Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
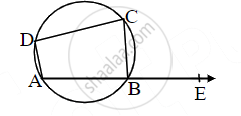
In the figure, ▢ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. If m(arc ABC) = 230°, then find ∠ABC, ∠CDA, ∠CBE.
उत्तर
m(arc ABC) = 230° .....(i) [Given]
∴ m(arc ADC) + m(arc ABC) = 360° .......[Degree measure of a circle is 360°]
∴ m(arc ADC) = 360° – m(arc ABC)
∴ m(arc ADC) = 360° – 230° .......[From (i)]
∴ m(arc ADC) = 130°
∠ABC = `1/2` m (arc ADC) ......[Inscribed angle theorem]
= `1/2 xx 130^circ`
= 65°
Now, ∠CDA = `1/2` m (arc ABC) ......[Inscribed angle theorem]
∴ ∠CDA = `1/2 xx 230^circ`
∴ ∠CDA = 115° ......(ii)
∠CBE = ∠CDA ......(iiii) [The exterior angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is equal to the interior opposite angle]
∴ ∠CBE = 115° .....[From (ii) and (iii)]
∴ ∠ABC = 65°, ∠CDA = 115°, ∠CBE = 115°.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Prove that "Opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary".
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral whose diagonals intersect at a point E. If ∠DBC = 70°, ∠BAC is 30°, find ∠BCD. Further, if AB = BC, find ∠ECD.
Let the vertex of an angle ABC be located outside a circle and let the sides of the angle intersect equal chords AD and CE with the circle. Prove that ∠ABC is equal to half the difference of the angles subtended by the chords AC and DE at the centre.
The lengths of two parallel chords of a circle are 6 cm and 8 cm. If the smaller chord is at distance 4 cm from the centre, what is the distance of the other chord from the centre?
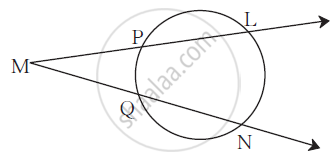
In the figure m(arc LN) = 110°,
m(arc PQ) = 50° then complete the following activity to find ∠LMN.
∠ LMN = `1/2` [m(arc LN) - _______]
∴ ∠ LMN = `1/2` [_________ - 50°]
∴ ∠ LMN = `1/2` × _________
∴ ∠ LMN = __________
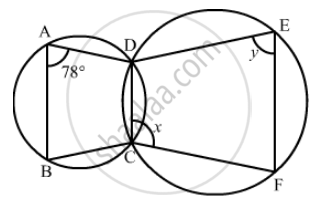
In the given figure, ∠BAD = 78°, ∠DCF = x° and ∠DEF = y°. Find the values of x and y.
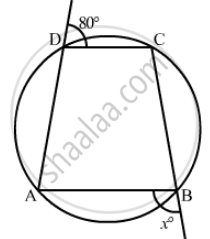
In the given figure, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. Find the value of x.
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in BC || AD, ∠ADC = 110° and ∠BAC = 50°. Find ∠DAC.
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in ∠DBC = 80° and ∠BAC = 40°. Find ∠BCD.
Prove that the centre of the circle circumscribing the cyclic rectangle ABCD is the point of intersection of its diagonals.
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which BA and CD when produced meet in E and EA = ED. Prove that AD || BC .
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which BA and CD when produced meet in E and EA = ED. Prove that EB = EC.
In the given figure, ABCD is a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle with centre O. CD is produced to E such that ∠AED = 95° and ∠OBA = 30°. Find ∠OAC.

PQRS is a cyclic quadrilateral such that PR is a diameter of the circle. If ∠QPR = 67° and ∠SPR = 72°, then ∠QRS =
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral such that AB is a diameter of the circle circumscribing it and ∠ADC = 140º, then ∠BAC is equal to ______.
If a pair of opposite sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are equal, prove that its diagonals are also equal.
ABCD is a parallelogram. A circle through A, B is so drawn that it intersects AD at P and BC at Q. Prove that P, Q, C and D are concyclic.
If bisectors of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD intersect the circle, circumscribing it at the points P and Q, prove that PQ is a diameter of the circle.
