A loudspeaker converts electrical signals into sound waves using electromagnetic principles. It consists of a coil, a permanent magnet, and a conical diaphragm. When an electric current flows through the coil, it interacts with the magnet's field, causing the diaphragm to vibrate. These vibrations create compressions and rarefactions in the air, generating sound waves that we can hear.
Topics
Living World and Classification of Microbes
Health and Diseases
Force and Pressure
- Force
- Types of Force: Contact Force
- Types of Force: Non-Contact Force
- Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
- Inertia and Mass
- Types of Inertia
- Thrust and Pressure
- Pressure on Solids
- Pressure of liquid
- Gas Pressure
- Atmospheric Pressure
- Buoyancy Force (Upthrust Force)
- Archimedes Principle
- Density of substance and Relative density
Current Electricity and Magnetism
Inside the Atom
Composition of Matter
- Matter (Substance)
- Characteristics of Particles (Molecules) of Matter
- States of Matter
- The Solid State
- The Liquid State
- The Gaseous State
- Elements
- Types of Element: Metals
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Type of Element: Metalloid
- Compound
- Types of Compound
- Mixture
- Types of Mixtures
- Solution
- Suspension Solution
- Colloidal Solution
- Molecular Formula of Compounds
- Valency
Metals and Nonmetals
- Types of Element: Metals
- Physical Properties of Metals
- Chemical Properties of Metal
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Physical Properties of Non-metal
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Chemical Properties of Non-metal
- Type of Element: Metalloid
- Uses of metals and nonmetals
- Nobel Metal
- Purity of Gold
- Corrosion of Metals
- Alloy
Pollution
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Air Pollution
- Prevention of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Water Pollution
- Prevention of Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution and its Causes
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Prevention of Soil Pollution
- Relationship of Soil Pollution with Air and Water Pollution
- Laws for Control, Regulation, and Prevention of Pollution by Indian Government
Disaster Management
Cell and Cell Organelles
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Structure of the Cell
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Plasma Membrane
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
Human Body and Organ System
- Human Body
- Human Organ System
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Human Respiratory System
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Human Heart
- Blood Vessels
- Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart)
- Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP"
- Blood
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Functions of Blood
- Blood Transfusion and Blood Groups (ABO and Rh system)
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Heart Related Conditions
Introduction to Acid and Base
Chemical Change and Chemical Bond
Measurement and Effects of Heat
Sound
Reflection of Light
Man Made Materials
Ecosystems
Life Cycle of Stars
- Introduction
- Parts of a Loudspeaker
- Working of a Loudspeaker
Introduction:
Parts of a Loudspeaker:
- Permanent Magnet: A fixed magnet inside the loudspeaker that creates a magnetic field.
- Coil: A wire wound around a core near the permanent magnet. When electric current flows through this coil, it produces a magnetic field.
- Conical Screen (Diaphragm): A lightweight, cone-shaped screen attached to the coil. This screen vibrates to generate sound waves.
- Input Signal: Electrical signals from a microphone or other audio source are sent to the loudspeaker.
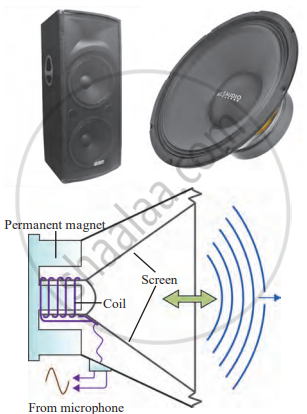
Internal construction of a loudspeaker
Working of a Loudspeaker:
- When an electric current flows through the coil, it produces a magnetic field around the coil. This magnetic field interacts with the field of the permanent magnet.
- Depending on the direction and strength of the current, the coil is either attracted to or repelled by the permanent magnet. This causes the coil to move back and forth.
- The coil is attached to the conical screen (diaphragm), so as the coil moves, the screen also moves back and forth.
- These vibrations generate sound waves in the surrounding air, similar to how a tuning fork produces sound.
- The frequency of the screen’s vibration determines the pitch of the sound and the amplitude of the screen’s vibration determines the loudness of the sound.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
