Topics
Field Visit
Location and Extent
Physiography and Drainage
- Physical Divisions of India
- The North Indian Mountains
- The Himalayas
- North Indian Plains
- The Peninsular Indian Plateau
- The Indian Coastal Plains
- The Indian Islands
- Physiography of Brazil
- Brazilian Highlands
- The Great Escarpment in Brazil
- Coastline of Brazil
- Brazilian Plains
- Brazilian Island
- Drainage of Brazil
- Drainage Systems of India
- Himalayan Rivers
- Peninsular Rivers
Climate
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Population
Human Settlements
Economy and Occupations
Tourism, Transport and Communication
Geography - Physical Divisions of India
Identification of Physical divisions
- Identification of Physical Divisions
Geography - North Indian Mountains
Himalayas
Associated mountains
- Concept of Associated Mountains
Geography - North Indian Plain Region
Deserts
- Desert
Western Plains
- Concept of Western Plains
Central Plains
- Concept on Central Plains
Delta region
- Concept of Delta Region
Eastern Plains
- Concept of Eastern Plains
Geography - Peninsular Plateau Region
Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
- Concept for Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
Malwa Plateau
- Concept on Malwa Plateau
Maharashtra Plateau
- Concept for Maharashtra Plateau
Karnataka Plateau
- Concept for Karnataka Plateau
Telangana Plateau
- Concept for Telangana Plateau
Geography - Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
Eastern Ghats
- Concept on Eastern Ghats
Sahyadries
- Concept on Sahyadries
Geography - Coastal Region
- Geography - Coastal Region
Eastern coastal plain
- Coastal Region - Eastern Coastal Plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Western coastal plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Geography - Indian Islands
- Geography - Indian Islands
Eastern Islands
- Indian Islands - Eastern Islands
Western Islands
- Indian Islands - Western Islands
Geography - Practical 1
Cartography
- Concept on Cartography
Geography - Practical 2
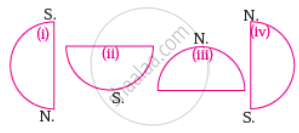
Two dimensional diagrams
- Two Dimensional Shapes
One dimensional diagrams
- Concept on One Dimensional Diagrams
Economics - Introduction of an Economy
Introduction of an Economy
- Economy
- Types of Economy
- Main Features of Economy
Economics - Basic problems of an economy solution
Solutions
- Concept for Capitalism
- Concept for Socialism
- Mixed Economy
Problems
- Introduction of Basic Problems of an Economy
- Problems- for Whom to Produce
- Problem - How Much to Produce
- Problem - by Whom to Produce
Economics - Inflation
Introduction
- Introduction of Inflation
Effects of inflation
- Effects of Inflation
Measures of Inflation
- Measures of Inflation
Causes of inflation
- Causes of Inflation
Economics - Public distribution system and consumer protection
- Measures of Inflation
Public Distribution system - meaning and explanation
- Public Distribution System - Meaning and Explanation
Introduction
- Introduction of Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Objectives of Public Distribution system
- Objectives of Public Distribution System
Remedial Measures
- Remedial Measures Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Consumer Protection
- Consumer Protection - Rights and Duties of Cunsumer, Food Adulteration
Drawbacks of Public Distribution system
- Drawbacks of Public Distribution System
Progress of Public Distribution system
- Progress of Public Distribution System
- Brazil : Location, Size and Extent
- Brazilian Standard Time
Definition
- Latitude: Latitude is the angle that a place on the surface of the globe is from the equator, either north or south.
- Longitude: An angular distance on the surface of the earth, measured either east or west from the prime meridian at Greenwich, is known as longitude.
- Angular distance: The angular distance between the points from the centers is called angular distance.
Notes
Brazil : Location, Size and Extent
|
Brazil: Location and Extent |
Location:
- Some part of Brazil lies in the northern hemisphere while most of it lies in the southern hemisphere and the western hemisphere.
- Brazil is the Northern part of the South American Continent.
- The Brazil mainland stretches from 5°15' N to 33°45' S latitudes and from 34°45' W to 73°48' W longitudes.
- The Equator (0°) and Tropic of Capricorn (23°30' S) pass through Brazil.
Size and Extent:
- Brazil covers a total area of 8.51 million square km. Brazil's total area accounts for approximately 5.6% of the world's total geographical area. Thus, Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world.
- The national territory is 4,397.53 km long from north to south and 4,320.53 km long from east to west.
- The Atlantic coast stretches 7,367 km along the east coast of Brazil. Brazil has 15,719 km in the west, measured in a clockwise direction from the south.
Brazilian Standard Time:
|
Brazilian Standard Time |
- Time in Brazil is calculated using standard time, and the country is divided into four standard time zones: UTC−02:00, UTC−03:00, UTC−04:00, and UTC−05:00.
- Brasilia (UTC−03:00) is the main time zone of Brazil and comprises the state's Goias, Tocantins, Para, Amapa, and the Federal District.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [18]
Identify the correct correlation and make a chain.
| A | B | C |
| 1) Ganga river | i) Pau Brasil | a) trees shed their leaves |
| 2) Amazon river | ii) sediments deposit | b) there are islands at its mouth |
| 3) Brazil | iii) Teak trees | c) country named after it |
| 4) Deciduous forests | iv) no sediments | d) distributaries at the mouth |