Topics
Field Visit
Location and Extent
Physiography and Drainage
- Physical Divisions of India
- The North Indian Mountains
- The Himalayas
- North Indian Plains
- The Peninsular Indian Plateau
- The Indian Coastal Plains
- The Indian Islands
- Physiography of Brazil
- Brazilian Highlands
- The Great Escarpment in Brazil
- Coastline of Brazil
- Brazilian Plains
- Brazilian Island
- Drainage of Brazil
- Drainage Systems of India
- Himalayan Rivers
- Peninsular Rivers
Climate
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Population
Human Settlements
Economy and Occupations
Tourism, Transport and Communication
Geography - Physical Divisions of India
Identification of Physical divisions
- Identification of Physical Divisions
Geography - North Indian Mountains
Himalayas
Associated mountains
- Concept of Associated Mountains
Geography - North Indian Plain Region
Deserts
- Desert
Western Plains
- Concept of Western Plains
Central Plains
- Concept on Central Plains
Delta region
- Concept of Delta Region
Eastern Plains
- Concept of Eastern Plains
Geography - Peninsular Plateau Region
Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
- Concept for Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
Malwa Plateau
- Concept on Malwa Plateau
Maharashtra Plateau
- Concept for Maharashtra Plateau
Karnataka Plateau
- Concept for Karnataka Plateau
Telangana Plateau
- Concept for Telangana Plateau
Geography - Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
Eastern Ghats
- Concept on Eastern Ghats
Sahyadries
- Concept on Sahyadries
Geography - Coastal Region
- Geography - Coastal Region
Eastern coastal plain
- Coastal Region - Eastern Coastal Plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Western coastal plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Geography - Indian Islands
- Geography - Indian Islands
Eastern Islands
- Indian Islands - Eastern Islands
Western Islands
- Indian Islands - Western Islands
Geography - Practical 1
Cartography
- Concept on Cartography
Geography - Practical 2
Two dimensional diagrams
- Two Dimensional Shapes
One dimensional diagrams
- Concept on One Dimensional Diagrams
Economics - Introduction of an Economy
Introduction of an Economy
- Economy
- Types of Economy
- Main Features of Economy
Economics - Basic problems of an economy solution
Solutions
- Concept for Capitalism
- Concept for Socialism
- Mixed Economy
Problems
- Introduction of Basic Problems of an Economy
- Problems- for Whom to Produce
- Problem - How Much to Produce
- Problem - by Whom to Produce
Economics - Inflation
Introduction
- Introduction of Inflation
Effects of inflation
- Effects of Inflation
Measures of Inflation
- Measures of Inflation
Causes of inflation
- Causes of Inflation
Economics - Public distribution system and consumer protection
- Measures of Inflation
Public Distribution system - meaning and explanation
- Public Distribution System - Meaning and Explanation
Introduction
- Introduction of Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Objectives of Public Distribution system
- Objectives of Public Distribution System
Remedial Measures
- Remedial Measures Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Consumer Protection
- Consumer Protection - Rights and Duties of Cunsumer, Food Adulteration
Drawbacks of Public Distribution system
- Drawbacks of Public Distribution System
Progress of Public Distribution system
- Progress of Public Distribution System
- Sex ratio
- Age and sex pyramid
- Population growth rate
- Life expectancy
- Literacy rate
Definition
Sex Ratio: Sex ratio means the numberof females per 1000 males in region.
Population Pyramid: A population pyramid (age structure diagram) or "age-sex pyramid" is a graphical illustration of the distribution of a population (typically that of a country or region of the world) by age groups and sex; it typically takes the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing.
Life Expectancy: This means the average number of years a person born in a country is expected to live.
Literacy Rate: The proportion of the adult population aged 15 years and over which is literate, expressed as a percentage of the corresponding population, total or for a given sex, in a given country, territory, or geographic area, at a specific point in time, usually mid-year. For statistical purposes, a person is literate who can with understanding both read and write a short simple statement on his/her everyday life.
Formula
`"Sex Ratio"= "Total number of females in a particular area"/"Total numbers of the male in the same area" × 1000`
Notes
Comparison of Population Composition Between India and Brazil
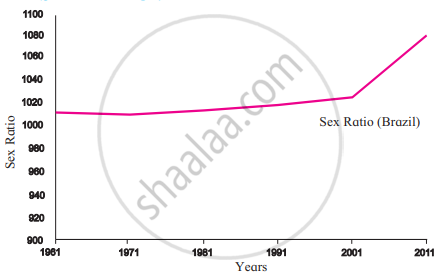
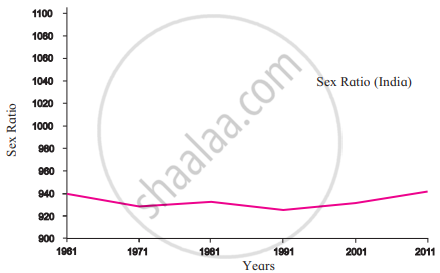
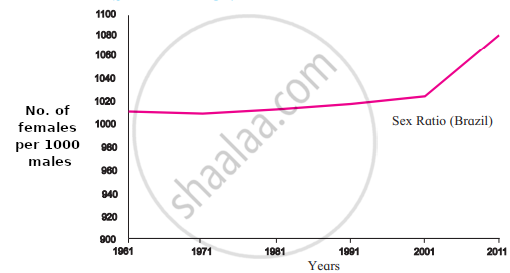
1. Sex Ratio:
|
Sex Ratio in Brazil |
|
Sex Ratio in India |
- The sex ratios of Brazil and India are depicted in this graph.
- The sex ratio means the number of females per 1000 males in the region.
- The characteristics of the population are prominently noticeable in both countries.
1. For decades, Brazil's sex ratio has been greater than 1000.
2. Taking into consideration the sex ratio in Brazil, the number of women has increased significantly more than the number of men since 2001.
3. In India, men outnumber women.
4. The sex ratio in India has fluctuated over the last few decades. There was a slight increase in the sex ratio after 1991. - The graph shows that in Brazil, women have always outnumbered men, whereas, in India, women have never outnumbered men.
2. Age and Sex Pyramid
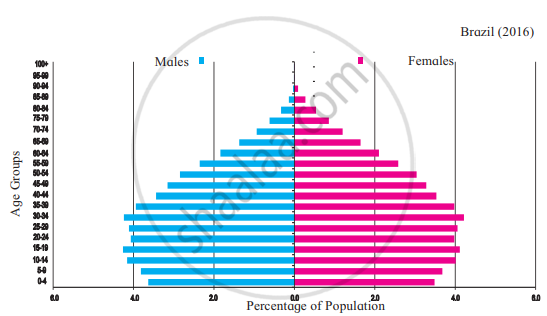 |
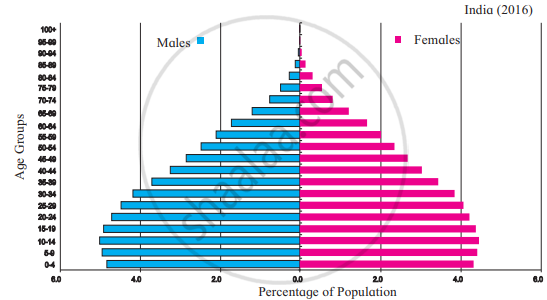 |
- This graph shows the age and sex of the population. It is also known as the population pyramid.
- It is used to study the age and sex-related aspects of a region’s population.
- This helps us to know the proportion of children, youth, and the elderly in our country.
- In this pyramid, we can see that the number of young people is more in both countries but the proportion of children is more in India while the proportion of people in the age group above 80 years is more in Brazil than in India.
- Brazil's population is gradually getting older, but the situation in India is different. In India, the proportion of youth is higher. This implies that India has a larger working population.
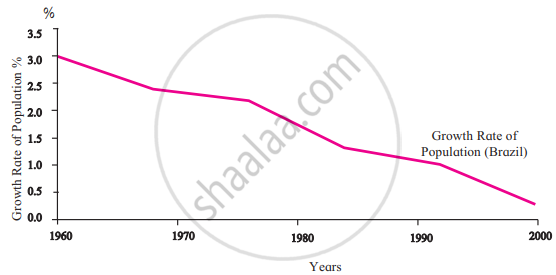
3. Population Growth Rate
|
|
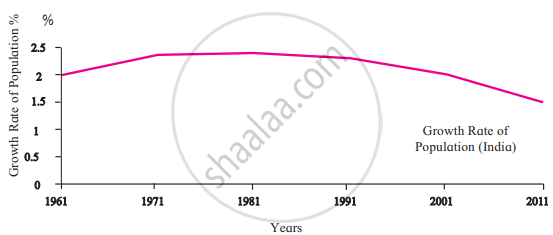 |
- These graphs show the growth rate of the population of Brazil and India.
- The lines show a downward trend, but it doesn’t mean the population is decreasing. It shows that the growth is lesser than in the previous decade.
- The growth is less and looking at the trend, in the near future, Brazil’s population may decrease.
- In Brazil, the rate of population growth has lessened significantly. However, this is not the case in India. Between 2001 and 2011, India's population increased by 18.2 crores.
- Until 1971, India's population growth rate was higher. The rate then stabilised. The rate of population growth is now lessening, but the population is still growing.
- It has been observed that Brazil's growth rate is decreasing, and the country's population may not increase in the next two decades.
4. Life Expectancy
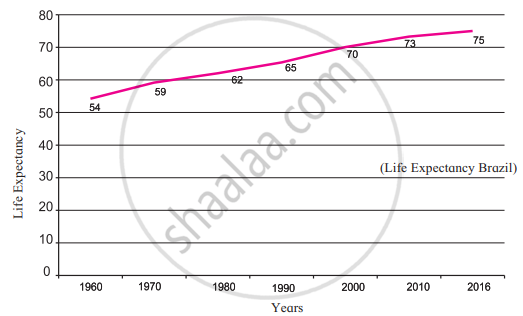 |
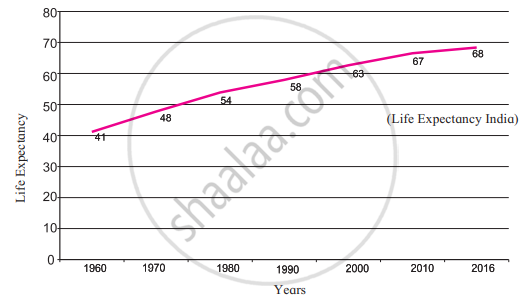 |
- These graphs show the life expectancy of Brazil and India
- Life expectancy means the average number of years a person born in a country is expected to live.
- This means that Indians live for 68 years on average whereas Brazilians on the counterpart live for 75 years on average.
- The life expectancy in India was around 41 years in 1960. But now it has increased. It will continue to increase in future.
- An increase in life expectancy is an indicator of a society's development. Improvements in healthcare facilities, advancements in the medical field, and increased access to nutritious food all contribute to an increase in average life expectancy. Life expectancy remains low in the majority of developing countries. However, it is rising as a result of socioeconomic development.
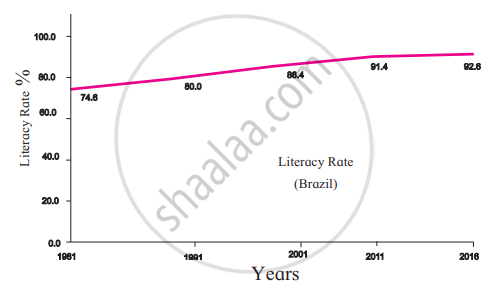
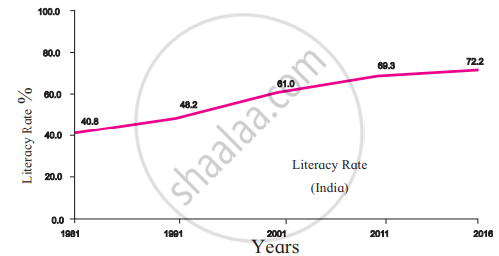
5. Literacy Rate
 |
 |
Text
Do you know?‘Save Girl, Teach Girl’ is the need of the hour in our country. |
Text
Do you know?Census of India conducts enumeration of population every ten years. Similarly, in Brazil, IBGE i.e. Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, carries out census every ten years. The first census survey of both the countries was carried out in 1872. In India, Census is conducted at the start of the decade. (1961, 1971, .......) In Brazil, Census is conducted at the end of the decade. (1960, 1970, .......) |
Example
What could be the reasons of lower sex ratio in any region?
Sex ratio refers to the number of females per thousand males in a region. India has a low sex ratio.
The reasons for lower sex ratio are as follows:
- Illiteracy: People are not aware of the role of women in modern society. This is because of child marriages where girls get married at an early age without having a chance to study and educate themselves.
- Female infanticide: Even though the Government has passed many Acts to stop this inhuman act, people still prefer to have a male child due to many reasons. Hence, girl babies are killed as soon as they are born.
- Domestic violence: Women are considered to be the weaker sex and hence crimes and violence against women is still a common feature in many of the rural households. This makes even the mother stop having a girl child.
- Female foeticide: Due to socio-economic issues like dowry, people destroy the girl foetus in the womb itself. Many laws have been made to prevent this.
- Poverty: Poverty is a major reason for the declining sex ratio. Families living under Below Poverty Line(BPL) generally do not want to have girl children.
- Lack of women empowerment: Due to lack of education, women do not enjoy equal opportunities in many of the rural areas, especially in northern India.
The lower sex ratio, even in the twenty-first century is really a cause of concern.
Example
In India, number of men outnumber women. Is this condition found in all the States of India? Find out!
In a country like India where we have a patriarchal society, the number of men outnumbers women.
This condition is found in almost all the states of India with Kerala as an exception.
Example
Is there a relationship between increase in life expectancy and growth of population? If yes, how?
- Yes, there is a relationship between increase in life expectancy and growth of population.
- Increased life expectancy means there are more people who live longer, which means healthier and better quality of life.
- This kind of population generally prefers fewer children which leads to decreased birth rates.
Example
If the proportion of dependent age groups increases in the composition of population, how will it affect the economy of a country?
- If the proportion of dependent age groups increases in the composition of population, it will have an adverse effect on the economy of a country.
- The reason is if the working population is less, the economic activities will reduce and will have a direct impact on the economic growth and development of that nation.
- The production will decrease in comparison to consumption leading to inflation also the per capita income and GDP will decrease.
- Export will reduce and imports will increase.
- The proportion of the working population will increase, slowing down the pace of development.
Example
Study the indices of density maps of both the countries. What difference do you find? What conclusions can you draw?
|
India Population Density |
|
Population density in Brazil |
The study of the indices of density maps of Brazil and India clearly explains the distribution of population among the various states of both the countries.
Brazil is three times bigger than India in terms of its area. But it accounts for only 2.8 per cent of the world’s population whereas India has 16.8 per cent of the world’s population.
The northern and southern states of India are densely populated whereas the central states have comparatively less population. The northeastern states are sparsely populated.
It can be understood that the total population of states like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana and Punjab is almost equal to that of Brazil’s total population.
The country of Brazil has a denser population in its eastern states. The western and northern states are very sparsely populated.
Example
What should be done so that our manpower is utilized properly, sex ratio improves and population growth is controlled? Write two to three sentences on each.
Manpower refers to the human resource of a country. The higher the population, the greater the manpower. The increased population can be a great asset if it is used properly and productively.
Steps to utilize manpower:
- Providing education and improving the standard of education enables the people of a country to gain appropriate skills and knowledge.
- Based on the skills, the manpower can be classified as skilled and unskilled sector and can be placed in various industries.
- Providing basic health facilities to all sections of labourers aid in increased productivity and prevents employees refraining from work due to health issues.
- In large scale sectors, many training programmes can be conducted to improve the talent hidden in the employees.
The number of females per thousand men is referred to as the Sex ratio. Generally, in a country like India, the sex ratio is very poor.
Steps to improve sex ratio:
- Educating and creating awareness among the masses about the role of women in the development of a country may improve the sex ratio.
- Making sure that the laws against female foeticide and infanticide are followed properly.
- Preventing child marriages to avoid the mortality of young girls.
- Granting equal rights to women and making them enjoy equal opportunities on par with men.
- Increasing the self-esteem of women through education, employment and independence.
Increasing population is always a concern and poses a serious threat to the economic development of the country.
Steps to control population:
- Making people, especially the rural masses understand the problems faced due to increased population.
- Adopting various birth control methods.
- Providing education and eradication of poverty which indirectly helps in population control. An educated person can understand the consequences of having too many children. Similarly, if poverty is eradicated, there will be an end to child labour. Child labour persuades a poor man to have children and send them to jobs to earn for himself and his family.
These are some of the steps that can be taken to utilize manpower, improve the sex ratio and control the population of a country.
Example
If the proportion of dependent age groups increases in the composition of population, how will it affect the economy of a country?
- If the proportion of dependent age groups increases in the composition of population, it will have an adverse effect on the economy of a country.
- The reason is if the working population is less, the economic activities will reduce and will have a direct impact on the economic growth and development of that nation.
- The production will decrease in comparison to consumption leading to inflation also the per capita income and GDP will decrease.
- Export will reduce and imports will increase.
- The proportion of the working population will increase, slowing down the pace of development.