Topics
Field Visit
Location and Extent
Physiography and Drainage
- Physical Divisions of India
- The North Indian Mountains
- The Himalayas
- North Indian Plains
- The Peninsular Indian Plateau
- The Indian Coastal Plains
- The Indian Islands
- Physiography of Brazil
- Brazilian Highlands
- The Great Escarpment in Brazil
- Coastline of Brazil
- Brazilian Plains
- Brazilian Island
- Drainage of Brazil
- Drainage Systems of India
- Himalayan Rivers
- Peninsular Rivers
Climate
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Population
Human Settlements
Economy and Occupations
Tourism, Transport and Communication
Geography - Physical Divisions of India
Identification of Physical divisions
- Identification of Physical Divisions
Geography - North Indian Mountains
Himalayas
Associated mountains
- Concept of Associated Mountains
Geography - North Indian Plain Region
Deserts
- Desert
Western Plains
- Concept of Western Plains
Central Plains
- Concept on Central Plains
Delta region
- Concept of Delta Region
Eastern Plains
- Concept of Eastern Plains
Geography - Peninsular Plateau Region
Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
- Concept for Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
Malwa Plateau
- Concept on Malwa Plateau
Maharashtra Plateau
- Concept for Maharashtra Plateau
Karnataka Plateau
- Concept for Karnataka Plateau
Telangana Plateau
- Concept for Telangana Plateau
Geography - Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
Eastern Ghats
- Concept on Eastern Ghats
Sahyadries
- Concept on Sahyadries
Geography - Coastal Region
- Geography - Coastal Region
Eastern coastal plain
- Coastal Region - Eastern Coastal Plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Western coastal plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Geography - Indian Islands
- Geography - Indian Islands
Eastern Islands
- Indian Islands - Eastern Islands
Western Islands
- Indian Islands - Western Islands
Geography - Practical 1
Cartography
- Concept on Cartography
Geography - Practical 2
Two dimensional diagrams
- Two Dimensional Shapes
One dimensional diagrams
- Concept on One Dimensional Diagrams
Economics - Introduction of an Economy
Introduction of an Economy
- Economy
- Types of Economy
- Main Features of Economy
Economics - Basic problems of an economy solution
Solutions
- Concept for Capitalism
- Concept for Socialism
- Mixed Economy
Problems
- Introduction of Basic Problems of an Economy
- Problems- for Whom to Produce
- Problem - How Much to Produce
- Problem - by Whom to Produce
Economics - Inflation
Introduction
- Introduction of Inflation
Effects of inflation
- Effects of Inflation
Measures of Inflation
- Measures of Inflation
Causes of inflation
- Causes of Inflation
Economics - Public distribution system and consumer protection
- Measures of Inflation
Public Distribution system - meaning and explanation
- Public Distribution System - Meaning and Explanation
Introduction
- Introduction of Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Objectives of Public Distribution system
- Objectives of Public Distribution System
Remedial Measures
- Remedial Measures Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Consumer Protection
- Consumer Protection - Rights and Duties of Cunsumer, Food Adulteration
Drawbacks of Public Distribution system
- Drawbacks of Public Distribution System
Progress of Public Distribution system
- Progress of Public Distribution System
Definition
- Island: An island is a region of land that is smaller than a continent and surrounded by water.
Notes
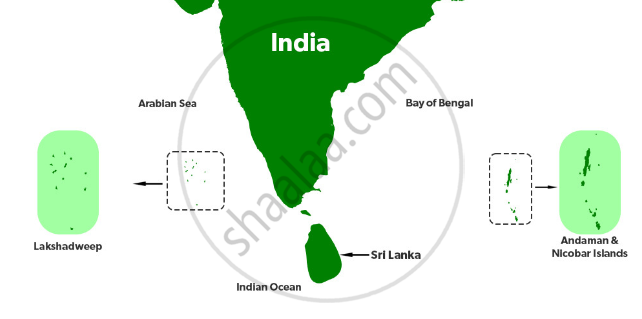
The Indian Islands:
|
Islands in India |
- Along the coast of India's mainland, there are numerous small and large islands.
- These are included in the coastal island group.
- Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep are India's two major island groups.
- The former group consists of 572 islands and are located in Bay of Bengal, and the later one has 27 islands and are located in Arabian Sea.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands are primarily of tectonic and volcanic origin.
a) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- These islands are situated on a raised portion of the submarine mountains.
- Since these islands are so close to the equator, the climate is hot and humid throughout the year, with dense forests.
- The island group covers an area of approximately 8,249 square kilometres.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are a group of more than 300 islands out of which 265 are uninhabited.
- The entire group of islands is divided into two. They are Andaman in the north and the Nicobar in the south. These island groups are extremely strategic for the country.
- The administrative capital of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands is Port Blair. The Ten Degree Channel separates the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Nicobar Island includes the southernmost point, Indira Point.
- The Great Andamans are five large islands that are grouped together, and to the south is the island of Little Andaman. There are 204 islets.
- These islands are highly dissected and rise to a height of 730 metres. There are 550 islands, the majority of which are too small to be inhabited.
- The Nicobar Islands are located 121 kilometres south of Little Andaman. There are 19 islands, seven of which are uninhabited. The main islands are Great Nicobar and Car Nicobar. These are volcanic islands. The Barren Island is home to India's only active volcano. Narcondam is another volcanic island in this group. They are surrounded by coral reefs and have narrow coastal plains.

An Island
b) Lakshadweep Islands
- This is a small group of coral islands off India's west coast. It has a total area of 32 square kilometres. Its administrative capital is Kavaratti. The Eight Degree Channel separates the Lakshadweep Islands from the Maldives. The uninhabited “Pitt Island” of this group has a bird sanctuary. Previously, it was divided into three sections: Laccadive, Minicoy, and Amindivi. In 1973, it was given the name Lakshadweep.
- It is a group of 36 islands, of which only 11 are inhabited. It is located approximately 280 to 480 kilometres off the coast of Kerala. It was established as a Union Territory in 1956 as the Laccadive, Minicoy, and Amindivi Islands, and renamed Lakshadweep in November 1973. The northern region is known as the Amindivis. The remaining islands are referred to as the Laccadives (including Minicoy Islands).
c) Offshore Islands
- India has a number of islands along its Western and Eastern coasts, in the Ganga delta region, and in the Gulf of Mannar. Many of these islands are uninhabited and are managed by neighbouring countries.
Text
|
Corals Coral polyps are microscopic organisms that live in colonies. They thrive in shallow, mud-free, warm water. Calcium carbonate is secreted by them. Coral secretions and skeletons form reefs, which are classified into three types: barrier reefs, fringing reefs, and atolls. Australia's Great Barrier Reef is an excellent example of the first type of coral reef. Atolls are coral reefs that are circular or horseshoe-shaped. |
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.