Topics
Number Systems
Real Numbers
Algebra
Polynomials
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Introduction to linear equations in two variables
- Graphical Method
- Substitution Method
- Elimination Method
- Cross - Multiplication Method
- Equations Reducible to a Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Consistency of Pair of Linear Equations
- Inconsistency of Pair of Linear Equations
- Algebraic Conditions for Number of Solutions
- Simple Situational Problems
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Relation Between Co-efficient
Quadratic Equations
- Quadratic Equations
- Solutions of Quadratic Equations by Factorization
- Solutions of Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
- Nature of Roots of a Quadratic Equation
- Relationship Between Discriminant and Nature of Roots
- Situational Problems Based on Quadratic Equations Related to Day to Day Activities to Be Incorporated
- Application of Quadratic Equation
Arithmetic Progressions
Coordinate Geometry
Lines (In Two-dimensions)
Constructions
- Division of a Line Segment
- Construction of Tangents to a Circle
- Constructions Examples and Solutions
Geometry
Triangles
- Similar Figures
- Similarity of Triangles
- Basic Proportionality Theorem (Thales Theorem)
- Criteria for Similarity of Triangles
- Areas of Similar Triangles
- Right-angled Triangles and Pythagoras Property
- Similarity of Triangles
- Application of Pythagoras Theorem in Acute Angle and Obtuse Angle
- Triangles Examples and Solutions
- Concept of Angle Bisector
- Similarity of Triangles
- Ratio of Sides of Triangle
Circles
Trigonometry
Introduction to Trigonometry
- Trigonometry
- Trigonometry
- Trigonometric Ratios
- Trigonometric Ratios and Its Reciprocal
- Trigonometric Ratios of Some Special Angles
- Trigonometric Ratios of Complementary Angles
- Trigonometric Identities
- Proof of Existence
- Relationships Between the Ratios
Trigonometric Identities
Some Applications of Trigonometry
Mensuration
Areas Related to Circles
- Perimeter and Area of a Circle - A Review
- Areas of Sector and Segment of a Circle
- Areas of Combinations of Plane Figures
- Circumference of a Circle
- Area of Circle
Surface Areas and Volumes
- Surface Area of a Combination of Solids
- Volume of a Combination of Solids
- Conversion of Solid from One Shape to Another
- Frustum of a Cone
- Concept of Surface Area, Volume, and Capacity
- Surface Area and Volume of Different Combination of Solid Figures
- Surface Area and Volume of Three Dimensional Figures
Statistics and Probability
Statistics
Probability
Internal Assessment
Notes
Recall that two angles are said to be complementary if their sum equals 90°. In
∆ABC, right-angled at B.
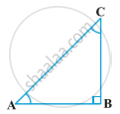
Let ∠A= θ
In ∆ABC,
∠A+∠B+∠C= 180° (Angle sum property)
θ+ 90°+∠C= 180°
∠C= 180°-90°-θ
∠C= (90°-θ)
Trigonometric ratios-
1) sin(90°-θ)= `"AB"/"AC"`= cosθ
2) cos(90°-θ)= `"BC"/"AC"`= sinθ
3)tan(90°-θ)= `"AB"/"BC"`= cotθ
4)cot(90°-θ)= `"BC"/"AB"`= tanθ
5)sec(90°-θ)= `"AC"/"BC"`= cosecθ
6)cosec(90°-θ)= `"AC"/"AB"`= secθ
Example: Evaluate `"sin18°"/"cos72°"`
solutioin- `"sin(90°-72°)"/"cos72°"`
sin(90°-θ)= cosθ= `"cos72°"/"cos72°"= 1`
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Video Tutorials
Shaalaa.com | Trigonometry Part 2
to track your progress
