Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
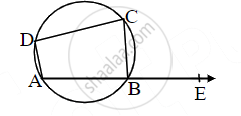
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. M (arc ABC) = 230°. Find ∠ABC, ∠CDA, and ∠CBE.
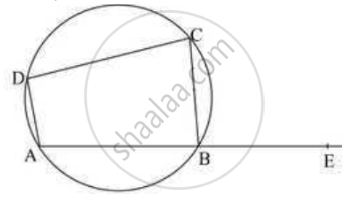
उत्तर

M(arc ABC) = 230°
M(arc ADC) = 360° - M(arc ABC) … complete circle is 360°
M(arc ADC) = 360° - 230° = 130°
∴ ∠AOC = 130°
The angle subtended by an arc at the point on a circle is equal to half of the angle subtended by the same arc at the center
Here arc ADC subtends ∠AOC at center and ∠ABC on a circle
∴ ∠ABC = (1/2) × ∠AOC
= 1/2 × 130°
= 65°
∴ ∠ABC = 65°
∠ABC + ∠CBE = 180° …linear pair of angles
∴ 65° + ∠CBE = 180°
∴ ∠CBE = 180° - 65° = 115°
∴ ∠CBE = 115°
∠CDA + ∠ABC = 180° …opposite pair of cyclic quadrilateral ABCD
∴ ∠CDA + 65° = 180°
∴ ∠CDA = 180° - 65° = 115°
∴ ∠CDA = 115°
Hence ∠ABC = 65°, ∠CDA = 115° and ∠CBE = 115°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A chord of a circle is equal to the radius of the circle. Find the angle subtended by the chord at a point on the minor arc and also at a point on the major arc.
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral whose diagonals intersect at a point E. If ∠DBC = 70°, ∠BAC is 30°, find ∠BCD. Further, if AB = BC, find ∠ECD.
If diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral are diameters of the circle through the vertices of the quadrilateral, prove that it is a rectangle.
Two circles intersect at two points B and C. Through B, two line segments ABD and PBQ are drawn to intersect the circles at A, D and P, Q respectively (see the given figure). Prove that ∠ACP = ∠QCD.

ABC and ADC are two right triangles with common hypotenuse AC. Prove that ∠CAD = ∠CBD.
Prove that a cyclic parallelogram is a rectangle.
Let the vertex of an angle ABC be located outside a circle and let the sides of the angle intersect equal chords AD and CE with the circle. Prove that ∠ABC is equal to half the difference of the angles subtended by the chords AC and DE at the centre.
Prove that the circle drawn with any side of a rhombus as diameter passes through the point of intersection of its diagonals.
The lengths of two parallel chords of a circle are 6 cm and 8 cm. If the smaller chord is at distance 4 cm from the centre, what is the distance of the other chord from the centre?
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in ∠DBC = 80° and ∠BAC = 40°. Find ∠BCD.
If the two sides of a pair of opposite sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are equal, prove that its diagonals are equal.
In the given figure, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which AC and BD are its diagonals. If ∠DBC = 55° and ∠BAC = 45°, find ∠BCD.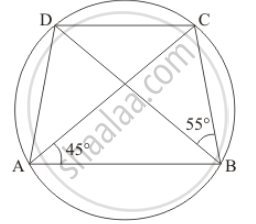
In the given figure, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which ∠BAD = 75°, ∠ABD = 58° and ∠ADC = 77°, AC and BD intersect at P. Then, find ∠DPC.

In a cyclic quadrilaterals ABCD, ∠A = 4x, ∠C = 2x the value of x is
In the figure, ▢ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. If m(arc ABC) = 230°, then find ∠ABC, ∠CDA, ∠CBE.
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral such that ∠A = 90°, ∠B = 70°, ∠C = 95° and ∠D = 105°.
ABCD is a parallelogram. A circle through A, B is so drawn that it intersects AD at P and BC at Q. Prove that P, Q, C and D are concyclic.
If bisectors of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD intersect the circle, circumscribing it at the points P and Q, prove that PQ is a diameter of the circle.
