Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Obtain an expression for the capillary rise or fall using the forces method.
उत्तर
- When a glass capillary tube is dipped into a liquid, then the liquid rises in the capillary against gravity.
Hence, the weight of the liquid column must be equal and opposite to the component of force due to surface tension at the point of contact. - The length of liquid in contact inside the capillary is the circumference 2πr.
Let, r = radius of the capillary tube
h = height of liquid level in the tube
T = surface tension of the liquid
ρ = density of liquid
g = acceleration due to gravity
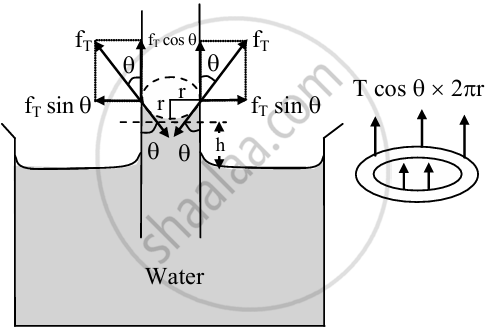
Rise of liquid in capillary tube - The force of magnitude fT acts tangentially on a unit length of liquid surface which is in contact with the wall of the capillary tube and is given as fT = T × 2πr
This force can be resolved into two components:
a. fT cosθ - vertically upward and
b. fT sinθ - along horizontal - The vertical component is effective. The horizontal component is not responsible for the capillary rise.
- The vertical component of force acting on the liquid column
(fT)v = force per unit length × circumference
= T cosθ × 2πr - Upward force balances the weight of the liquid in the capillary.
W = mg = Vρg = πr2hρg
where V = volume of liquid rise in the tube (ignoring the liquid in the concave meniscus.)
m = mass of the liquid in the capillary rise. This must be equal and opposite to the vertical component of the force due to surface tension. - If the liquid in the meniscus is neglected, then for equilibrium.,
2πr T cos θ = πr2 h ρg
∴ `h = (2T cos theta)/(r rho g )` ...(1) - This is the required expression for the rising or fall of liquid in a capillary tube.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive Laplace’s law for spherical membrane of bubble due to surface tension.
Explain why The angle of contact of mercury with glass is obtuse, while that of water with glass is acute
Explain why Water with detergent dissolved in it should have small angles of contact.
Fill in the blanks using the word(s) from the list appended with each statement
Surface tension of liquids generally . . . with temperatures (increases / decreases)
Mercury has an angle of contact equal to 140° with soda lime glass. A narrow tube of radius 1.00 mm made of this glass is dipped in a trough containing mercury. By what amount does the mercury dip down in the tube relative to the liquid surface outside? Surface tension of mercury at the temperature of the experiment is 0.465 N m–1. Density of mercury = 13.6 × 103 kg m–3
Two narrow bores of diameters 3.0 mm and 6.0 mm are joined together to form a U-tube open at both ends. If the U-tube contains water, what is the difference in its levels in the two limbs of the tube? Surface tension of water at the temperature of the experiment is 7.3 × 10–2 N m–1. Take the angle of contact to be zero and density of water to be 1.0 × 103 kg m–3 (g = 9.8 m s–2)
The total free surface energy of a liquid drop is `pisqrt2` times the surface tension of the liquid. Calculate the diameter of the drop in S.l. unit.
State any two characteristics of the angle of contact
The contact angle between water and glass is 0°. When water is poured in a glass to the maximum of its capacity, the water surface is convex upward. The angle of contact in such a situation is more than 90°. Explain.
The force of surface tension acts tangentially to the surface whereas the force due to air pressure acts perpendicularly on the surface. How is then the force due to excess pressure inside a bubble balanced by the force due to the surface tension?
Frictional force between solids operates even when they do not move with respect to each other. Do we have viscous force acting between two layers even if there is no relative motion?
A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
Viscosity is a property of
The properties of a surface are different from those of the bulk liquid because the surface molecules
(a) are smaller than other molecules
(b) acquire charge due to collision from air molecules
(c) find different type of molecules in their range of influence
(d) feel a net force in one direction.
The contact angle between a solid and a liquid is a property of
(a) the material of the solid
(b) the material of the liquid
(c) the shape of the solid
(d) the mass of the solid
When a capillary tube is dipped into a liquid, the liquid neither rises nor falls in the capillary.
(a) The surface tension of the liquid must be zero.
(b) The contact angle must be 90°.
(c) The surface tension may be zero.
(d) The contact angle may be 90°.
Find the surface energy of water kept in a cylindrical vessel of radius 6.0 cm. Surface tension of water = 0.075 J m−2.
The lower end of a capillary tube of radius 1 mm is dipped vertically into mercury. (a) Find the depression of mercury column in the capillary. (b) If the length dipped inside is half the answer of part (a), find the angle made by the mercury surface at the end of the capillary with the vertical. Surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1 and the contact angle of mercury with glass −135 °.
Two large glass plates are placed vertically and parallel to each other inside a tank of water with separation between the plates equal to 1 mm. Find the rise of water in the space between the plates. Surface tension of water = 0.075 Nm−1.
Consider an ice cube of edge 1.0 cm kept in a gravity-free hall. Find the surface area of the water when the ice melts. Neglect the difference in densities of ice and water.
A ferry boat has internal volume 1 m3 and weight 50 kg.(a) Neglecting the thickness of the wood, find the fraction of the volume of the boat immersed in water.(b) If a leak develops in the bottom and water starts coming in, what fraction of the boat's volume will be filled with water before water starts coming in from the sides?
A cubical box is to be constructed with iron sheets 1 mm in thickness. What can be the minimum value of the external edge so that the cube does not sink in water? Density of iron = 8000 kg/m3 and density of water = 1000 kg/m3.
Solve the previous problem if the lead piece is fastened on the top surface of the block and the block is to float with its upper surface just dipping into water.
A hollow spherical body of inner and outer radii 6 cm and 8 cm respectively floats half-submerged in water. Find the density of the material of the sphere.
Derive an expression for capillary rise for a liquid having a concave meniscus.
A drop of mercury of radius 0.2 cm is broken into 8 droplets of the same size. Find the work done if the surface tension of mercury is 435.5 dyn/cm.
Insect moves over the surface of water because of ______.
Define surface tension
What will be the shape of the liquid meniscus for the obtuse angle of contact?
The property of _______ of a liquid surface enables the water droplets to move upward in plants.
How does surface tension help a plant?
Define the surface tension of a liquid.
What is capillarity?
A capillary of diameter d mm is dipped in water such that the water rises to a height of 30 mm. If the radius of the capillary is made `(2/3)` of its previous value, then compute the height up to which water will rise in the new capillary?
The surface tension of the two liquids is respectively 20 and 60 dyne cm-1. The liquids drop from the ends of two tubes of the same radius. The ratio of the weights of the two drops is ______
If the surface tension of a soap solution is 3 × 10-2 N/m then the work done in forming a soap film of 20 cm × 5 cm will be ______.
Soap solution is used for cleaning dirty clothes because ______.
The wear and tear in the machine part is due to ______.
Why is raindrop spherical in nature?
The angle of contact at the interface of water-glass is 0°, Ethylalcohol-glass is 0°, Mercury-glass is 140° and Methyliodide-glass is 30°. A glass capillary is put in a trough containing one of these four liquids. It is observed that the meniscus is convex. The liquid in the trough is ______.
Is surface tension a vector?
The sap in trees, which consists mainly of water in summer, rises in a system of capillaries of radius r = 2.5 × 10–5 m. The surface tension of sap is T = 7.28 × 10–2 Nm–1 and the angle of contact is 0°. Does surface tension alone account for the supply of water to the top of all trees?
The free surface of oil in a tanker, at rest, is horizontal. If the tanker starts accelerating the free surface will be titled by an angle θ. If the acceleration is a ms–2, what will be the slope of the free surface?
Two mercury droplets of radii 0.1 cm. and 0.2 cm. collapse into one single drop. What amount of energy is released? The surface tension of mercury T = 435.5 × 10–3 Nm–1.
The sufrace tension and vapour pressure of water at 20°C is 7.28 × 10–2 Nm–1 and 2.33 × 103 Pa, respectively. What is the radius of the smallest spherical water droplet which can form without evaporating at 20°C?
Surface tension is exhibited by liquids due to force of attraction between molecules of the liquid. The surface tension decreases with increase in temperature and vanishes at boiling point. Given that the latent heat of vaporisation for water Lv = 540 k cal kg–1, the mechanical equivalent of heat J = 4.2 J cal–1, density of water ρw = 103 kg l–1, Avagadro’s No NA = 6.0 × 1026 k mole–1 and the molecular weight of water MA = 18 kg for 1 k mole.
- Estimate the energy required for one molecule of water to evaporate.
- Show that the inter–molecular distance for water is `d = [M_A/N_A xx 1/ρ_w]^(1/3)` and find its value.
- 1 g of water in the vapor state at 1 atm occupies 1601 cm3. Estimate the intermolecular distance at boiling point, in the vapour state.
- During vaporisation a molecule overcomes a force F, assumed constant, to go from an inter-molecular distance d to d ′. Estimate the value of F.
- Calculate F/d, which is a measure of the surface tension.
A liquid flows out drop by drop from a vessel through a vertical tube with an internal diameter of 2 mm, then the total number of drops that flows out during 10 grams of the liquid flow out ______. [Assume that the diameter of the neck of a drop at the moment it breaks away is equal to the internal diameter of tube and surface tension is 0.02 N/m].
In a U-tube, the radii of two columns are respectively r1 and r2. When a liquid of density ρ(θ = 0°) is filled in it, a level difference of h is observed on two arms, then the surface tension of the liquid is ______.
The excess pressure inside a liquid drop is 500 Nm-2. If the radius of the drop is 2 mm, the surface tension of the liquid is x × 10-3 Nm-1. The value of x is ______.
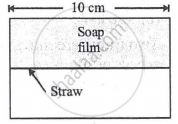
A soap film of surface tension 3 × 10-2 formed in a rectangular frame can support a straw as shown in Fig. If g = 10 ms-12, the mass of the straw is ______.
The surface tension of a soap solution is T. The work done in blowing a soap bubble of diameter d to that of a diameter 2d is ______.
Find the work done when a drop of mercury of radius 2 mm breaks into 8 equal droplets. [Surface tension of mercury = 0.4855 J/m2].
Define angle of contact.
