Topics
Introducing Biology
- Growth of Biology
- Branches of Biology
- Applied Biology
- Study of Biology Helps Us in Many Ways
- Study of Biology Helps Us in Many Ways
Basic Biology
Cell : the Unit of Life
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- The Invention of the Microscope and the Discovery of Cell
- Cell Theory
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
- Structure of the Cell
- Plasma Membrane
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Ribosomes - "The sites of protein synthesis"
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Centrosome and Centrioles
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Protoplasm
- Every Activity of a Living Organism is the Outcome of Cellular Activity
Tissues : Plant and Animal Tissues
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Plant Tissues
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Protective Tissue
- Simple Permanent Tissues (Supporting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Xylem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Phloem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Animal Tissues
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
Flowering Plants
The Flower
Pollination and Fertilization
- Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Artificial Pollination
- Fertilization in Plants
- Fertilization Process
Plant Physiology
Seeds - Structure and Germination
- The Seed
- Classification and Structure of Seeds
- Structure of a Dicotyledonous Seed
- Structure of Monocotyledonous Seed
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Some Experiments on Germination
- Germination in Some Common Seeds
- The Seedling
Respiration in Plants
- Respiration
- Phases of Respiration: Glycolysis
- Phases of Respiration: Electron Transport System (Ets) and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Phases of Respiration: Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle Or Kreb’s Cycle)
- Phases of Respiration: Pyruvate Oxidation (Link Reaction)
- Phases of Respiration: Fermentation
- Formation of ATP
- Respiration Vs. Burning (Combustion)
- Respiration in Plant
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Experiments on Respiration in Plants
- Respiration and Photosynthesis
- Organs of Respiratory Exchange
Diversity in Living Organisms / Eco Systems
Five Kingdom Classification
- Biodiversity
- Biological Classification
- Biological Classification
- Concept of Species
- Two Kingdom Classification
- Three Kingdom Classification
- Four Kingdom Classification
- Five Kingdom Classification
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Fungi
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Animalia
- Differences Between Plantae (Plants) and Animalia (Animals)
- Kingdom Plantae: Thallophyta (Algae)
- Division II- Bryophytes
- Division III- Pteridophytes
- Division I-Gymnosperms
- Division II- Angiosperms
- Phylum: Porifera
- Phylum: Cnidaria/Coelenterata
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes
- Invertebrate: Phylum Nematoda
- Phylum: Annelida
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Phylum: Mollusca
- Phylum: Echinodermata
- Chordata: Vertebrata
- Invertebrata and Vertebrata
- Nomenclature
- Taxonomy and Systematics
Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi
- Bacteria
- Life Processes in Bacteria
- Useful Role of Bacteria in Medicine
- Useful Role of Bacteria in Agriculture
- Useful Role of Bacteria in Industry
- Harmful Role of Bacteria
- Fungi
- Economic Importance of Fungi
- Structure and Function of an Ecosystem
Human Anatomy and Physiology
Nutrition
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Food and Its Types
- Component of Food
- Carbohydrates
- Fats (Lipids)
- Proteins
- Component of Food: Minerals
- Vitamin and Minerals
- Water
- A Balanced Diet
- Deficiency Diseases
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Carbohydrates
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Fats
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Proteins
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Vitamin
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Minerals
Digestive System
- Need for Digestive System
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- The Salivary Glands
- Swallowing and Peristalsis
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Pancreas
- Absorption of Food
- The Large Intestine
- Assimilation of Food
- Liver
- Experiments on Digestion
- Test for Carbohydrates/Starch
- Test for Protein
- Test for Fats
Skeleton - Movement and Locomotion
Skin - "The Jack of All Trades"
- The Skin
- Structure of the Skin
- The Skin Proper
- Derivation of the Skin
- Skin and Heat Regulation of Body
The Respiratory System
- Respiration
- Respiration
- Formation of ATP
- Human Respiratory System
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Parts of Respiration
- Human Respiratory System
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Capacities of the Lungs
- Inspired Air Vs. Expired Air
- Hypoxia and Asphyxiation
- Experiments on Breathing and Respiration
Health and Hygiene
Hygiene - [A Key to Healthy Life]
- Health
- Hygiene
- Types of Hygiene: Personal Hygiene
- Types of Hygiene: Public Hygiene (Community)
- Vector Borne Diseases
- Control of Disease Carriers (Vectors)
- Contamination of Water and Water Borne Diseases
- Waterborne Diseases Caused by Bacteria
- Waterborne Diseases Caused by Virus
- Protozoan Diseases
Diseases : Cause and Control
Aids to Health
- Health
- Types of Hygiene: Personal Hygiene
- Types of Hygiene: Public Hygiene (Community)
- Immunity
- Defence System in Our Body: Local Defence System
- Defence System in Our Body: Immune System
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Antitoxins
- Antiseptics and Disinfectants
- Antibiotics
- Sulphonamide Group of Medicines
Health Organisation
- Common Health Problems in India
- Categories of Health Organisation
- International Bodies: Red Cross
- International Bodies: WHO (World Health Organisation)
Waste Generation and Management
- Waste and Its Categories
- Methods of Safe Disposal of Waste
Vegetative Propagation
Biotechnology Applications
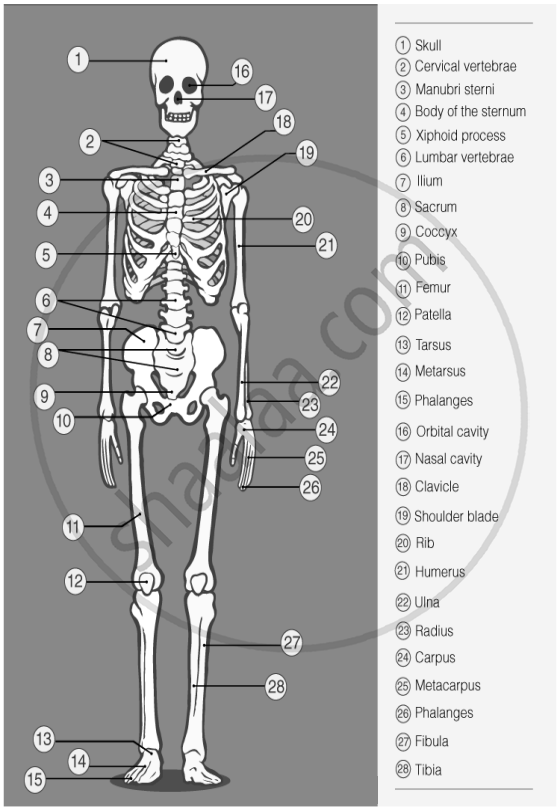
- Introduction of The Human Skeleton System
- Function of Human Skeleton
- Parts of the Skeleton
- Structure of a Bone
Introduction of Human Skeleton System:
The skeletal system is the framework of the body made of bones and connective tissues. It protects and supports the body’s organs and tissues. The human skeleton has 206 bones. The skeletal system is made up of bones and cartilage. It has two important functions:
- Supports the body by giving it shape and strength.
- Facilitates movement by helping the body move.
Each bone is a living part of the body made up of cells, protein fibers, and minerals. The skeleton acts like a scaffold, providing support and protection for soft tissues like muscles and organs.
Functions of the Skeletal System:
1. Gives shape and support to our body.
2. Protects internal organs:
- The skull protects the brain.
- The rib cage protects the heart and lungs.
- The backbone protects the spinal cord.
3. Allows movement of different body parts by working with muscles.
4. Bone marrow inside hollow bones makes blood cells.
Parts of the Skeleton:
1. Skull
The skull acts like a helmet to protect the brain. It supports and protects the face and brain. The skull is made up of 22 bones that are joined together and do not move.
2. Rib cage
The rib cage protects the heart and lungs. It has 24 ribs arranged in 12 pairs. The rib cage has three main functions:
- Protection of organs.
- Support for the upper body.
- Helps in breathing (respiration).
The sternum is a long, flat bone in the front of the rib cage.
3. Backbone
The backbone surrounds and protects the spinal cord. It runs from the skull to the pelvis. It supports the body’s weight and helps distribute it evenly. The backbone has an "S" shape when viewed from the side, which helps balance the body.
4. Limbs
Limbs include arms (upper limbs) and legs (lower limbs). They help us do many activities, like walking, running, and climbing. Arms and legs are attached to the torso, allowing us to move from one place to another.
Key components of the skeletal system:
- Bones: Hard structures that make up the skeleton and give the body support and shape.
- Joints: Places where two bones meet, allowing the body to move.
- Cartilage: Soft, flexible tissue that cushions bones and allows smooth movement in joints.
- Ligaments: Strong tissues that connect bones to other bones and help hold joints together.
- Tendons: Tough tissues that connect muscles to bones, helping in movement.
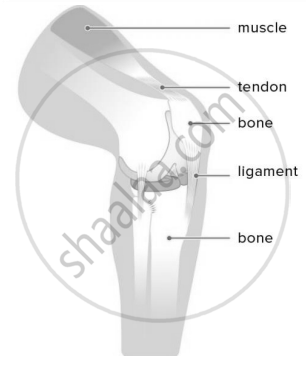
| Cartilage | Tendons | Ligaments |
|---|---|---|
| Tough | Attaches bone to muscle | Attaches bone to bone |
| Flexible | Sturdy | Elastic |
| At the end of the bones | Non-elastic | Stabilize |
| Cushions | Size changes depending on the muscle | Made of many fibres |
| Anchor | Strong |
5. Joints
There are two kinds of joints:
1. Immovable Joints: Also called fixed joints, these joints do not allow any movement between bones. The bones are interlocked and held together by connective tissue or are fused together. For example: Joints in the skull and ribs.
2. Movable Joints: Most joints in the body are freely movable. The ends of the bones in these joints are covered with cartilage, which provides a smooth surface for easy movement. Examples of movable joints:
- Ball-and-socket: Found in shoulders and hips, allowing a wide range of movement.
- Pivot joint: Allows rotation, like in the neck.
- Hinge joint: Works like a door hinge, allowing movement in one direction, like in the elbows and knees.
- Gliding joint: Allows bones to slide over each other, like in the wrists.

Structure of a bone:
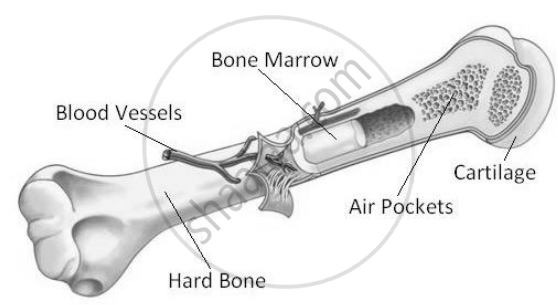
Bones have a hard outer layer called cortical (compact) bone, which is strong and tough. Inside the bone, there is a spongy inner layer called trabecular (cancellous) bone, which is lighter.
- Bones have their own blood supply and nerves, which help them grow and repair themselves as we age.
- Bones are made of calcium, phosphorus, and collagen (a fibrous substance), making them strong but lightweight because they are hollow inside.
- Bone marrow, found inside bones, produces red blood cells.
- A child is born with 300 soft bones, which fuse together as the child grows, leaving 206 bones in an adult.
- The smallest bone in the human body is the stape, found inside the ear.
