Topics
Field Visit
Location and Extent
Physiography and Drainage
- Physical Divisions of India
- The North Indian Mountains
- The Himalayas
- North Indian Plains
- The Peninsular Indian Plateau
- The Indian Coastal Plains
- The Indian Islands
- Physiography of Brazil
- Brazilian Highlands
- The Great Escarpment in Brazil
- Coastline of Brazil
- Brazilian Plains
- Brazilian Island
- Drainage of Brazil
- Drainage Systems of India
- Himalayan Rivers
- Peninsular Rivers
Climate
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Population
Human Settlements
Economy and Occupations
Tourism, Transport and Communication
Geography - Physical Divisions of India
Identification of Physical divisions
- Identification of Physical Divisions
Geography - North Indian Mountains
Himalayas
Associated mountains
- Concept of Associated Mountains
Geography - North Indian Plain Region
Deserts
- Desert
Western Plains
- Concept of Western Plains
Central Plains
- Concept on Central Plains
Delta region
- Concept of Delta Region
Eastern Plains
- Concept of Eastern Plains
Geography - Peninsular Plateau Region
Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
- Concept for Chhotta Nagpur Plateau
Malwa Plateau
- Concept on Malwa Plateau
Maharashtra Plateau
- Concept for Maharashtra Plateau
Karnataka Plateau
- Concept for Karnataka Plateau
Telangana Plateau
- Concept for Telangana Plateau
Geography - Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
Eastern Ghats
- Concept on Eastern Ghats
Sahyadries
- Concept on Sahyadries
Geography - Coastal Region
- Geography - Coastal Region
Eastern coastal plain
- Coastal Region - Eastern Coastal Plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Western coastal plain
- Concept for Western Coastal Plain
Geography - Indian Islands
- Geography - Indian Islands
Eastern Islands
- Indian Islands - Eastern Islands
Western Islands
- Indian Islands - Western Islands
Geography - Practical 1
Cartography
- Concept on Cartography
Geography - Practical 2
Two dimensional diagrams
- Two Dimensional Shapes
One dimensional diagrams
- Concept on One Dimensional Diagrams
Economics - Introduction of an Economy
Introduction of an Economy
- Economy
- Types of Economy
- Main Features of Economy
Economics - Basic problems of an economy solution
Solutions
- Concept for Capitalism
- Concept for Socialism
- Mixed Economy
Problems
- Introduction of Basic Problems of an Economy
- Problems- for Whom to Produce
- Problem - How Much to Produce
- Problem - by Whom to Produce
Economics - Inflation
Introduction
- Introduction of Inflation
Effects of inflation
- Effects of Inflation
Measures of Inflation
- Measures of Inflation
Causes of inflation
- Causes of Inflation
Economics - Public distribution system and consumer protection
- Measures of Inflation
Public Distribution system - meaning and explanation
- Public Distribution System - Meaning and Explanation
Introduction
- Introduction of Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Objectives of Public Distribution system
- Objectives of Public Distribution System
Remedial Measures
- Remedial Measures Public Distribution System and Consumer Protection
Consumer Protection
- Consumer Protection - Rights and Duties of Cunsumer, Food Adulteration
Drawbacks of Public Distribution system
- Drawbacks of Public Distribution System
Progress of Public Distribution system
- Progress of Public Distribution System
Definition
- Population Distribution: The term 'Population Distribution' refers to the way the people are spaced over the earth’s surface.
Notes
Distribution of the Population in India:
- The term 'Population Distribution' refers to the way the people are spaced over the earth’s surface.
- Because of the wide variation in resource availability, India's population distribution is quite uneven.
- The population is mostly concentrated in industrialised areas and good agricultural lands. High mountains, arid lands, densely forested areas, and some remote corners, on the other hand, are sparsely populated, and some are even uninhabited.
- The major factors influencing population distribution in our country are terrain, climate, soil, water bodies, mineral resources, industries, transportation, and urbanisation, religion, culture, political issues, economy, human settlements, employment opportunity etc.
 |
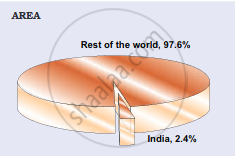 |
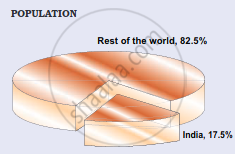
| India’s Share of World’s Area and Population | |
- India's population was 1,210.6 million in March 2011, accounting for 17.5% of the world's population. These 1.21 billion people are dispersed unevenly across our country's vast area of 3.28 million square kilometres, which accounts for 2.4% of the world's area.
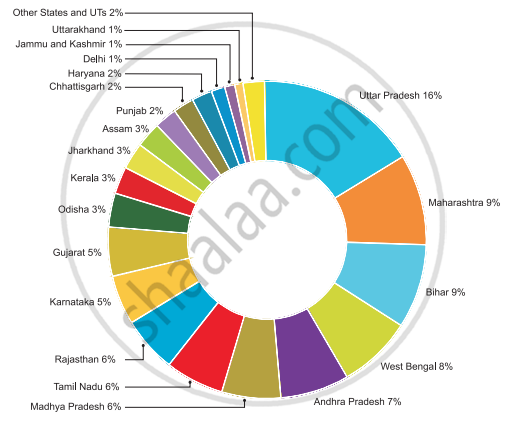
- With a population of 199.5 million, Uttar Pradesh is the most populous state in the country, followed by Maharashtra (112.3 million), Bihar (103.8 million), West Bengal (91.3 million), and the combined Andhra Pradesh and Telangana (84.6 million). These five states are home to roughly half of the country's population.
- Sikkim is India's least populous state (0.61 million). Rajasthan, India's largest state by area, has only 5.5% of the total population.
- Among Union territories Delhi is the most populous with population of 16.75 million whereas Lakshadweep has a population of only 64,429 people.
|
Distribution of Population |
Example
Study the maps and answer the questions.
 |
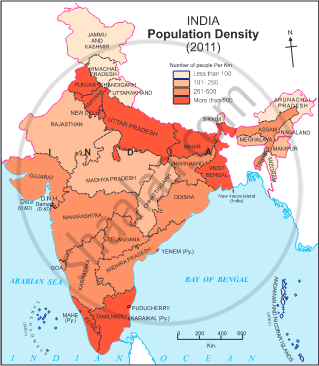 |
- States with highest population density.
- States with lowest population density.
- On the basis of the maps given above, classify the distribution population in India in the following table.
Sr. No. Population Density
(per sq. km.)Name of the States/Union
Territories1 less than 100 2 101 to 250 3 251 to 500 4 more than 501 - Correlate the climate and physiography of India with its population distribution and write a note on it.
- West Bengal, Bihar, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Mizoram.
-
Sr. No. Population Density
(per sq. km.)Name of the States/Union
Territories1 less than 100 Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim. 2 101 to 250 Meghalaya, Manipur, Nagaland, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chattisgarh. 3 251 to 500 Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha, Jharkhand, Assam, Tripura. 4 more than 501 West Bengal, Bihar, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala and Tamil Nadu, Delhi, Chandigarh, Puducherry, Diu, Daman, Dadra Nagar, Haveli, Andaman and Nicobar Islands. - (i) Climate and population distribution are closely inter-related.
(ii) Temperature and rainfall are the two elements of climate which greatly influence the population distribution.
(iii) Dense population is found in regions with mild climate and moderate rainfall.
E.g. the northern plain as well as the coastal plains of India
(iv) Places with heavy rainfall, inaccessibility and dense forests have low population.
E.g. northeastern states in India
(v) The snow-covered regions due to extremely cold climatic conditions have less population.
E.g. the northernmost part of Jammu and Kashmir
(vi) In certain regions, due to less rainfall and extreme climatic conditions population is sparse.
E.g. Westernmost part of India in the Thar desert, Rajasthan
Example
What could be the reason of uneven distribution of population in India?
- Geographical factors like soil fertility, pleasant climate, water accessibility, and topography affect the distribution of the population.
- Socioeconomic factors like economic opportunities, literacy rate, and accessibility to transportation and communication facilities affect the distribution of the population in India.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.