispersion medium begins to move.
(iv) Dispersion medium becomes stationary.
In a reaction, catalyst changes:
(i) physically
(ii) qualitatively
(iii) chemically
(iv) quantitatively
Which of the following phenomenon occurs when a chalk stick is dipped in ink?
(i) Adsorption of coloured substance.
(ii) Adsorption of solvent.
(iii) Absorption and adsorption both of solvent.
(iv) Absoprtion of solvent.
Short Answer Type
Why is it important to have clean surface in surface studies?
Why is chemisorption referred to as activated adsorption?
What type of solutions are formed on dissolving different concentrations of soap in water?
What happens when gelatin is mixed with gold sol?
How does it become possible to cause artificial rain by spraying silver iodide on the clouds?
Gelatin which is a peptide is added in icecreams. What can be its role?
What is collodion?
Why do we add alum to purify water?
What happens when electric field is applied to colloidal solution?
What causes brownian motion in colloidal dispersion?
A colloid is formed by adding \[\ce{FeCl3}\] in excess of hot water. What will happen if excess sodium chloride is added to this colloid?
How do emulsifying agents stabilise the emulsion?
Why are some medicines more effective in the colloidal form?
Why does leather get hardened after tanning?
How does the precipitation of colloidal smoke take place in Cottrell precipitator?
How will you distinguish between dispersed phase and dispersion medium in an emulsion?
On the basis of Hardy-Schulze rule explain why the coagulating power of phosphate is higher than chloride.
Why does bleeding stop by rubbing moist alum?
Why is \[\ce{Fe(OH)3}\] colloid positively charged, when prepared by adding \[\ce{FeCl3}\] to hot water?
Why do physisorption and chemisorption behave differently with rise in temperature?
What happens when dialysis is prolonged?
Why does the white precipitate of silver halide become coloured in the presence of dye eosin.
What is the role of activated charcoal in gas mask used in coal mines?
How does a delta form at the meeting place of sea and river water?
Give an example where physisorption changes to chemisorption with rise in temperature. Explain the reason for change.
Why is desorption important for a substance to act as good catalyst?
What is the role of diffusion in heterogenous catalysis?
How does a solid catalyst enhance the rate of combination of gaseous molecules?
Do the vital functions of the body such as digestion get affected during fever? Explain your answer.
Method of formation of solution is given in Column I. Match it with the type of solution given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Sulphur vapours passed through cold water | (a) Normal electrolyte solution |
| (ii) Soap mixed with water above critical micelle concentration | (b) Molecular colloids |
| (iii) White of egg whipped with water | (c) Associated colloid |
| (iv) Soap mixed with water below critical micelle concentration | (d) Macro molecular colloids |
Match the statement given in Column I with the phenomenon given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Dispersion medium moves in an electric field | (a) Osmosis |
| (ii) Solvent molecules pass through semi permeable membrane towards solvent side |
(b) Electrophoresis |
| (iii) Movement of charged colloidal particles under the influence of applied electric potential towards oppositely charged electrodes |
(c) Electroosmosis |
| (iv) Solvent molecules pass through semi permeable membranes towards solution side |
(d) Reverse osmosis |
Match the items given in Column I and Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Protective colloid | (a) \[\ce{FeCl3 + NaOH}\] |
| (ii) Liquid-liquid colloid | (b) Lyophilic colloids |
| (iii) Positively charged colloid | (c) Emulsion |
| (iv) Negatively charged colloid | (d) \[\ce{FeCl3}\] + hot water |
Match the types of colloidal systems given in Column I with the name given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Solid in liquid | (a) Foam |
| (ii) Liquid in solid | (b) Sol |
| (iii) Liquid in liquid | (c) Gel |
| (iv) Gas in liquid | (d) Emulsion |
Match the items of Column I and Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Dialysis | (a) Cleansing action of soap |
| (ii) Peptisation | (b) Coagulation |
| (iii) Emulsification | (c) Colloidal sol formation |
| (iv) Electrophoresis | (d) Purification |
Match the items of Column I and Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Butter | (a) dispersion of liquid in liquid |
| (ii) Pumice stone | (b) dispersion of solid in liquid |
| (iii) Milk | (c) dispersion of gas in solid |
| (iv) Paints | (d) dispersion of liquid in solid |
Assertion: An ordinary filter paper impregnated with collodion solution stops the flow of colloidal particles.
Reason: Pore size of the filter paper becomes more than the size of colloidal particle.
Assertion and reason both are correct and the reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
Assertion: Colloidal solutions show colligative properties.
Reason: Colloidal particles are large in size.
Assertion and reason both are correct and the reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
Assertion: Colloidal solutions do not show brownian motion.
Reason: Brownian motion is responsible for stability of sols.
Assertion and reason both are correct and the reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
Assertion: Coagulation power of Al3+ is more than Na+.
Reason: Greater the valency of the flocculating ion added, greater is its power to cause precipitation (Hardy Schulze rule).
Assertion and reason both are correct and the reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
Assertion: Detergents with low CMC are more economical to use.
Reason: Cleansing action of detergents involves the formation of micelles. These are formed when the concentration of detergents becomes equal to CMC.
Assertion and reason both are correct and the reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
What is the role of adsorption in heterogenous catalysis?
What are the applications of adsorption in chemical analysis?
What is the role of adsorption in froth floatation process used especially for concentration of sulphide ores?
What do you understand by shape selective catalysis? Why are zeolites good shape selective catalysts?
Solutions for 5: Surface Chemistry
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 5 - Surface Chemistry NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 5 - Surface Chemistry - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 5 - Surface Chemistry
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE 5 (Surface Chemistry) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 5 Surface Chemistry are Types of Adsorption, Enzyme Catalysis, Classification Based on Nature of Interaction Between Dispersed Phase and Dispersion Medium, Properties of Colloidal Solutions, Emulsions, Distinction Between Adsorption and Absorption, Mechanism of Adsorption, Adsorption Isotherms (Freundlich and Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm), Adsorption from Solution Phase, Applications of Adsorption, Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis, Adsorption Theory of Heterogeneous Catalysis, Shape-selective Catalysis by Zeolites, Catalysts in Industry, Colloids, Classification Based on Type of Particles of the Dispersed Phase, Multimolecular, Macromolecular and Associated Colloids, Preparation of Colloids, Purification of Colloidal Solutions, Colloids Around Us, Introduction of Adsorption, Classification Based on Physical State of Dispersed Phase and Dispersion Medium.
Using NCERT Exemplar Chemistry [English] Class 12 solutions Surface Chemistry exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Chemistry [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Surface Chemistry Chemistry [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.