Topics
Plant Life
The Leaf
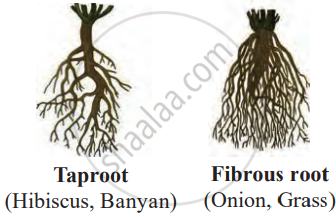
- Root
- Types of Root
- Shoot System
- Stem
- The Structure of a Plant
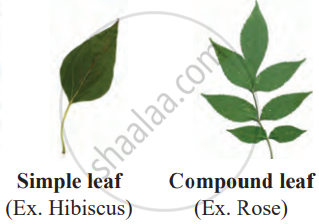
- Types of Leaf
- Autotrophic Plants
- Insectivorous Plants
- Significance of Photosynthesis
- Transpiration
- Significance of Transpiration
- Modifications of Leaf
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Flower
The Flower
- Flower
- Structure of a Bisexual Flower
- Types of Flower
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Fertilization Process
- Fruit
- The Seed
- Classification and Structure of Seeds
- Structure of a Dicotyledonous Seed
- Structure of Monocotyledonous Seed
- Formation of Seed and Fruit
- Germination in Some Common Seeds
The Cell
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- The Invention of the Microscope and the Discovery of Cell
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Cell Theory
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Structure of the Cell
- Plasma Membrane
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Cell Division: an Essential Life Process
- Protoplasm
Human Body
Digestive System
- Food and Its Types
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Component of Food
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- Tongue
- The Salivary Glands
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Absorption of Food
- The Large Intestine
- Assimilation of Food
- The Aching Tooth
- Oral Health
Respiratory System
Circulatory System
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Blood
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Functions of Blood
- Human Heart
- Blood Vessels
- Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart)
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP"
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Blood Transfusion and Blood Groups (ABO and Rh system)
- Keeping the Heart Healthy
Health and Hygiene
Habitat and Adaptation
- Habitat
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Adaptations of Plants
- Adaptation in Aquatic Plants (Hydrophytes)
- Adaptation in Desert Plants (Xerophytes)
- Adaptation in plants of snowy regions
- Adaptations in Seeds for Transport Through Air
- Adaptation in Animals
- Adaptation in Aquatic Animals
- Adaptation in Desert Animals
- Adaptation in Mountain Animal
- Adaptation in Aerial Animals
The Structure of a Plant
Plants have different parts, and each part has a special role. The Two Main Parts of a Plant:
- Stem: This part of the plant grows above the ground.
- Root: This part grows below the ground.
The roots, stems, and leaves are the most important parts of a plant. From time to time, plants also produce flowers that help in reproduction. These flowers later turn into fruits with seeds that grow into new plants.
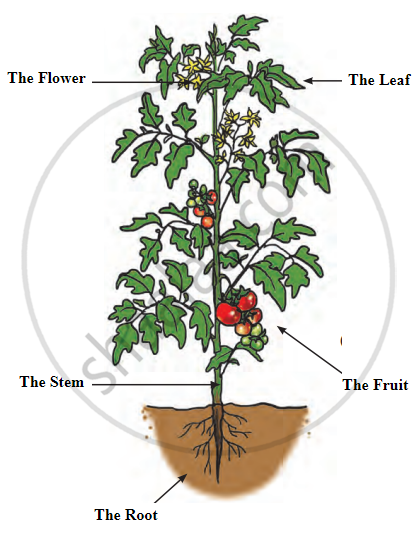
The structure of a plant
Plant Parts and Their Functions:
| Plant Part | Structure/Type | Main Functions | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flower | Colorful, fragrant, with stalk (long or short) | Helps in reproduction; produces seeds | Attracts pollinators |
| Leaf | Flat; Simple or Compound | Performs photosynthesis; makes food | Uses sunlight, water, and CO₂ |
| Stem | Varies in height and thickness | Supports plant; transports water, nutrients, and food | Stores food in some plants; helps in reproduction |
| Fruit | Various shapes and sizes; contains seeds | Houses seeds; aids in reproduction | Examples: beans, pea pods |
| Root | Grows underground; Taproot or Fibrous | Anchors plant; absorbs and transports water and nutrients | Stores food in some plants like carrots and radish |
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
