Topics
Field Visit
Location and Extent
Physiography and Drainage
- Physical Divisions of India
- The North Indian Mountains
- The Himalayas
- North Indian Plains
- The Peninsular Indian Plateau
- The Indian Coastal Plains
- The Indian Islands
- Physiography of Brazil
- Brazilian Highlands
- The Great Escarpment in Brazil
- Coastline of Brazil
- Brazilian Plains
- Brazilian Island
- Drainage of Brazil
- Drainage Systems of India
- Himalayan Rivers
- Peninsular Rivers
Climate
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Population
Human Settlements
Economy and Occupations
Tourism, Transport and Communication
Geography - Physical Divisions of India
Identification of Physical divisions
- Identification of Physical Divisions
Geography - North Indian Mountains
Himalayas
Associated mountains
- Concept of Associated Mountains
Geography - North Indian Plain Region
Deserts
- Desert
Western Plains
- Concept of Western Plains
Central Plains
- Concept on Central Plains
Delta region
- Concept of Delta Region
Eastern Plains
- Concept of Eastern Plains
Geography - Peninsular Plateau Region
Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
- Concept for Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
Malwa Plateau
- Concept on Malwa Plateau
Maharashtra Plateau
- Concept for Maharashtra Plateau
Karnataka Plateau
- Concept for Karnataka Plateau
Telangana Plateau
- Concept for Telangana Plateau
Geography - Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
Eastern Ghats
- Concept on Eastern Ghats
Sahyadries
- Concept on Sahyadries
Geography - Coastal Region
- Geography - Coastal Region
Eastern coastal plain
- Coastal Region - Eastern Coastal Plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Western coastal plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Geography - Indian Islands
- Geography - Indian Islands
Eastern Islands
- Indian Islands - Eastern Islands
Western Islands
- Indian Islands - Western Islands
Geography - Practical 1
Cartography
- Concept on Cartography
Geography - Practical 2
Two dimensional diagrams
- Two Dimensional Shapes
One dimensional diagrams
- Concept on One Dimensional Diagrams
Economics - Introduction of an Economy
Introduction of an Economy
- Economy
- Types of Economy
- Main Features of Economy
Economics - Basic problems of an economy solution
Solutions
- Concept for Capitalism
- Concept for Socialism
- Mixed Economy
Problems
- Introduction of Basic Problems of an Economy
- Problems- for Whom to Produce
- Problem - How Much to Produce
- Problem - by Whom to Produce
Economics - Inflation
Introduction
- Introduction of Inflation
Effects of inflation
- Effects of Inflation
Measures of Inflation
- Measures of Inflation
Causes of inflation
- Causes of Inflation
Economics - Public distribution system and consumer protection
- Measures of Inflation
Public Distribution system - meaning and explanation
- Public Distribution System - Meaning and Explanation
Introduction
- Introduction of Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Objectives of Public Distribution system
- Objectives of Public Distribution System
Remedial Measures
- Remedial Measures Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Consumer Protection
- Consumer Protection - Rights and Duties of Cunsumer, Food Adulteration
Drawbacks of Public Distribution system
- Drawbacks of Public Distribution System
Progress of Public Distribution system
- Progress of Public Distribution System
Notes
India Transport
- Roadways: India has a more dense transportation network than Brazil. Every year, roads carry approximately 85% of passengers and 70% of goods.
- Railways: The development of railways has facilitated merchandise and passenger transportation. Railways are critical to the economic growth of India. The railway network is comparatively less dense in hill states, northeastern states, central India, and Rajasthan, whereas it is dense in the North Indian Plains. Railways are critical in a large country with long distances.
- Waterways: Waterways are a cheap mode of transportation. Waterways account for about 1% of the total transportation in the country. It includes rivers, canals, backwaters, creeks, and so on. Approximately 95 percent of India’s foreign trade moves through ocean routes. These are used for transportation between the islands and the rest of the country in addition to international trade.
- Airways: Airways in India are more developed than in Brazil, and the use of internal airways is growing.
Example
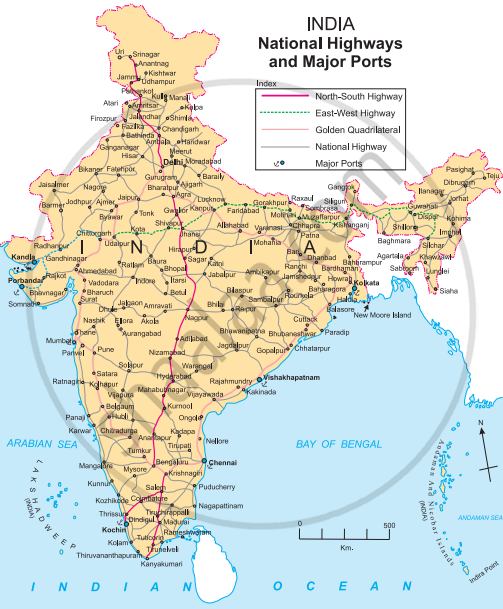
Look at the transport maps of India given in fig and answer the following questions.
 |
 |
- Which means of transport are visible on the map?
- In which part of India is the density of railways more?
- Name five important ports and airports of India.
- Which parts of India have a sparse network of transport? What could be the reason?
- The means of transport visible on the map are waterways, railways and airways.
- The density of railways is more in the Northern Plains region.
- Ports: Mumbai ,Vishakhapatanam, Haldia, Chennai and Kandla.
Airports: Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Chennai, and Kolkata. - The north and the north-east parts of India have a sparse network of transport. Due to mountainous and snow covered areas in the north and the dense inaccesible forest areas of the north-east, the transportation network is sparse here. Also these regions have low population and lack of economic opportunities.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.


