Advertisements
Chapters
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board chapter 5 - Geometry Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board chapter 5 - Geometry - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-8-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Geometry
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board 5 Geometry Exercise 5.1 [Pages 165 - 166]
Fill in the blanks with the correct term mention in option.
Corresponding sides of similar triangles are _________
in proportion
similar
corresponding
congruent
shape
area
equal
Similar triangles have the same ________ but not necessarily the same size
in proportion
similar
corresponding
congruent
shape
area
equal
In any triangle _______ sides are opposite to equal angles
in proportion
similar
corresponding
congruent
shape
area
equal
The symbol ≡ is used to represent ________ triangles
in proportion
similar
corresponding
congruent
shape
area
equal
The symbol ~ is used to represent _________ triangles
in proportion
similar
corresponding
congruent
shape
area
equal
In the given figure, ∠CIP ≡ ∠COP and ∠HIP ≡ ∠HOP. Prove that IP ≡ OP.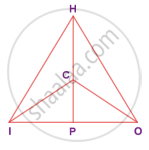
In the given figure, AC ≡ AD and ∠CBD ≡ ∠DEC. Prove that ∆BCF ≡ ∆EDF.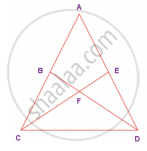
In the given figure, ΔBCD is isosceles with base BD and ∠BAE ≡∠DEA. Prove that AB ≡ ED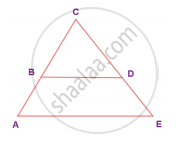
In the given figure, D is the midpoint of OE and ∠CDE = 90°. Prove that ΔODC ≡ ΔEDC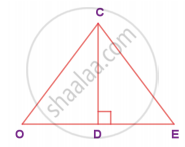
Is ΔPRQ ≡ ΔQSP? Why?
From the given figure, prove that ΔABC ~ ΔEDF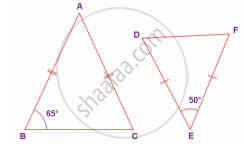
In the given figure YH || TE. Prove that ΔWHY ~ ΔWET and also find HE and TE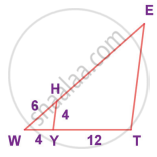
In the given figure, if ΔEAT ~ ΔBUN, find the measure of all angles.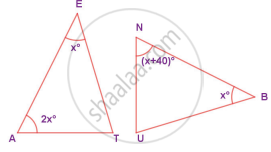
In the given figure, UB || AT and CU ≡ CB Prove that ΔCUB ~ ΔCAT and hence ΔCAT is isosceles.
Objective Type Questions
Two similar triangles will always have ________ angles
acute
obtuse
right
matching
If in triangles PQR and XYZ, `"PQ"/"XY" = "QR"/"ZX"` then they will be similar if
∠Q = ∠Y
∠P = ∠Y
∠Q = ∠X
∠P = ∠Z
A flag pole 15 m high casts a shadow of 3 m at 10 a.m. The shadow cast by a building at the same time is 18.6 m. The height of the building is
90 m
91 m
92 m
93 m
If ∆ABC – ∆PQR in which ∠A = 53° and ∠Q = 77°, then ∠R is
50°
60°
70°
80°
In the figure, which of the following statements is true?
AB = BD
BD < CD
AC = CD
BC = CD
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board 5 Geometry Exercise 5.2 [Pages 177 - 179]
Fill in the blanks:
If in a ΔPQR, PR2 = PQ2 + QR2, then the right angle of ∆PQR is at the vertex ________
If ‘l‘ and ‘m’ are the legs and ‘n’ is the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle then, l2 = ________
If the sides of a triangle are in the ratio 5 : 12 : 13 then, it is ________
The medians of a triangle cross each other at _______
The centroid of a triangle divides each medians in the ratio _______
Say True or False
8, 15, 17 is a Pythagorean triplet
True
False
In a right angled triangle, the hypotenuse is the greatest side
True
False
In any triangle the centroid and the incentre are located inside the triangle
True
False
The centroid, orthocentre, and incentre of a triangle are collinear
True
False
The incentre is equidistant from all the vertices of a triangle
True
False
Check whether given sides are the sides of right-angled triangles, using Pythagoras theorem
8, 15, 17
Check whether given sides are the sides of right-angled triangles, using Pythagoras theorem
12, 13, 15
Check whether given sides are the sides of right-angled triangles, using Pythagoras theorem
30, 40, 50
Check whether given sides are the sides of right-angled triangles, using Pythagoras theorem
9, 40, 41
Check whether given sides are the sides of right-angled triangles, using Pythagoras theorem
24, 45, 51
Find the unknown side in the following triangles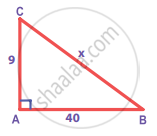
Find the unknown side in the following triangles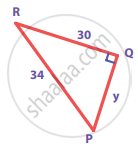
Find the unknown side in the following triangles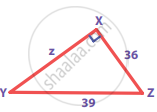
An isosceles triangle has equal sides each 13 cm and a base 24 cm in length. Find its height
Find the distance between the helicopter and the ship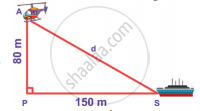
In triangle ABC, line I, is a perpendicular bisector of BC.
If BC = 12 cm, SM = 8 cm, find CS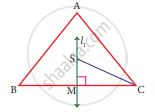
Identify the centroid of ∆PQR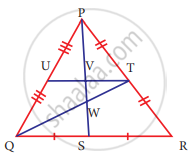
Name the orthocentre of ∆PQR
In the given figure, A is the midpoint of YZ and G is the centroid of the triangle XYZ. If the length of GA is 3 cm, find XA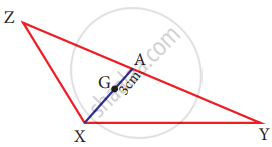
If I is the incentre of ∆XYZ, ∠IYZ = 30° and ∠IZY = 40°, find ∠YXZ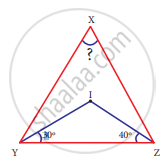
Objective Type Questions
If ∆GUT is isosceles and right angled, then ∠TUG is ________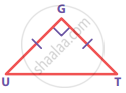
30°
40°
45°
55°
The hypotenuse of a right angled triangle of sides 12 cm and 16 cm is __________
28 cm
20 cm
24 cm
21 cm
The area of a rectangle of length 21 cm and diagonal 29 cm is __________
609 cm2
580 cm2
420 cm2
210 cm2
The sides of a right angled triangle are in the ratio 5 : 12 : 13 and its perimeter is 120 units then, the sides are ______________
25, 36, 59
10, 24, 26
36, 39, 45
20, 48, 52
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board 5 Geometry Exercise 5.3 [Pages 179 - 180]
Miscellaneous Practice Problems
In the figure, given that ∠1 = ∠2 and ∠3 ≡ ∠4. Prove that ∆MUG ≡ ∆TUB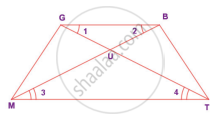
From the figure, prove that ∆SUN ~ ∆RAY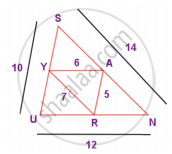
The height of a tower is measured by a mirror on the ground at R by which the top of the tower’s reflection is seen. Find the height of the tower. If ∆PQR ~ ∆STR
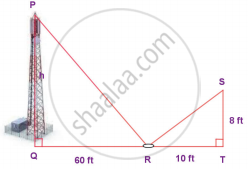
Find the length of the support cable required to support the tower with the floor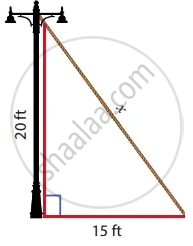
Rithika buys an LED TV which has a 25 inches screen. If its height is 7 inches, how wide is the screen? Her TV cabinet is 20 inches wide. Will the TV fit into the cabinet? Give reason
Challenging problems
In the figure, ∠TMA ≡∠IAM and ∠TAM ≡ ∠IMA. P is the midpoint of MI and N is the midpoint of AI. Prove that ΔPIN ~ ΔATM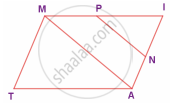
In the figure, if ∠FEG ≡ ∠1 then, prove that DG2 = DE.DF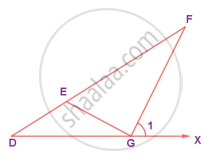
The diagonals of the rhombus is 12 cm and 16 cm. Find its perimeter. (Hint: the diagonals of rhombus bisect each other at right angles)
In the figure, find AR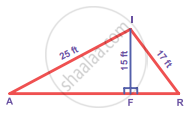
In ∆DEF, DN, EO, FM are medians and point P is the centroid. Find the following
If DE = 44, then DM = ?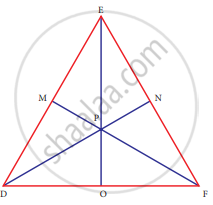
In ∆DEF, DN, EO, FM are medians and point P is the centroid. Find the following
If PD = 12, then PN = ?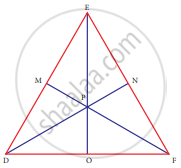
In ∆DEF, DN, EO, FM are medians and point P is the centroid. Find the following
If DO = 8, then FD = ?
In ∆DEF, DN, EO, FM are medians and point P is the centroid. Find the following
If OE = 36 then EP = ?
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board 5 Geometry Exercise 5.4 [Page 192]
Construct the following quadrilaterals with the given measurements and also find their area.
ABCD, AB = 5 cm, BC = 4.5 cm, CD = 3.8 cm, DA = 4.4 cm and AC = 6.2 cm
Construct the following quadrilaterals with the given measurements and also find their area.
PLAY, PL = 7 cm, LA = 6 cm, AY = 6 cm, PA = 8 cm and LY = 7 cm
Construct the following quadrilaterals with the given measurements and also find their area.
PQRS, PQ = QR = 3.5 cm, RS = 5.2 cm, SP = 5.3 cm and ∠Q = 120°
Construct the following quadrilaterals with the given measurements and also find their area.
MIND, MI = 3.6 cm, ND = 4 cm, MD = 4 cm, ∠M = 50° and ∠D = 100°
Construct the following quadrilaterals with the given measurements and also find their area.
AGRI, AG = 4.5 cm, GR = 3.8 cm, ∠A = 60°, ∠G = 110° and ∠R = 90°
Construct the following trapeziums with the given measures and also find their area.
AIMS with `bar("AI") || bar("SM")`, = 6 cm, IM = 5 cm, AM = 9 cm and MS = 6.5 cm
Construct the following trapeziums with the given measures and also find their area.
CUTE with `bar("CU") || bar("ET")`, CU = 7 cm, ∠UCE = 80° CE = 6 cm and TE = 5 cm
Construct the following trapeziums with the given measures and also find their area.
ARMY with `bar("AR") || bar("YM")`, AR = 7 cm, RM = 6.5 cm ∠RAY = 100° and ∠ARM = 60°
Construct the following trapeziums with the given measures and also find their area.
CITY with `bar("CI") || bar("YT")`, CI = 7 cm, IT = 5.5 cm, TY = 4 cm and YC = 6 cm
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board 5 Geometry Exercise 5.5 [Page 209]
Construct the following parallelograms with the given measurements and find their area.
ARTS, AR = 6 cm, RT = 5 cm and ∠ART = 70°
Construct the following parallelograms with the given measurements and find their area.
CAMP, CA = 6 cm, AP = 8 cm and CP = 5.5 cm
Construct the following parallelograms with the given measurements and find their area.
EARN, ER = 10 cm, AN = 7 cm and ∠EOA = 110° where `bar("ER")` and `bar("AN")` intersect at O
Construct the following parallelograms with the given measurements and find their area.
GAIN, GA = 7.5 cm, GI = 9 cm and ∠GAI = 100°
Construct the following rhombuses with the given measurements and also find their area.
FACE, FA = 6 cm and FC = 8 cm
Construct the following rhombuses with the given measurements and also find their area.
CAKE, CA = 5 cm and ∠A = 65°
Construct the following rhombuses with the given measurements and also find their area.
LUCK, LC = 7.8 cm and UK = 6 cm
Construct the following rhombuses with the given measurements and also find their area.
PARK, PR = 9 cm and ∠P = 70°
Construct the following rectangles with the given measurements and also find their area.
HAND, HA = 7 cm and AN = 4 cm
Construct the following rectangles with the given measurements and also find their area.
LAND, LA = 8 cm and AD = 10 cm
Construct the following squares with the given measurements and also find their area.
EAST, EA = 6.5 cm
Construct the following squares with the given measurements and also find their area.
WEST, WS = 7.5 cm
Solutions for 5: Geometry
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board chapter 5 - Geometry Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board chapter 5 - Geometry - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-8-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board chapter 5 - Geometry
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 5 (Geometry) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board chapter 5 Geometry are Congruency of Shapes, Similar Figures, Congruence of Triangles, Criteria for Congruence of Triangles, SSS Congruence Criterion, SAS Congruence Criterion, ASA Congruence Criterion, RHS Congruence Criterion, Similarity of Triangles, Converse of Pythagoras Theorem, Point of Concurrency, Median of a Triangle, Altitudes of a Triangle, Perpendicular Bisectors of a Triangle, Circumcentre of a Triangle, The Property of the Angle Bisectors of a Triangle, Constructing a Quadrilateral When the Lengths of Four Sides and a Diagonal Are Given, Constructing a Quadrilateral When Two Diagonals and Three Sides Are Given, Construct a Quadrilateral When Its Four Sides and One Angle Are Given., Construction of a Rhombus When One Side and One Angle Are Given., Construction of a Rhombus When Two Diagonals Are Given., Right-angled Triangles and Pythagoras Property, Construction of a Square When Its Diagonal is Given., Constructing a Quadrilateral When Three Sides and Two Included Angles Are Given, Constructing a Quadrilateral When Two Adjacent Sides and Three Angles Are Known, Constructing a trapezium when its three sides and one diagonal are given, Constructing a Trapezium When Its Three Sides and One Angle Are Given, Constructing a Trapezium When Its Two Sides and Two Angles Are Given., Constructing a Trapezium When Its Four Sides Are Given., Constructing a Parallelogram When Its Two Adjacent Sides and One Angle Are Given., Constructing a Parallelogram When Its Two Adjacent Sides and One Diagonal Are Given., Constructing a Parallelogram When Its Two Diagonals and One Included Angle Are Given., Constructing a Parallelogram When Its One Side, One Diagonal and One Angle Are Given., Construction of a Rhombus When One Side and One Diagonal Are Given., Construction of a Rhombus When One Diagonal and One Angle Are Given., Construction of a Rectangle When Its Length and Breadth Are Given., Construction of a Rectangle When a Side and a Diagonal Are Given., Construction of a Square When Its Side is Given..
Using Samacheer Kalvi Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board solutions Geometry exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Geometry Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
