Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Prove that: `tan^(-1)(1/2)+tan^(-1)(1/5)+tan^(-1)(1/8)=pi/4`
उत्तर
To prove `tan^(-1)(1/2)+tan^(-1)(1/5)+tan^(-1)(1/8)=pi/4` we will use the following formula
`tan^(-1)+tan^(-1)y=tan^(-1)((x+y)/(1-xy)),xy<1`
`Let S=tan^(-1)(1/2)+tan^(-1)(1/5)+tan^(-1)(1/8)`
`S=[tan^(-1)(1/2)+tan^(-1)(1/5)]+tan^(-1)(1/8)`
`S=tan^(-1)((1/2+1/5)/(1-1/2 xx 1/5))+tan^(-1)(1/8)`
`S=tan^(-1)(7/9)+tan^(-1)(1/8)`
`=tan^(-1)((7/9+1/8)/(1-(7/9)xx(1/8)))`
`=tan^(-1)((56+9)/(72-7))`
`S=tan^(-1)(65/65)=tan^(-1)1=pi/4`
Hence, `tan^(-1)(1/2)+tan^(-1)(1/5)+tan^(-1)(1/8)=pi/4`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Prove that `2tan^(-1)(1/5)+sec^(-1)((5sqrt2)/7)+2tan^(-1)(1/8)=pi/4`
Find the value of `cot(tan^(-1) a + cot^(-1) a)`
Prove that:
`tan^(-1) sqrtx = 1/2 cos^(-1) ((1-x)/(1+x)) , x in [0, 1]`
Prove that `tan {pi/4 + 1/2 cos^(-1) a/b} + tan {pi/4 - 1/2 cos^(-1) a/b} = (2b)/a`
Prove that
\[2 \tan^{- 1} \left( \frac{1}{5} \right) + \sec^{- 1} \left( \frac{5\sqrt{2}}{7} \right) + 2 \tan^{- 1} \left( \frac{1}{8} \right) = \frac{\pi}{4}\] .
Solve for x : \[\cos \left( \tan^{- 1} x \right) = \sin \left( \cot^{- 1} \frac{3}{4} \right)\] .
Find: ∫ sin x · log cos x dx
Find the value of `sin^-1[cos(sin^-1 (sqrt(3)/2))]`
Find the value of `cot[sin^-1 3/5 + sin^-1 4/5]`
Prove that `sin^-1 3/5 - cos^-1 12/13 = sin^-1 16/65`
Prove that `tan^-1x + tan^-1y + tan^-1z = tan^-1[(x + y + z - xyz)/(1 - xy - yz - zx)]`
Simplify: `tan^-1 x/y - tan^-1 (x - y)/(x + y)`
Evaluate tan (tan–1(– 4)).
Evaluate `cos[cos^-1 ((-sqrt(3))/2) + pi/6]`
Prove that `tan^-1 ((sqrt(1 + x^2) + sqrt(1 - x^2))/((1 + x^2) - sqrt(1 - x^2))) = pi/2 + 1/2 cos^-1x^2`
If cos–1x > sin–1x, then ______.
If y = `2 tan^-1x + sin^-1 ((2x)/(1 + x^2))` for all x, then ______ < y < ______.
The value of expression 2 `"sec"^-1 2 + "sin"^-1 (1/2)`
The value of `"cos"^-1 ("cos" ((33pi)/5))` is ____________.
If `6"sin"^-1 ("x"^2 - 6"x" + 8.5) = pi,` then x is equal to ____________.
`"cos"^-1 1/2 + 2 "sin"^-1 1/2` is equal to ____________.
If `"sin"^-1 (1 - "x") - 2 "sin"^-1 ("x") = pi/2,` then x is equal to ____________.
The Government of India is planning to fix a hoarding board at the face of a building on the road of a busy market for awareness on COVID-19 protocol. Ram, Robert and Rahim are the three engineers who are working on this project. “A” is considered to be a person viewing the hoarding board 20 metres away from the building, standing at the edge of a pathway nearby. Ram, Robert and Rahim suggested to the firm to place the hoarding board at three different locations namely C, D and E. “C” is at the height of 10 metres from the ground level. For viewer A, the angle of elevation of “D” is double the angle of elevation of “C” The angle of elevation of “E” is triple the angle of elevation of “C” for the same viewer. Look at the figure given and based on the above information answer the following:
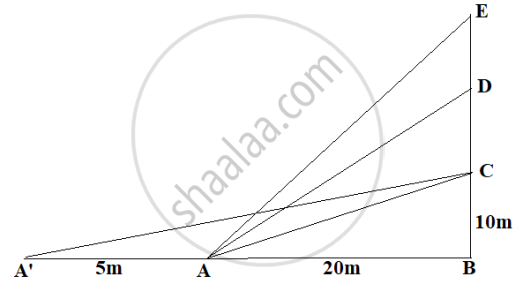
𝐴' Is another viewer standing on the same line of observation across the road. If the width of the road is 5 meters, then the difference between ∠CAB and ∠CA'B is ______.
What is the value of cos (sec–1x + cosec–1x), |x| ≥ 1
Find the value of `cos^-1 (1/2) + 2sin^-1 (1/2) ->`:-
`sin^-1(1 - x) - 2sin^-1 x = pi/2`, tan 'x' is equal to
`50tan(3tan^-1(1/2) + 2cos^-1(1/sqrt(5))) + 4sqrt(2) tan(1/2tan^-1(2sqrt(2)))` is equal to ______.
`"tan" ^-1 sqrt3 - "cot"^-1 (- sqrt3)` is equal to ______.
The value of cosec `[sin^-1((-1)/2)] - sec[cos^-1((-1)/2)]` is equal to ______.
