Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
We have,
\[x\frac{dy}{dx} + y = x e^x \]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{dy}{dx} + \frac{1}{x}y = e^x . . . . . \left( 1 \right)\]
Clearly, it is a linear differential equation of the form
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + Py = Q\]
where
\[P = \frac{1}{x} \]
\[Q = e^x \]
\[ \therefore \text{I.F.} = e^{\int P\ dx} \]
\[ = e^{\int\frac{1}{x} dx} \]
\[ = e^{log x} \]
\[ = x \]
\[\text{Multiplying both sides of }\left( 1 \right)\text{ by }x,\text{ we get }\]
\[x\left( \frac{dy}{dx} + \frac{1}{x}y \right) = x e^x \]
\[ \Rightarrow x\frac{dy}{dx} + y = x e^x \]
Integrating both sides with respect to x, we get
\[xy = \int x e^x dx + C\]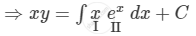
\[ \Rightarrow xy = x\int e^x dx - \int\left( \frac{d}{dx}\left( x \right)\int e^x dx \right)dx + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow xy = x e^x - e^x + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow xy = \left( x - 1 \right) e^x + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \left( \frac{x - 1}{x} \right) e^x + \frac{C}{x}\]
\[\text{ Hence, }y = \left( \frac{x - 1}{x} \right) e^x + \frac{C}{x}\text{ is the required solution.}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve the following differential equation: `(x^2-1)dy/dx+2xy=2/(x^2-1)`
Find the integrating factor of the differential equation.
`((e^(-2^sqrtx))/sqrtx-y/sqrtx)dy/dx=1`
\[\frac{dy}{dx}\] + y tan x = cos x
\[\frac{dy}{dx}\] + y cot x = x2 cot x + 2x
Find the equation of the curve passing through the point (0, 2) given that the sum of the coordinates of any point on the curve exceeds the magnitude of the slope of the tangent to the curve at that point by 5.
The slope of the tangent to the curve at any point is the reciprocal of twice the ordinate at that point. The curve passes through the point (4, 3). Determine its equation.
The decay rate of radium at any time t is proportional to its mass at that time. Find the time when the mass will be halved of its initial mass.
Experiments show that radium disintegrates at a rate proportional to the amount of radium present at the moment. Its half-life is 1590 years. What percentage will disappear in one year?
Solve the differential equation: (x + 1) dy – 2xy dx = 0
Solve the differential equation: (1 + x2) dy + 2xy dx = cot x dx
Solve the differential equation `"dy"/"dx" + y/x` = x2.
`("e"^(-2sqrt(x))/sqrt(x) - y/sqrt(x))("d"x)/("d"y) = 1(x ≠ 0)` when written in the form `"dy"/"dx" + "P"y` = Q, then P = ______.
`("d"y)/("d"x) + y/(xlogx) = 1/x` is an equation of the type ______.
Correct substitution for the solution of the differential equation of the type `("d"x)/("d"y) = "g"(x, y)` where g(x, y) is a homogeneous function of the degree zero is x = vy.
Polio drops are delivered to 50 K children in a district. The rate at which polio drops are given is directly proportional to the number of children who have not been administered the drops. By the end of 2nd week half the children have been given the polio drops. How many will have been given the drops by the end of 3rd week can be estimated using the solution to the differential equation `"dy"/"dx" = "k"(50 - "y")` where x denotes the number of weeks and y the number of children who have been given the drops.
Which of the following solutions may be used to find the number of children who have been given the polio drops?
Solve the differential equation:
`"dy"/"dx" = 2^(-"y")`
If `x (dy)/(dx) = y(log y - log x + 1)`, then the solution of the dx equation is
Form the differential equation of the family of parabolas having vertex at origin and axis along positive y-axis.
Find the general solution of the differential equation: (x3 + y3)dy = x2ydx
If y = y(x) is the solution of the differential equation `(1 + e^(2x))(dy)/(dx) + 2(1 + y^2)e^x` = 0 and y(0) = 0, then `6(y^'(0) + (y(log_esqrt(3))))^2` is equal to ______.
Let y = y(x) be the solution of the differential equation, `(x^2 + 1)^2 ("dy")/("d"x) + 2x(x^2 + 1)"y"` = 1, such that y(0) = 0. If `sqrt("ay")(1) = π/32` then the value of 'a' is ______.
If y = f(x), f'(0) = f(0) = 1 and if y = f(x) satisfies `(d^2y)/(dx^2) + (dy)/(dx)` = x, then the value of [f(1)] is ______ (where [.] denotes greatest integer function)
