Topics
Food: Where Does It Come From?
- Food Variety
- Ingredients of Food
- Plant Sources
- Plant as Food (Plant Product)
- Animal Sources
- Animal Products used as Food
- Classification of Animal
- Food and Its Types
Science
Components of Food
- Food and Its Types
- What Do Different Food Items Contain?
- Test for Carbohydrates/Starch
- Test for Protein
- Test for Fats
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Component of Food
- Carbohydrates
- Fats (Lipids)
- Proteins
- Vitamin and Minerals
- Component of Food: Minerals
- A Balanced Diet
- Obesity and Its Prevention
- Deficiency Diseases
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Vitamin
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Minerals
Sorting Materials into Groups
Fibre to Fabric
- Fabrics
- Fibre
- Plant Fibres: Cotton
- Plant Fibre: Jute Fibre
- Fibre to Yarn to Fabric
- History of Clothing Material
Separation of Substances
- Mixture
- Types of Mixtures
- Separation of Mixtures
- Methods of Separation
- Handpicking Method
- Threshing Method
- Winnowing Method
- Sieving Method
- Sedimentation Method
- Decantation Method
- Filtration Method
- Evaporation Method
- Simple Distillation Method
- Solution
- Water - a Universal Solvent
- Components of Solutions
- Different Types of Solutions
- Saturated Solutions
Getting to Know Plants
- Plant Forms and Functions
- Classification of Plants
- Stem
- The Structure of a Plant
- Photosynthesis: Food-Making Process in Plants
- Process of Photosynthesis
- Transpiration
- Root
- Types of Root
- Flower
- Structure of a Bisexual Flower
Body Movements
- Human Body and Its Movements
- Joints and Its Classification
- Human Skeleton System
- The Human Skeleton: Appendicular Skeleton
- The Human Skeleton: Axial Skeleton
- Bone and Its Types
- Muscles and Its Types
- Muscular System
- Movement in Different Animals
Changes Around Us
- Changes-Physical and Chemical
- Classification of Change: Reversible and Irreversible Changes
- Classification of Change: Desirable and Undesirable Changes
- Classification of Change: Natural and Man-made Changes
- Classification of Change: Periodic and Non-periodic Changes
- Classification of Change: Slow and Fast Changes
- Classification of Change: Physical Changes
- Chemical Reaction
- Effect of Heat on Solid, Liquid and Gases
The Living Organisms - Characteristics and Habitats
- Biodiversity
- Habitat
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Structure and Function of an Ecosystem
- Adaptations of Plants
- Adaptation in Desert Plants (Xerophytes)
- Adaptation in plants of snowy regions
- Adaptation in Grassland Plants (Mesophytes)
- Adaptation in Aquatic Plants (Hydrophytes)
- Adaptation in Animals
- Adaptation in Desert Animals
- Adaptation in Mountain Animal
- Adaptation in Forest and Grassland Animals
- Adaptation in Aquatic Animals
- Characteristics of Organisms
Motion and Measurement of Distances
- Story of Transport
- Measurements
- Unit and Its Types
- Unit Systems
- International System of Units (Si System)
- Devices for Measuring Length
- Measuring the Length of a Curved Line
- Motion and Rest
- Types of Motion
- Multiple Motion
Light, Shadows and Reflections
Electricity and Circuits
- Electricity
- Electric cell
- A Bulb Connected to an Electric Cell
- Electric Circuit
- Electric Switch
- Conductors and Insulators
Fun with Magnets
- Magnet
- Uses of Magnets
- Discovery of Magnets
- Classification of Magnets
- Magnetic and Non-magnetic Materials
- Magnetic Pole
- Finding Directions with a Magnet
- Making a Magnet
- Magnetic Properties
- Demagnetization of a Magnet
Air Around Us
- Air Around Us
- Composition and Components of Air
- Importance of Air
- How is the Oxygen in the Atmosphere Replaced?
Water
Garbage In, Garbage Out
- Waste and Its Categories
- Disposal of Waste Water
- Solid Waste Management
- Vermicomposting
- Waste Separation Exercise
- Recycling of Paper
- Man-made Fibre: Plastics
- Harmful Effects of Plastics
- Recycling of Plastic
History of Clothing Material:
- The need for clothes: As humans evolved, their bodies changed. One important change was the reduction in body hair. Since they no longer had much body hair to protect themselves from the cold, heat, and rain, they needed something else. This is how the need for clothes arose.
- Early clothing: In the very early times, people didn’t wear clothes. Later, they started using bark and leaves from trees to cover their bodies. As humans learnt to hunt, they began using the skins of animals they hunted to keep warm and protect themselves.
- The development of cloth: As time passed, people discovered how to make yarn from materials like cotton and wool. Once they learnt how to spin yarn into cloth, they began using cotton cloth in many different ways, such as for making clothes, blankets, and more.
- Textile industry in Mumbai: Mumbai became an important centre for the textile industry (the industry that makes fabric and clothes). The humid weather in Mumbai made it easier to spin long threads used to make cloth. Textile mills (factories that produce fabric) in Mumbai became famous worldwide. Many people from all over India came to work in these textile mills. Over time, Mumbai also became a major centre for financial activity (business and trade) in India.
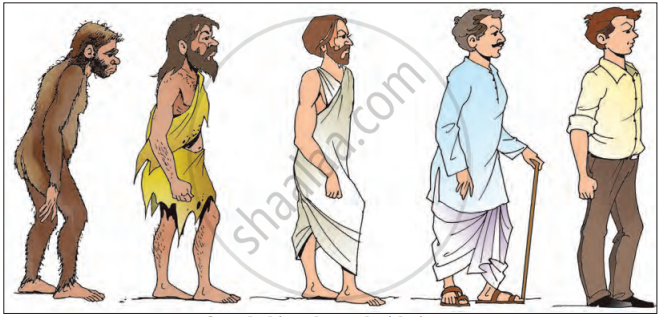
Our clothing changed with time
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
