Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following system freely allows the exchange of energy and matter with its environment?
Options
Closed
Isolated
Open
partially closed
Solution
Open
RELATED QUESTIONS
In changing the state of a gas adiabatically from an equilibrium state A to another equilibrium state B, an amount of work equal to 22.3 J is done on the system. If the gas is taken from state A to B via a process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is 9.35 cal, how much is the net work done by the system in the latter case? (Take 1 cal = 4.19 J)
A steam engine delivers 5.4×108 J of work per minute and services 3.6 × 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the efficiency of the engine? How much heat is wasted per minute?
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if heat is added to it?
A cylinder containing a gas is lifted from the first floor to the second floor. What is the amount of work done on the gas? What is the amount of work done by the gas? Is the internal energy of the gas increased? Is the temperature of the gas increased?
A force F is applied on a block of mass M. The block is displaced through a distance d in the direction of the force. What is the work done by the force on the block? Does the internal energy change because of this work?
The outer surface of a cylinder containing a gas is rubbed vigorously by a polishing machine. The cylinder and its gas become warm. Is the energy transferred to the gas heat or work?
Can work be done by a system without changing its volume?
Figure shows two processes A and B on a system. Let ∆Q1 and ∆Q2 be the heat given to the system in processes A and B respectively. Then ____________ .
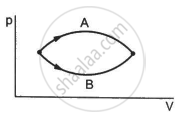
Consider the following two statements.
(A) If heat is added to a system, its temperature must increase.
(B) If positive work is done by a system in a thermodynamic process, its volume must increase.
A gas is contained in a metallic cylinder fitted with a piston. The piston is suddenly moved in to compress the gas and is maintained at this position. As time passes the pressure of the gas in the cylinder ______________ .
The pressure p and volume V of an ideal gas both increase in a process.
(a) Such a process is not possible.
(b) The work done by the system is positive.
(c) The temperature of the system must increase.
(d) Heat supplied to the gas is equal to the change in internal energy.
A gas is taken along the path AB as shown in figure. If 70 cal of heat is extracted from the gas in the process, calculate the change in the internal energy of the system.
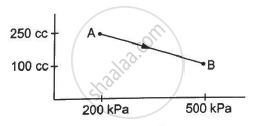
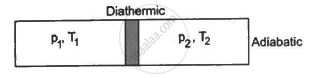
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of volume V with adiabatic walls containing an ideal gas. The internal energy of this ideal gas is given by 1.5 nRT. The tube is divided into two equal parts by a fixed diathermic wall. Initially, the pressure and the temperature are p1, T1 on the left and p2, T2 on the right. The system is left for sufficient time so that the temperature becomes equal on the two sides. (a) How much work has been done by the gas on the left part? (b) Find the final pressures on the two sides. (c) Find the final equilibrium temperature. (d) How much heat has flown from the gas on the right to the gas on the left?
Which of the following is correct, when the energy is transferred to a system from its environment?
Define heat.
When does a system lose energy to its surroundings and its internal energy decreases?
A system releases 100 kJ of heat while 80 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
derive the relation between the change in internal energy (∆U), work is done (W), and heat (Q).
The internal energy of a system is ______
An ideal gas is compressed at a constant temperature. Its internal energy will ____________.
Figure shows the P-V diagram of an ideal gas undergoing a change of state from A to B. Four different parts I, II, III and IV as shown in the figure may lead to the same change of state.

- Change in internal energy is same in IV and III cases, but not in I and II.
- Change in internal energy is same in all the four cases.
- Work done is maximum in case I
- Work done is minimum in case II.
A gas is compressed at a constant pressure of 50 N/m2 from a volume of 10 m3 to a volume of 4 m3. Energy of 100 J is then added to the gas by heating. Its internal energy is ______.
If a gas is compressed adiabatically:
The internal energy of one mole of argon at 300 K is ______. (R = 8.314 J/mol.K)
A steam engine delivers 4.8 x 108 Jof work per minute and services 1.2 x 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the percentage efficiency of the engine?
A system releases 125 kJ of heat while 104 kJ work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
