| Muscle Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Voluntary Muscles | Muscles we can control, like those in arms, legs, and face | Muscles used for talking, running, and eating |
| Involuntary Muscles | Muscles that work automatically without our control | Heart, stomach, and intestines |
Topics
Introducing Biology
- Growth of Biology
- Branches of Biology
- Applied Biology
- Study of Biology Helps Us in Many Ways
- Study of Biology Helps Us in Many Ways
Basic Biology
Cell : the Unit of Life
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- The Invention of the Microscope and the Discovery of Cell
- Cell Theory
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
- Structure of the Cell
- Plasma Membrane
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Ribosomes - "The sites of protein synthesis"
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Centrosome and Centrioles
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Protoplasm
- Every Activity of a Living Organism is the Outcome of Cellular Activity
Tissues : Plant and Animal Tissues
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Plant Tissues
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Protective Tissue
- Simple Permanent Tissues (Supporting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Xylem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissue: Phloem Structure and Function (Conducting Tissue)
- Animal Tissues
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
Flowering Plants
The Flower
Pollination and Fertilization
- Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Artificial Pollination
- Fertilization in Plants
- Fertilization Process
Plant Physiology
Seeds - Structure and Germination
- The Seed
- Classification and Structure of Seeds
- Structure of a Dicotyledonous Seed
- Structure of Monocotyledonous Seed
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Some Experiments on Germination
- Germination in Some Common Seeds
- The Seedling
Respiration in Plants
- Respiration
- Phases of Respiration: Glycolysis
- Phases of Respiration: Electron Transport System (Ets) and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Phases of Respiration: Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle Or Kreb’s Cycle)
- Phases of Respiration: Pyruvate Oxidation (Link Reaction)
- Phases of Respiration: Fermentation
- Formation of ATP
- Respiration Vs. Burning (Combustion)
- Respiration in Plant
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Experiments on Respiration in Plants
- Respiration and Photosynthesis
- Organs of Respiratory Exchange
Diversity in Living Organisms / Eco Systems
Five Kingdom Classification
- Biodiversity
- Biological Classification
- Biological Classification
- Concept of Species
- Two Kingdom Classification
- Three Kingdom Classification
- Four Kingdom Classification
- Five Kingdom Classification
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Fungi
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Animalia
- Differences Between Plantae (Plants) and Animalia (Animals)
- Kingdom Plantae: Thallophyta (Algae)
- Division II- Bryophytes
- Division III- Pteridophytes
- Division I-Gymnosperms
- Division II- Angiosperms
- Phylum: Porifera
- Phylum: Cnidaria/Coelenterata
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes
- Invertebrate: Phylum Nematoda
- Phylum: Annelida
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Phylum: Mollusca
- Phylum: Echinodermata
- Chordata: Vertebrata
- Invertebrata and Vertebrata
- Nomenclature
- Taxonomy and Systematics
Economic Importance of Bacteria and Fungi
- Bacteria
- Life Processes in Bacteria
- Useful Role of Bacteria in Medicine
- Useful Role of Bacteria in Agriculture
- Useful Role of Bacteria in Industry
- Harmful Role of Bacteria
- Fungi
- Economic Importance of Fungi
- Ecosystem
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
Human Anatomy and Physiology
Nutrition
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Food and Its Types
- Component of Food
- Carbohydrates
- Fats (Lipids)
- Proteins
- Component of Food: Minerals
- Vitamin and Minerals
- Water
- A Balanced Diet
- Deficiency Diseases
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Carbohydrates
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Fats
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Proteins
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Vitamin
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Minerals
Digestive System
- Need for Digestive System
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- The Salivary Glands
- Swallowing and Peristalsis
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Pancreas
- Absorption of Food
- The Large Intestine
- Assimilation of Food
- Liver
- Experiments on Digestion
- Test for Carbohydrates/Starch
- Test for Protein
- Test for Fats
Skeleton - Movement and Locomotion
Skin - "The Jack of All Trades"
- The Skin
- Structure of the Skin
- The Skin Proper
- Derivation of the Skin
- Skin and Heat Regulation of Body
The Respiratory System
- Respiration
- Respiration
- Formation of ATP
- Human Respiratory System
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Parts of Respiration
- Human Respiratory System
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Capacities of the Lungs
- Inspired Air Vs. Expired Air
- Hypoxia and Asphyxiation
- Experiments on Breathing and Respiration
Health and Hygiene
Hygiene - [A Key to Healthy Life]
- Health
- Hygiene
- Types of Hygiene: Personal Hygiene
- Types of Hygiene: Public Hygiene (Community)
- Vector Borne Diseases
- Control of Disease Carriers (Vectors)
- Contamination of Water and Water Borne Diseases
- Waterborne Diseases Caused by Bacteria
- Waterborne Diseases Caused by Virus
- Protozoan Diseases
Diseases : Cause and Control
Aids to Health
- Health
- Types of Hygiene: Personal Hygiene
- Types of Hygiene: Public Hygiene (Community)
- Immunity
- Defence System in Our Body: Local Defence System
- Defence System in Our Body: Immune System
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Antitoxins
- Antiseptics and Disinfectants
- Antibiotics
- Sulphonamide Group of Medicines
Health Organisation
- Common Health Problems in India
- Categories of Health Organisation
- International Bodies: Red Cross
- International Bodies: WHO (World Health Organisation)
Waste Generation and Management
- Waste and Its Categories
- Methods of Safe Disposal of Waste
Vegetative Propagation
Biotechnology Applications
- Introduction
- Types of Muscles
- Activity
Introduction:
Muscles are bundles of fibres that can contract and relax as required. The muscular system helps our body move and carry out essential functions. Different muscles work either voluntarily (under our control) or involuntarily (without our control). Tendons connect muscles to bones, and when they contract, they move our bones at the joints. We use muscles for various movements like talking, laughing, walking, jumping, throwing, etc.
Types of Muscles:
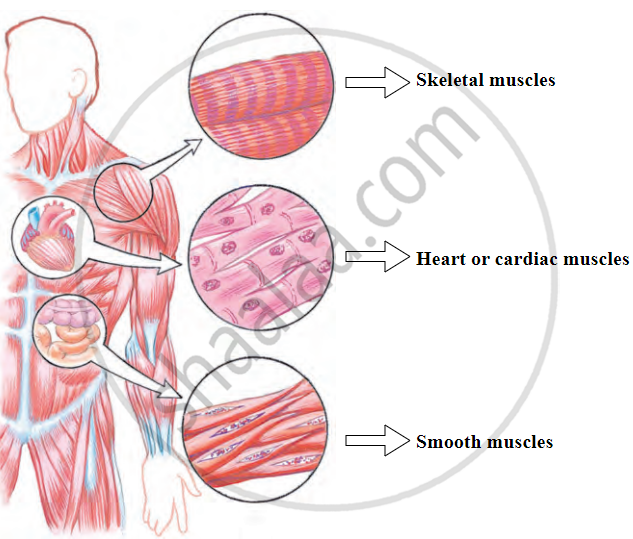
Muscles in the human body
Activity
Activity: To observe how muscles in the arm contract and relax during movement.
- Hold your arm straight at the elbow (180°).
- Bend the arm at the elbow to 90°.
- Touch your shoulder with the fingers of the same arm.
- Notice which muscles contract and which relax during each movement.
During these movements:
- The biceps (front upper arm) muscle contracts when the arm bends.
- The triceps (back upper arm) muscle relaxes.
- The triceps contract when the arm is straightened, and the biceps relax.
- Muscles always work in pairs: one group contracts while the other relaxes to enable smooth movement. This coordinated action allows us to perform various body functions effectively.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
