Topics
Basic Concepts in Geometry
Angles
Integers
Operations on Fractions
- Concept of Fractions
- Conversion Between Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers
- Addition of Fraction
- Subtraction of Fraction
- Fraction on the Number Line
- Multiplication of Fraction
- Concept of Reciprocal or Multiplicative Inverse
- Division of Fractions
Decimal Fractions
Bar Graphs
Symmetry
Divisibility
HCF-LCM
Equations
Ratio and Proportion
Percentage
Profit –Loss
Banks and Simple Interest
Triangles and Their Properties
Quadrilaterals
Geometrical Constructions
- Perpendicular Lines
- Drawing a Perpendicular to a Line at a Point on the Line
- Drawing a perpendicular to a line from a point outside the line
- The Perpendicular Bisector
- Drawing the perpendicular bisector of a segment using a compass.
- Carl Gauss’s Clever Trick
Three Dimensional Shapes
Concept of Comparing Integers
1. Use of Inequality Symbols
- Inequality symbols are used to indicate the order or comparison between numbers.
- The symbol
<means "is less than," while the other>means "is greater than."
2. Ordering of Whole Numbers
- When a number
ais to the left of another numberbOn the number line, we write:a < b(Read as: a is less than b). - When a number
ais to the right of another numberb, we write:a > b(Read as: a is greater than b).
3. Ordering of Integers
- Integers, like whole numbers, can also be compared using inequality symbols.
- The number line is a helpful tool for comparing and ordering integers.
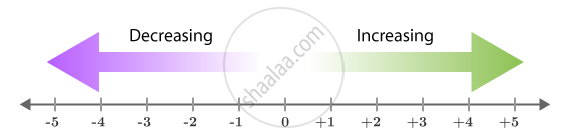
4. Direction and Value on a Number Line
- As we move from left to right, the value of the numbers increases.
- As we move from right to left, the value of the numbers decreases.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
