Topics
Number Systems
Real Numbers
Algebra
Polynomials
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Introduction to linear equations in two variables
- Graphical Method
- Substitution Method
- Elimination Method
- Cross - Multiplication Method
- Equations Reducible to a Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Consistency of Pair of Linear Equations
- Inconsistency of Pair of Linear Equations
- Algebraic Conditions for Number of Solutions
- Simple Situational Problems
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Relation Between Co-efficient
Quadratic Equations
- Quadratic Equations
- Solutions of Quadratic Equations by Factorization
- Solutions of Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
- Nature of Roots of a Quadratic Equation
- Relationship Between Discriminant and Nature of Roots
- Situational Problems Based on Quadratic Equations Related to Day to Day Activities to Be Incorporated
- Application of Quadratic Equation
Arithmetic Progressions
Coordinate Geometry
Lines (In Two-dimensions)
Constructions
- Division of a Line Segment
- Construction of Tangents to a Circle
- Constructions Examples and Solutions
Geometry
Triangles
- Similar Figures
- Similarity of Triangles
- Basic Proportionality Theorem (Thales Theorem)
- Criteria for Similarity of Triangles
- Areas of Similar Triangles
- Right-angled Triangles and Pythagoras Property
- Similarity of Triangles
- Application of Pythagoras Theorem in Acute Angle and Obtuse Angle
- Triangles Examples and Solutions
- Concept of Angle Bisector
- Similarity of Triangles
- Ratio of Sides of Triangle
Circles
Trigonometry
Introduction to Trigonometry
- Trigonometry
- Trigonometry
- Trigonometric Ratios
- Trigonometric Ratios and Its Reciprocal
- Trigonometric Ratios of Some Special Angles
- Trigonometric Ratios of Complementary Angles
- Trigonometric Identities
- Proof of Existence
- Relationships Between the Ratios
Trigonometric Identities
Some Applications of Trigonometry
Mensuration
Areas Related to Circles
- Perimeter and Area of a Circle - A Review
- Areas of Sector and Segment of a Circle
- Areas of Combinations of Plane Figures
- Circumference of a Circle
- Area of Circle
Surface Areas and Volumes
- Surface Area of a Combination of Solids
- Volume of a Combination of Solids
- Conversion of Solid from One Shape to Another
- Frustum of a Cone
- Concept of Surface Area, Volume, and Capacity
- Surface Area and Volume of Different Combination of Solid Figures
- Surface Area and Volume of Three Dimensional Figures
Statistics and Probability
Statistics
Probability
Internal Assessment
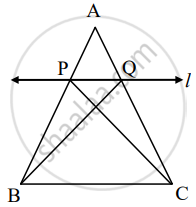
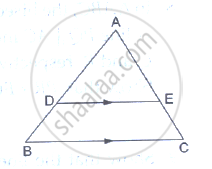
- Theorem: If a line parallel to a side of a triangle intersects the remaining sides in two distinct points, then the line divides the sides in the same proportion.
Notes
Theorem: If a line parallel to a side of a triangle intersects the remaining sides in two distinct points, then the line divides the sides in the same proportion.
Given: In D ABC line l || line BC and line l intersects AB and AC in point P and Q respectively
To prove: `"AP"/"PB"="AQ"/"QC"`
Construction: Draw seg PC and seg BQ
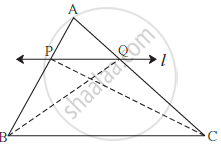
Proof: Δ APQ and Δ PQB have equal heights.
`therefore (A(triangle APQ))/(A(triangle PQB))="AP"/"PB"` .....................(I) (areas proportionate to bases)
`therefore (A(triangle APQ))/(A(triangle PQC))="AQ"/"QC"`................... (II) (areas proportionate to bases)
seg PQ is a common to base of Δ PQB and ΔPQC. seg PQ || seg BC,
hence Δ PQB and Δ PQC have equal heights.
`A(triangle PQB)=A(triangle PQC)` ................(III)
`(A(triangle APQ))/(A(triangle PQB))=(A(triangle APQ))/(A(triangle PQC))` .......... [from (I), (II) and (III)]
`therefore "AP"/"PB"="AQ"/"QC"` .......... [from (I) and (II)]