Topics
Electronic Components/ Study of Components and Circuits
- Introduction to Electronic Components
- Classification Of Components
- Resistors
- Types of Resistors
- Capacitors
- Types of Capacitors
- Inductors
- Basics of Transformers
- Basics of Semiconductor Devices
- PN Junction Diode
- Half Wave Rectifier
- Types of diodes
- Transistors
- Transistor Amplifier
- Basic of Transistor as a Switch
- Switch Mode power Supply (SMPS)
- Classification of IC’S
Logic Gates and Sequential Circuit
- Introduction of Logic gates and sequential circuits
- Basics of Logic Gates
- Types of gates
- Odd/Even Parity
- DE-MORGAN'S Theorem
- NAND Gate is an Universal Building Block
- HALF ADDER AND FULL ADDER
- Multiplexers
- Demultiplexer
- Encoder
- Decoder
- FLIP-FLOPS
- Counters
- Shift Registers
Functional Hardware of Pc
Peripheral Devices
- Construction
- Working
Transformers
A transformer has two inductors: the primary winding, which receives AC from an external source, and the secondary winding, where voltage is induced. It transfers AC between high and low voltages.
Construction & Working
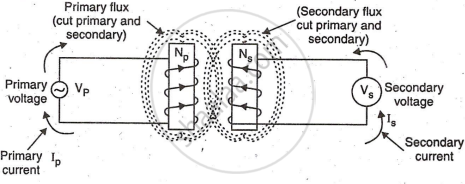
The winding which is normally connected to the mains is called as 'Primary winding' and other winding across which output is obtained is called 'Secondary Winding' Both windings are wound on a core, which is laminated type.
Working: When AC voltage is applied to the primary winding, it generates changing magnetic flux. The nearby secondary winding cuts this flux, inducing voltage as per Faraday's law. The induced voltage depends on the primary and secondary turns, determined by the turns ratio.

If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
