Topics
Field Visit
Location and Extent
Physiography and Drainage
- Physical Divisions of India
- The North Indian Mountains
- The Himalayas
- North Indian Plains
- The Peninsular Indian Plateau
- The Indian Coastal Plains
- The Indian Islands
- Physiography of Brazil
- Brazilian Highlands
- The Great Escarpment in Brazil
- Coastline of Brazil
- Brazilian Plains
- Brazilian Island
- Drainage of Brazil
- Drainage Systems of India
- Himalayan Rivers
- Peninsular Rivers
Climate
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Population
Human Settlements
Economy and Occupations
Tourism, Transport and Communication
Geography - Physical Divisions of India
Identification of Physical divisions
- Identification of Physical Divisions
Geography - North Indian Mountains
Himalayas
Associated mountains
- Concept of Associated Mountains
Geography - North Indian Plain Region
Deserts
- Desert
Western Plains
- Concept of Western Plains
Central Plains
- Concept on Central Plains
Delta region
- Concept of Delta Region
Eastern Plains
- Concept of Eastern Plains
Geography - Peninsular Plateau Region
Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
- Concept for Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
Malwa Plateau
- Concept on Malwa Plateau
Maharashtra Plateau
- Concept for Maharashtra Plateau
Karnataka Plateau
- Concept for Karnataka Plateau
Telangana Plateau
- Concept for Telangana Plateau
Geography - Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
Eastern Ghats
- Concept on Eastern Ghats
Sahyadries
- Concept on Sahyadries
Geography - Coastal Region
- Geography - Coastal Region
Eastern coastal plain
- Coastal Region - Eastern Coastal Plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Western coastal plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Geography - Indian Islands
- Geography - Indian Islands
Eastern Islands
- Indian Islands - Eastern Islands
Western Islands
- Indian Islands - Western Islands
Geography - Practical 1
Cartography
- Concept on Cartography
Geography - Practical 2
Two dimensional diagrams
- Two Dimensional Shapes
One dimensional diagrams
- Concept on One Dimensional Diagrams
Economics - Introduction of an Economy
Introduction of an Economy
- Economy
- Types of Economy
- Main Features of Economy
Economics - Basic problems of an economy solution
Solutions
- Concept for Capitalism
- Concept for Socialism
- Mixed Economy
Problems
- Introduction of Basic Problems of an Economy
- Problems- for Whom to Produce
- Problem - How Much to Produce
- Problem - by Whom to Produce
Economics - Inflation
Introduction
- Introduction of Inflation
Effects of inflation
- Effects of Inflation
Measures of Inflation
- Measures of Inflation
Causes of inflation
- Causes of Inflation
Economics - Public distribution system and consumer protection
- Measures of Inflation
Public Distribution system - meaning and explanation
- Public Distribution System - Meaning and Explanation
Introduction
- Introduction of Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Objectives of Public Distribution system
- Objectives of Public Distribution System
Remedial Measures
- Remedial Measures Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Consumer Protection
- Consumer Protection - Rights and Duties of Cunsumer, Food Adulteration
Drawbacks of Public Distribution system
- Drawbacks of Public Distribution System
Progress of Public Distribution system
- Progress of Public Distribution System
- Development of Communication in Brazil
Notes
Communication in Brazil
|
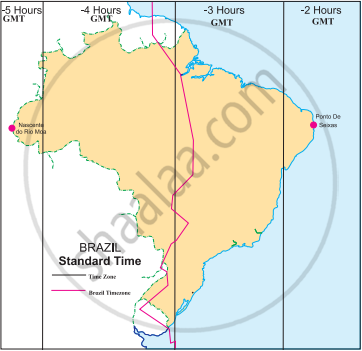
Brazilian Standard Time |
- The difference between two extreme points is approximately 168 minutes (2 hours 48 minutes) due to the vast longitudinal extent of the country. There are various 'time zones' in the country. There are four time zones in Brazil. It is 2, 3, 4 or 5 hours behind GMT. The red line on the map represents the GMT-03 time zone, which is the official Brazilian time, BRT. It is three hours behind GMT.
Development of Communication in Brazil
- There exist an advanced and efficient telecommunication services in Brazil. This industry includes landlines, mobile services, television, radio broadcasting and computer/internet access. Today, more than 45% of the Brazilian population has internet access.
- The telecommunications infrastructure is relatively modern, especially in central and southern Brazil. However, the north and north-west are drastically less developed.
- Over recent years, mobile telephones have led the rapid expansion of telecommunication services in Brazil. The nature of Brazilian territory, particularly land mass size and large pockets of unpopulated and densely vegetated areas, create significant barrier to expanding telecommunications coverage.
- Brazil is working on developing technology to launch domestic satellites into space using its own rockets.
Example
It is 12 noon at Delhi. What would be the local time in Brasilia?
Sun rises in the east and sets in the west. Thus sun moves from east to west as the earth rotates from west to east. Earth can be seen as a sphere of 360 ̊. Earth rotates this 360 ̊ in 24 hours.
Rotation of earth in 1 hour = 360/24 = 15 ̊
The time in India is 12.00 noon. It has the longitudinal time zone in the coordinates 82.5 ̊ E. The longitudinal coordinates that determine the time of Brasilia are 47.52 ̊ W.
The difference in longitude between Brasilia and India = 47.52 ̊ W + 82.5 ̊ E
= 130.02 ̊ E
Difference in time = 130.02/15 = 8.6 hours
= 8 hours + (0.6*60) minutes
= 8 hours 36 minutes (approx.)
Since the earth rotates from west to east, time zone at 82.5 ̊ E will be ahead of 47.52 ̊ W. Thus Brasilian time would be behind the Indian time by 8 hours 36 minutes.
Time in Brasilia = 3.24 AM
Example
Read the map in the fig and answer the following questions:
 |
- How many divisions can you see in the map?
- What do these divisions signify?
- What does the term ‘behind the GMT’ mean ?
- Which part of Brazil is ahead of the other ?
- By how many minutes is this part ahead of others?
- What does the red line in the map show?
- We can see 4 divisions in the map.
- These divisions signify the time zones in Brazil.
- The Greenwich Meridian Time is a time set with reference to 0° longitude that passes through Greenwich. The countries lying to the west of 0° longitude are ’behind the GMT’.
- The easternmost part of Brazil is ahead of the other parts.
- 60 to 180 minutes.
- The red line in the map is the official BRT which is in the GMT-03 time zone. It is 3 hours behind GMT.
Example
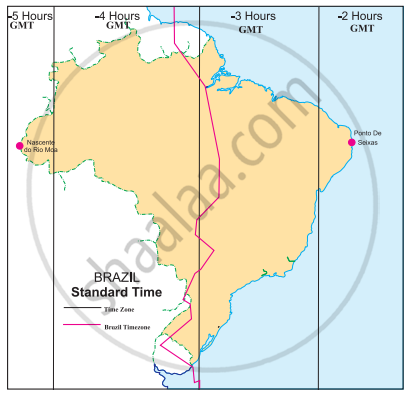
Given are the westernmost and easternmost extreme points of Brazil mainland in figure. Calculate the difference in time between the two points in minutes.
 |
Westernmost point: Nascente do Rio Moa (07°32'33'' S, 70°59' W)
Easternmost point: Ponta do Seixas, Paraíba (07°09' 28''S, 34°47' W)
Westernmost point: Nascente do Rio Moa (07°32'33'' S, 70°59' W) Easternmost point: Ponta do Seixas, Paraíba (07°09' 28''S, 34°47' W)
The difference in time between the Easternmost and the Westernmost part of Brazil is 168 minutes.
Example
Saurabh and Ashwini work for a MNC. Two of their regional head offices are located in Brazil in Rio De Janeiro and Manaus, respectively. Both of them have to contact either of the head offices constantly. As they have to adjust timings according to their head offices, find out their corresponding timings in India, if they work according to office timings in Brazil i.e 10am. to 5 pm.
- Let's assume Saurabh is coordinating with Rio De Janeiro’s head office and Ashwini is coordinating with the head office of Manaus.
- Brazil has four time zones. It is behind the GMT by 2, 3, 4 or 5 hours.
- Rio De Janeiro is in the 2nd time zone which is 3 hours behind GMT (GMT-03) and Manaus is the 3rd time zone which is 4 hours behind GMT (GMT-04).
- Now, the time difference between GMT and 1ST is of 5 hours 30 mins.
- They have to make following adjustments :
| Saurabh | ||
| Rio De Janeiro | GMT | IST |
| 10 a.m. | 1 p.m. | 6.30 p.m. |
| 5 p.m. | 8 p.m. | 1.30 a.m. |
| Ashwini | ||
| Manaus | GMT | IST |
| 10 a.m. | 2 p.m. | 7.30 p.m. |
| 5 p.m. | 9 p.m. | 2.30 a.m. |
Rio De Janeiro is in the 2nd time zone which is 3 hours behind GMT (GMT-03) and Manaus is the 3rd time zone which is 4 hours behind GMT (GMT-04)
Corresponding timings in India Saurabh: 6.30 p.m. to 1.30 a.m. Ashwini: 7.30 p.m. to 2.30 a.m.
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [10]
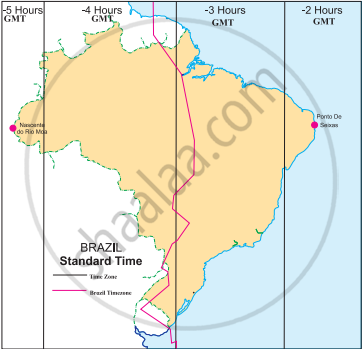
Read the map in the fig and answer the following questions:
 |
- How many divisions can you see in the map?
- What do these divisions signify?
- What does the term ‘behind the GMT’ mean ?
- Which part of Brazil is ahead of the other ?
- By how many minutes is this part ahead of others?
- What does the red line in the map show?
Given are the westernmost and easternmost extreme points of Brazil mainland in figure. Calculate the difference in time between the two points in minutes.
 |
Westernmost point: Nascente do Rio Moa (07°32'33'' S, 70°59' W)
Easternmost point: Ponta do Seixas, Paraíba (07°09' 28''S, 34°47' W)
Westernmost point: Nascente do Rio Moa (07°32'33'' S, 70°59' W) Easternmost point: Ponta do Seixas, Paraíba (07°09' 28''S, 34°47' W)