Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If O is the center of the circle in the figure alongside, then complete the table from the given information.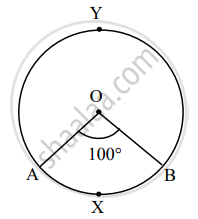
The type of arc
| Type of circular arc | Name of circular arc | Measure of circular arc |
| Minor arc | ||
| Major arc |
Solution
| Type of arc | Name of the arc | Measure of the arc |
| Minor arc | arc AXB | 100° |
| Major arc | arc AYB | 260° |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two circles touch each other externally at P. AB is a common tangent to the circles touching them at A and B. The value of ∠ L APB is
(A) 30°
(B) 45°
(C) 60°
(D) 90°
In Fig. 1, QR is a common tangent to the given circles, touching externally at the point T. The tangent at T meets QR at P. If PT = 3.8 cm, then the length of QR (in cm) is :
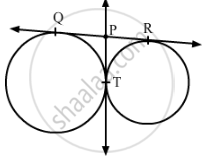
(A) 3.8
(B) 7.6
(C) 5.7
(D) 1.9
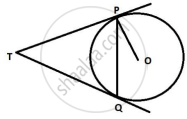
Two tangents TP and TQ are drawn to a circle with centre O from an external point T. Prove that ∠PTQ = 2∠OPQ.
Fill in the blanks:
A circle divides the plane, on which it lies, in __________ parts.
Write True or False. Give reason for your answer.
Line segment joining the centre to any point on the circle is a radius of the circle.
Write True or False. Give reason for your answer.
A circle is a plane figure.
A chord PQ of a circle of radius 10 cm substends an angle of 60° at the centre of circle. Find the area of major and minor segments of the circle.
O is the center of a circle of radius 8cm. The tangent at a point A on the circle cuts a line through O at B such that AB = 15 cm. Find OB
In figure OQ : PQ = 3 : 4 and perimeter of ΔPDQ = 60cm. determine PQ, QR and OP.
In the given figure, if arc AB = arc CD, then prove that the quadrilateral ABCD is an isosceles– trapezium (O is the centre of the circle).
If the area of a circle is equal to sum of the areas of two circles of diameters 10 cm and 24 cm, then the diameter of the larger circle (in cm) is:
AB and CD are common tangents to two circles of equal radii. Prove that AB = CD.
ABC is a right triangle in which ∠B = 90°. If AB = 8 cm and BC = 6 cm, find the diameter of the circle inscribed in the triangle.
ABC is a triangle with AB = 10 cm, BC = 8 cm and AC = 6 cm (not drawn to scale). Three circles are drawn touching each other with the vertices as their centres. Find the radii of the three circles.
Draw a circle of radius 3.6 cm. In the circle, draw a chord AB = 5 cm. Now shade the minor segment of the circle.
If a chord AB subtends an angle of 60° at the centre of a circle, then angle between the tangents at A and B is also 60°.
If an isosceles triangle ABC, in which AB = AC = 6 cm, is inscribed in a circle of radius 9 cm, find the area of the triangle.
Draw two acute angles and one obtuse angle without using a protractor. Estimate the measures of the angles. Measure them with the help of a protractor and see how much accurate is your estimate
Draw any circle and mark
- it's centre
- a radius
- a diameter
- a sector
- a segment
- a point in its interior
- a point in its exterior
- an arc
If an are subtends an angle of 90° at the centre of a circle, then the ratio of its length to the circumference of the circle is ______.
